xgboost的使用
1.首先导入包
import xgboost as xgb
2.使用以下的函数实现交叉验证训练xgboost。
bst_cvl = xgb.cv(xgb_params, dtrain, num_boost_round=50,
nfold=3, seed=0, feval=xg_eval_mae, maximize=False, early_stopping_rounds=10)
3.cv参数说明:函数cv的第一个参数是对xgboost训练器的参数的设置,具体见以下
xgb_params = { 'seed': 0, 'eta': 0.1, 'colsample_bytree': 0.5, 'silent': 1, 'subsample': 0.5, 'objective': 'reg:linear', 'max_depth': 5, 'min_child_weight': 3 }
参数说明如下:
Xgboost参数
- 'booster':'gbtree',
- 'objective': 'multi:softmax', 多分类的问题
- 'num_class':10, 类别数,与 multisoftmax 并用
- 'gamma':损失下降多少才进行分裂,gammar越大越不容易过拟合。
- 'max_depth':树的最大深度。增加这个值会使模型更加复杂,也容易出现过拟合,深度3-10是合理的。
- 'lambda':2, 控制模型复杂度的权重值的L2正则化项参数,参数越大,模型越不容易过拟合。
- 'subsample':0.7, 随机采样训练样本
- 'colsample_bytree':0.7, 生成树时进行的列采样
- 'min_child_weight':正则化参数. 如果树分区中的实例权重小于定义的总和,则停止树构建过程。
- 'silent':0 ,设置成1则没有运行信息输出,最好是设置为0.
- 'eta': 0.007, 如同学习率
- 'seed':1000,
- 'nthread':7, cpu 线程数
4.cv参数说明:dtrain是使用下面的函数DMatrix得到的训练集
dtrain = xgb.DMatrix(train_x, train_y)
5.cv参数说明:feval参数是自定义的误差函数
def xg_eval_mae(yhat, dtrain): y = dtrain.get_label() return 'mae', mean_absolute_error(np.exp(y), np.exp(yhat))
6.cv参数说明:nfold是交叉验证的折数, early_stopping_round是多少次模型没有提升后就结束, num_boost_round是加入的决策树的数目。
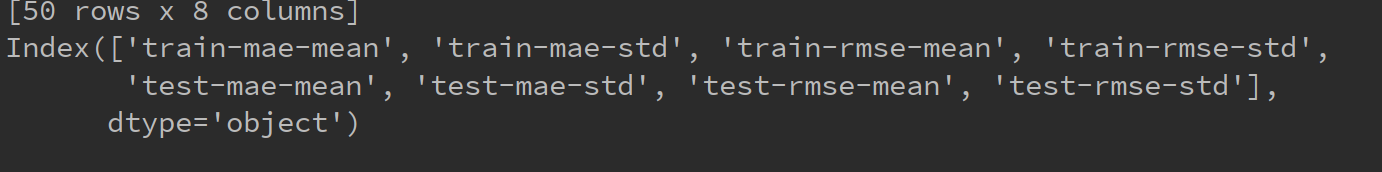
7. bst_cv是cv返回的结果,是一个DataFram的类型,其列为以下列组成
8.自定义评价函数:具体见这个博客:https://blog.csdn.net/wl_ss/article/details/78685984
def customedscore(preds, dtrain): label = dtrain.get_label() pred = [int(i>=0.5) for i in preds] confusion_matrixs = confusion_matrix(label, pred) recall =float(confusion_matrixs[0][0]) / float(confusion_matrixs[0][1]+confusion_matrixs[0][0]) precision = float(confusion_matrixs[0][0]) / float(confusion_matrixs[1][0]+confusion_matrixs[0][0]) F = 5*precision* recall/(2*precision+3*recall)*100 return 'FSCORE',float(F)
这种自定义的评价函数可以用于XGboost的cv函数或者train函数中的feval参数
还有一种定义评价函数的方式,如下
def mae_score(y_ture, y_pred): return mean_absolute_error(y_true=np.exp(y_ture), y_pred=np.exp(y_pred))
这种定义的函数可以用于gridSearchCV函数的scorning参数中。
xgboost调参步骤
第一步:确定n_estimators参数
首先初始化参数的值
xgb1 = XGBClassifier(max_depth=3, learning_rate=0.1, n_estimators=5000, silent=False, objective='binary:logistic', booster='gbtree', n_jobs=4, gamma=0, min_child_weight=1, subsample=0.8, colsample_bytree=0.8, seed=7)
用cv函数求得参数n_estimators的最优值。
cv_result = xgb.cv(xgb1.get_xgb_params(), dtrain, num_boost_round=xgb1.get_xgb_params()['n_estimators'], nfold=5, metrics='auc', early_stopping_rounds=50, callbacks=[xgb.callback.early_stop(50), xgb.callback.print_evaluation(period=1,show_stdv=True)])
第二步、确定max_depth和min_weight参数
param_grid = {'max_depth':[1,2,3,4,5],
'min_child_weight':[1,2,3,4,5]}
grid_search = GridSearchCV(xgb1,param_grid,scoring='roc_auc',iid=False,cv=5)
grid_search.fit(train[feature_name],train['label'])
print('best_params:',grid_search.best_params_)
print('best_score:',grid_search.best_score_)
第三步、gamma参数调优
首先将上面调好的参数设置好,如下所示
xgb1 = XGBClassifier(max_depth=2, learning_rate=0.1, n_estimators=33, silent=False, objective='binary:logistic', booster='gbtree', n_jobs=4, gamma=0, min_child_weight=9, subsample=0.8, colsample_bytree=0.8, seed=7)
然后继续网格调参
param_grid = {'gamma':[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]}
grid_search = GridSearchCV(xgb1,param_grid,scoring='roc_auc',iid=False,cv=5)
grid_search.fit(train[feature_name],train['label'])
print('best_params:',grid_search.best_params_)
print('best_score:',grid_search.best_score_)
第四步、调整subsample与colsample_bytree参数
param_grid = {'subsample':[i/10.0 for i in range(5,11)],
'colsample_bytree':[i/10.0 for i in range(5,11)]}
grid_search = GridSearchCV(xgb1,param_grid,scoring='roc_auc',iid=False,cv=5)
grid_search.fit(train[feature_name],train['label'])
print('best_params:',grid_search.best_params_)
print('best_score:',grid_search.best_score_)
第五步、调整正则化参数
param_grid = {'reg_lambda':[i/10.0 for i in range(1,11)]}
grid_search = GridSearchCV(xgb1,param_grid,scoring='roc_auc',iid=False,cv=5)
grid_search.fit(train[feature_name],train['label'])
print('best_params:',grid_search.best_params_)
print('best_score:',grid_search.best_score_)
最后我们使用较低的学习率以及使用更多的决策树,可以用CV来实现这一步骤
xgb1 = XGBClassifier(max_depth=2, learning_rate=0.01, n_estimators=5000, silent=False, objective='binary:logistic', booster='gbtree', n_jobs=4, gamma=2.1, min_child_weight=9, subsample=0.8, colsample_bytree=0.8, seed=7, )
- 仅仅靠参数的调整和模型的小幅优化,想要让模型的表现有个大幅度提升是不可能的。
- 要想让模型的表现有一个质的飞跃,需要依靠其他的手段,诸如,特征工程(feature egineering) ,模型组合(ensemble of model),以及堆叠(stacking)等
具体的关于调参的知识请看以下链接:
https://www.cnblogs.com/TimVerion/p/11436001.html
http://www.pianshen.com/article/3311175716/



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号