【智能无线小车系列十】智能小车一体化测试
前面介绍了那么多,完成的设计思路是这样的:
使用 树莓派 ,Arduino , 小车底盘 Arduino电机扩展板。摄像头,步进电机, USB无线网卡。
结构如下:PC <---TCP---> 树莓派 <---Serial-->Arduino<---Serial-->步进电机
PC为主控端,树莓派为服务端,Arduino为下位机驱动步进电机。PC做为主控端通过WIFI发送指令给树莓派(服务端),树莓派再将指令通过Serial 发给下位机Arduino控制下边的硬件。摄像头连接树莓派并将视频回传给PC端。后续可以考虑加入手机端控制,试想通过手机来控制小车,并将视频回传给手机,这感觉棒极了!不过这里的手机端尚未实现,不过技术上式完全可行的,实现与否应该就是时间的问题吧。
下面开始进行测试:
1、Arduino端:下面的代码执行的功能是:通过树莓派传输控制指令控制小车基本运动,具体操作指令如下,数字按键表示的是键盘上的按键。其中,按键8:——前进,按键2——后退,按键4——左转弯,按键6——右转弯,按键5——停止。
将PC通过USB数据线与Arduino连接起来,编译上述代码,然后将其烧制到Arduino板上即可。烧制完成之后,断开数据线。
int pin1=8; int pin2=9; int speedpin1=11; int pin3=6; int pin4=7; int speedpin2=10; char sign; void setup() { // put your setup code here, to run once: pinMode(pin1,OUTPUT); pinMode(pin2,OUTPUT); pinMode(speedpin1,OUTPUT); pinMode(pin3,OUTPUT); pinMode(pin4,OUTPUT); pinMode(speedpin2,OUTPUT); Serial.begin(9600); } void loop() { // put your main code here, to run repeatedly: if(Serial.available()) { sign=Serial.read(); switch (sign){ case '6'://right { analogWrite(speedpin1,200);//set the PWM speed as 100 analogWrite(speedpin2,200);//set the PWM speed as 100 digitalWrite(pin1,HIGH); digitalWrite(pin2,LOW); digitalWrite(pin3,HIGH); digitalWrite(pin4,LOW); break; } case '2'://backward { analogWrite(speedpin1,200);//set the PWM speed as 100 analogWrite(speedpin2,200);//set the PWM speed as 100 digitalWrite(pin1,LOW); digitalWrite(pin2,HIGH); digitalWrite(pin3,HIGH); digitalWrite(pin4,LOW); break; } case '4'://left { analogWrite(speedpin1,200);//set the PWM speed as 100 analogWrite(speedpin2,200);//set the PWM speed as 100 digitalWrite(pin1,LOW); digitalWrite(pin2,HIGH); digitalWrite(pin3,LOW); digitalWrite(pin4,HIGH); break; } case '8'://forward { analogWrite(speedpin1,200);//set the PWM speed as 100 analogWrite(speedpin2,200);//set the PWM speed as 100 digitalWrite(pin1,HIGH); digitalWrite(pin2,LOW); digitalWrite(pin3,LOW); digitalWrite(pin4,HIGH); break; } case '5'://stop { analogWrite(speedpin1,0);//set the PWM speed as 0 analogWrite(speedpin2,0);//set the PWM speed as 0 break; } Serial.flush(); } } }
2、树莓派:树莓派扮演者服务器的角色。打开树莓派之后,编译并运行OLSR自组网协议。
1)配置网络为ad-hoc网络:
编辑如下的脚本程序,完成后保存为"wlan0.sh"。
1 #!/bin/sh 2 #DEV=$1 3 ifconfig eth0 down 4 ifconfig wlan0 down 5 iwconfig wlan0 mode ad-hoc essid 522 channel 3 6 ifconfig wlan0 up 7 ifconfig wlan0 192.168.1.52/24 8 echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/all/accept_source_route
这里需要注意的是,每张网卡由于每次由于所插位置的不同系统为其分配的“wlanX”名中的“X”均不相同,但是只要保持其物理位置不变,该名称也不会再发生变化。因而针对每个位置的每张网卡,在做上述修改之前需要使用命令:iwconfig 查看系统为其指定的名称以替换上述代码中的“wlan0”。不同网卡应当配置不同的ip地址,即每次都需要修改“192.168.1.52/24”中的值。
由于不希望每次打开树莓派都要重复进行上述配置,因而希望将上述脚本添加到树莓派开机自启动程序列表中。
不少网友们建议修改"rc.local"文件,然而 "rc.local"的执行是随机的,即不能保证每次开机都能执行,稳定性较差,故而考虑别的方法。比较稳妥的方法之一是执行脚本添加到/etc/init.d目录下。具体操作如下:
首先,切换到root权限,然后将"wlan0.sh"移动至/etc/init.d目录下。
接下来需要修改"wlan0.sh"的执行权限,执行命令:
root@raspiberrypi :/home/pi #chmod 777 /etc/init.d/wlan0.sh
然后把脚本加入到启动清单:
root@raspiberrypi :/home/pi # update-rc.d wlan0.sh defaults
最后重启系统,发现IP地址成功地开机就自动配置为我们设置好的IP地址了。
root@raspiberrypi :/home/pi # reboot
如果希望删除某个开机自启动项,可以使用如下的指令:
pi@raspberrypi $ sudo update-rc.d -f wlan0.sh remove
2)编译/运行olsrd源代码
1.首先从http://www.olsr.org/?q=download下载olsrd源码
2.解压 tar包
tar jxvf olsrd-0.6.6.tar.bz2
3.编译与安装
解压后会生成一个olsrd-0.6.6文件
#cd olsrd-0.6.6 //进入olsrd-0.6.6目录
首先,切换进入olsrd-0.6.8的文件目录,里面的文件目录结构如下所示:
通常在ubuntu下编译(make)的时候会提示错误,提示缺少flex、bison,所以在编译make之前我们需要安装flex、bison两个插件,需要联网。安装命令为:
root@raspiberrypi #olsrd-0.6.8 $ apt-get install flex bison //在root权限下
pi@raspiberrypi #olsrd-0.6.8 $ Sudo apt-get install flex bison //在普通模式下
下载并安装完成之后编译文件,
pi@raspiberrypi #olsrd-0.6.8 $make // 编译 pi@raspiberrypi #olsrd-0.6.8 $make install // 编译后会生成olsrd目标文件,安装olsrd
pi@raspiberrypi #olsrd-0.6.8 $make clean // 清除之前编译生成的中间文件 pi@raspiberrypi #olsrd-0.6.8 $make libs // 编译库文件 pi@raspiberrypi #olsrd-0.6.8 $make install_libs // 安装库
安装成功后,修改配置文件"/etc/olsrd/oldrd.conf",添加相应的网卡接口
用vim 打开/etc/olsrd/olsrd.config
pi@raspiberrypi #olsrd-0.6.8 $ vim /etc/olsrd/olsrd.config
在配置文件的最后有 “<OLSRd-Interface1>” “<OLSRd-Interface2>” ,在其后添加 “wlanX”,其中X为你的工作无线网卡。
可以通过iwconfig 查看当前使用的无线网卡,通常为“wlan0”。
最后,运行olsrd
pi@raspiberrypi #olsrd-0.6.8 $sudo olsrd
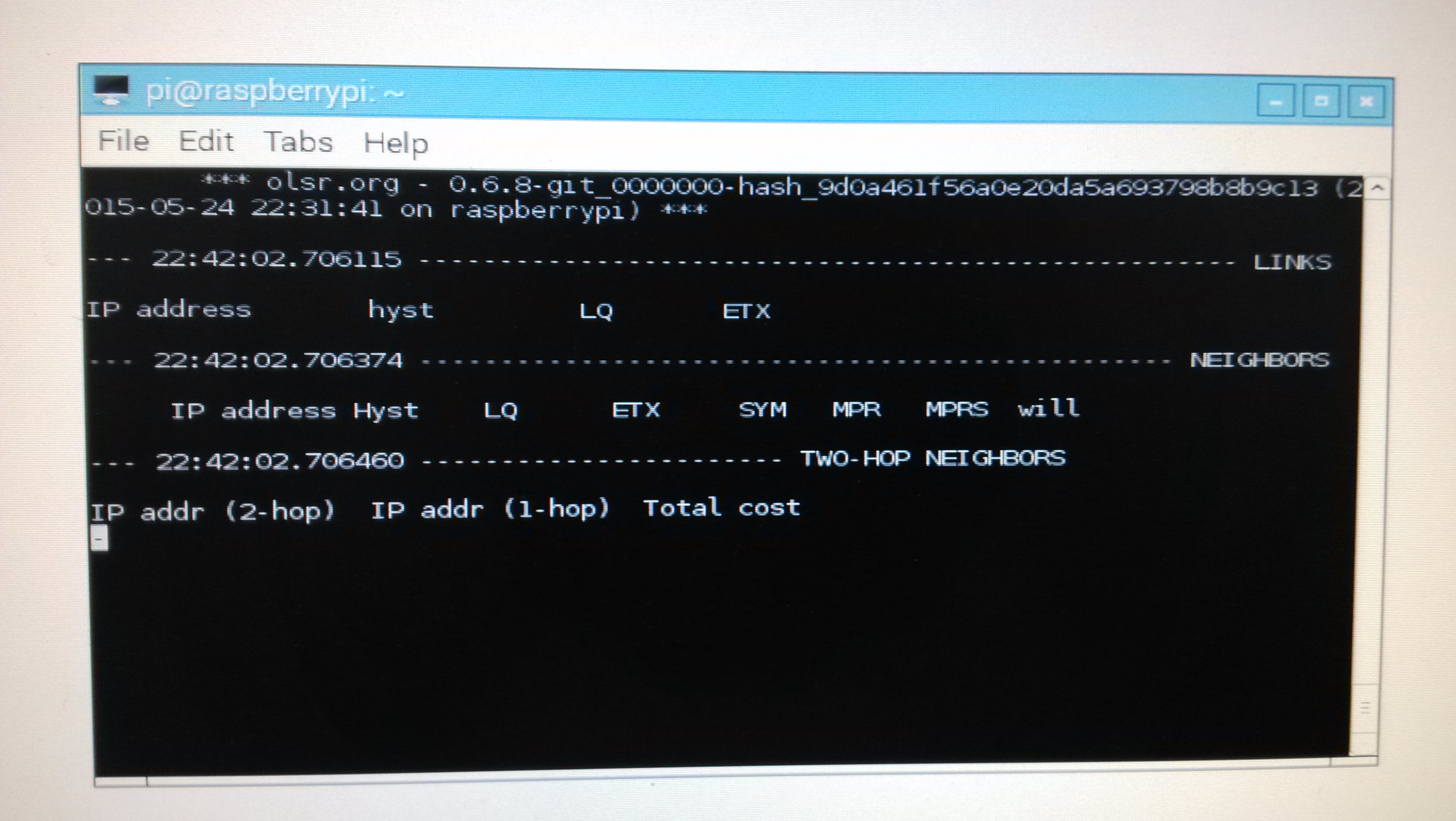
如果出现以下的界面,说明运行成功了。
3)运行小车上的服务器程序
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 import socket 3 import serial 4 sock=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM) 5 sock.bind (('192.168.1.24',8180)) 6 sock.listen(5) 7 while True: 8 print "aaaaaaaaaaaa" 9 connection,address=sock.accept() 10 print "client ip is " 11 print address 12 try: 13 connection.settimeout(5) 14 buf=connection.recv(1) 15 ser=serial.Serial('/dev/ttyACM0',9600) 16 ser.write(buf) 17 print "wwwwwwwwwwww" 18 print buf 19 except socket.timeout: 20 print "timeout" 21 connection.close()
上述配置完成之后,我们考虑将其全部依次添加到开机自启动项之中,这样树莓派每次加电启动之后就会自动运行我们的olsrd协议。完整的配置文件内容如下:
备注:其中olsrd程序所在位置“/usr/local/sbin/olsrd”是通过指令“which olsrd”查找到的。
3. PC 端:打开PC之后,编译并运行OLSR自组网协议。接下来运行下列python客户端程序“client.py”。
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 import socket 3 sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) 4 5 sock.connect(('192.168.1.25',8180)) 6 7 import time 8 #time.sleep(2) 9 buff=raw_input('enter:') 10 sock.send(buff) 11 print "aaaaaaaaaa" 12 sock.close()
上述为python代码均为单击测试代码,多机测试代码如下:
小车作为client端,代码如下:

1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 import socket 3 import time 4 5 #create the TCP socket 6 sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) 7 8 #"192.168.1.25" is the sever's IP address 9 #"8180" is the port number of the sever 10 sock.connect(('192.168.1.25',8180)) 11 12 13 #time.sleep(2) 14 while True: 15 #the receive thread is obstructed until it receive data from the sever , 16 #or it won't run the next tatement 17 buff=sock.recv(1) 18 #when the link is disconnected ,the client will pirint "recv data is :" repeatedly 19 print "recv data is :" 20 print buff 21 #print "recv data is :{0}".foramt(buff) 22 #read form the serial ,/dev/ttyACM0 is the name of the equipment and 9600 23 #is the rate of bote 24 ser=serial.Serial('/dev/ttyACM0',9600) 25 ser.write(buf) 26 27 sock.close()
PC作为csever端,代码如下:

1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 from multiprocessing import Process, Value 3 import socket 4 import serial 5 import time 6 7 #"l" respresent an interger,"0" represents the original value 8 num=Value('l',0) 9 handle=Value('l',0) 10 value_change=Value('l',0) 11 12 13 #user self-defined function 14 def hand(client,count): 15 while True: 16 if value_change.value==1 and num.value==count: 17 print "ready to send" 18 temp=handle.value 19 client.send(str(temp)) 20 print "handle send success." 21 while value_change.value: 22 temp=0 23 time.sleep(0.7) 24 client.close() 25 26 27 28 #mian function 29 if __name__ == '__main__': 30 sock=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM) 31 print "socket create success." 32 sock.bind (('192.168.1.12',8180)) 33 sock.listen(1) 34 count=1 35 36 while True: 37 client, addr = sock.accept() 38 print "connect from :" 39 print addr 40 #fork a process to handle a new connecting client 41 t = Process(target = hand, args = [client,count]) 42 t.start() 43 #t.join() 44 print "process create success." 45 46 count=count+1 47 48 flag=raw_input("all the client connected?(y/n)") 49 if flag=="y": 50 #when all the client is connected 51 #continue to send info to control 52 #need to change for dymacially connected and disconnected 53 while True: 54 value_temp=raw_input("which client do you want to handle :") 55 handle_temp=raw_input("your handle :") 56 #get the number of the client need to contorl 57 num.value=int(value_temp) 58 #get the information that need to send to the client 59 handle.value=int(handle_temp) 60 #set the condition that all the client need to read 61 value_change.value=1; 62 #delay for 1 sescond for all the client to read from the shared memory 63 time.sleep(1) 64 #cancel the condition that all the client need to read 65 value_change.value=0; 66 s.close()
参考资料:
http://linux.51yip.com/search/iwconfig






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号