2-分类
引入#
import sys
assert sys.version_info >= (3, 5)
# Is this notebook running on Colab or Kaggle?
IS_COLAB = 'google.colab' in sys.modules
IS_KAGGLE = 'kaggle_secrets' in sys.modules
import sklearn
assert sklearn.__version__ >= '0.20'
import numpy as np
import os
np.random.seed(42)
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
mpl.rc('axes', labelsize=14)
mpl.rc('xtick', labelsize=12)
mpl.rc('ytick', labelsize=12)
PROJECT_ROOT_DIR = '.' # 实际应该是..更好一些,项目目录,但是每个章节内容保存在该章节文件夹也ok
CHAPTER_ID = 'classification'
IMAGES_PATH = os.path.join(PROJECT_ROOT_DIR, 'images', CHAPTER_ID)
# exist_ok:是否在目录存在时触发异常。如果exist_ok为False(默认值),则在目标目录已存在的情况下触发FileExistsError异常;
# 如果exist_ok为True,则在目标目录已存在的情况下不会触发FileExistsError异常。
os.makedirs(IMAGES_PATH, exist_ok=True)
def save_fig(fig_id, tight_layout=True, fig_extension='png', resolution=300):
path = os.path.join(IMAGES_PATH, fig_id + '.' + fig_extension)
print('Saving figure', fig_id)
if tight_layout:
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig(path, format=fig_extension, dpi=resolution)
加载数据集#
数据探索及数据集划分#
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
some_digit = X[0]
some_digit_image = some_digit.reshape(28, 28)
plt.imshow(some_digit_image, cmap=mpl.cm.binary)
plt.axis('off')
save_fig('some_digit_plot')
plt.show()
y = y.astype(np.uint8)
def plot_digit(data):
image = data.reshape(28, 28)
plt.imshow(image, cmap=mpl.cm.binary, interpolation='nearest') # 临近插值
plt.axis('off')
def plot_digits(instances, images_per_row=10, **options):
size = 28
images_per_row = min(len(instances), images_per_row)
images = [instance.reshape(size, size) for instance in instances]
n_rows = (len(instances) - 1) // images_per_row + 1
row_images = []
n_empty = n_rows * images_per_row - len(instances)
images.append(np.zeros((size, size * n_empty)))
for row in range(n_rows):
rimages = images[row * images_per_row : (row + 1) * images_per_row]
# 水平合并,合并列
row_images.append(np.concatenate(rimages, axis=1))
image = np.concatenate(row_images, axis=0)
plt.imshow(image, cmap=mpl.cm.binary, **options)
plt.axis('off')
plt.figure(figsize=(9, 9))
example_images = X[:100]
plot_digits(example_images, images_per_row=10)
save_fig('more_digits_plot')
plt.show()
# mnist数据集已经划分好训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = X[:60000], X[60000:], y[:60000], y[60000:]
二分类#
y_train_5 = (y_train == 5)
y_test_5 = (y_test == 5)
from sklearn.linear_model import SGDClassifier
sgd_clf = SGDClassifier(max_iter=1000, tol=1e-3, random_state=42) # 容差,停止迭代参数
sgd_clf.fit(X_train, y_train_5)
sgd_clf.predict([some_digit]) # array([ True])
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
# 三折
cross_val_score(sgd_clf, X_train, y_train_5, cv=3, scoring='accuracy') # array([0.95035, 0.96035, 0.9604 ])
分层抽样#
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold
from sklearn.base import clone
skfolds = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=3, shuffle=True, random_state=42)
for train_index, test_index in skfolds.split(X_train, y_train_5):
clone_clf =clone(sgd_clf)
X_train_folds = X_train[train_index]
y_train_folds = y_train_5[train_index]
X_test_fold = X_train[test_index]
y_test_fold = y_train_5[test_index]
clone_clf.fit(X_train_folds, y_train_folds)
y_pred = clone_clf.predict(X_test_fold)
n_correct = sum(y_pred == y_test_fold)
print(n_correct / len(y_pred)) # 0.9669 0.91625 0.96785
准确率并不是一个好的评价指标#
from sklearn.base import BaseEstimator
class Never5Classifier(BaseEstimator):
def fit(self, X, y=None):
pass
def predict(self, X):
return np.zeros((len(X), 1), dtype=bool)
never_5_clf = Never5Classifier()
cross_val_score(never_5_clf, X_train, y_train_5, cv=3, scoring='accuracy') # array([0.91125, 0.90855, 0.90915])
混淆矩阵:横轴实际,纵轴预测#
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_predict
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
y_train_pred = cross_val_predict(sgd_clf, X_train, y_train_5, cv=3)
confusion_matrix(y_train_5, y_train_pred) # array([[53892, 687], [ 1891, 3530]])
精度/精确率#
from sklearn.metrics import precision_score, recall_score
precision_score(y_train_5, y_train_pred) # 0.8370879772350012
cm = confusion_matrix(y_train_5, y_train_pred)
cm[1, 1] / (cm[0, 1] + cm[1, 1]) # 0.8370879772350012
召回率#
recall_score(y_train_5, y_train_pred) # 0.6511713705958311
cm[1, 1] / (cm[1, 0] + cm[1, 1]) # 0.6511713705958311
f1#
from sklearn.metrics import f1_score
f1_score(y_train_5, y_train_pred) # 0.7325171197343846
2 / (1/(cm[1, 1] / (cm[0, 1] + cm[1, 1])) + 1/(cm[1, 1] / (cm[1, 0] + cm[1, 1]))) # 0.7325171197343847
自定义分类阈值#
y_scores = sgd_clf.decision_function([some_digit])
y_scores # array([2164.22030239])
threshold = 0
y_some_digit_pred = (y_scores > threshold)
y_some_digit_pred # array([ True])
threshold = 8000
y_some_digit_pred = (y_scores > threshold)
y_some_digit_pred # array([False])
# 默认阈值是0
from sklearn.metrics import precision_recall_curve
y_scores = cross_val_predict(sgd_clf, X_train, y_train_5, cv=3, method='decision_function')
precisions, recalls, thresholds = precision_recall_curve(y_train_5, y_scores)
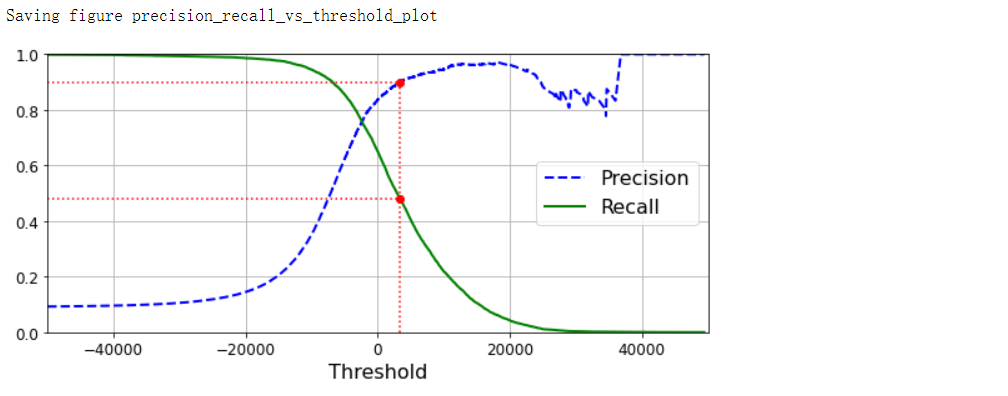
def plot_precision_recall_vs_threshold(precisions, recalls, thresholds):
plt.plot(thresholds, precisions[:-1], 'b--', label='Precision', linewidth=2)
plt.plot(thresholds, recalls[:-1], 'g-', label='Recall', linewidth=2)
plt.legend(loc='center right', fontsize=16)
plt.xlabel('Threshold', fontsize=16)
plt.grid(True)
plt.axis([-50000, 50000, 0, 1])
recall_90_precision = recalls[np.argmax(precisions >= 0.90)]
threshold_90_precision = thresholds[np.argmax(precisions >= 0.90)]
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 4))
plot_precision_recall_vs_threshold(precisions, recalls, thresholds)
plt.plot([threshold_90_precision, threshold_90_precision], [0, 0.9], 'r:')
plt.plot([-50000, threshold_90_precision], [0.9, 0.9], 'r:')
plt.plot([-50000, threshold_90_precision], [recall_90_precision, recall_90_precision], 'r:')
plt.plot([threshold_90_precision], [0.9], 'ro')
plt.plot([threshold_90_precision], [recall_90_precision], 'ro')
save_fig('precision_recall_vs_threshold_plot')
plt.show()
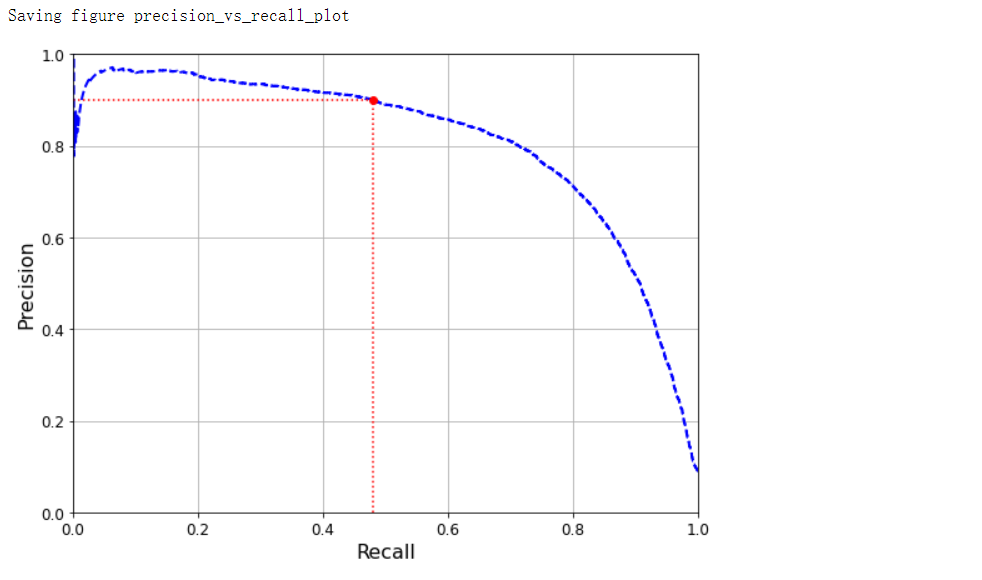
PR曲线#
def plot_precision_vs_recall(precisions, recalls):
plt.plot(recalls, precisions, 'b--', linewidth=2)
plt.xlabel('Recall', fontsize=16)
plt.ylabel('Precision', fontsize=16)
plt.axis([0, 1, 0, 1])
plt.grid(True)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plot_precision_vs_recall(precisions, recalls)
plt.plot([recall_90_precision, recall_90_precision], [0.0, 0.9], 'r:')
plt.plot([0.0, recall_90_precision], [0.9, 0.9], 'r:')
plt.plot([recall_90_precision], [0.9], 'ro')
save_fig('precision_vs_recall_plot')
plt.show()
# 自定义阈值
# 满足条件第一个下标
threshold_90_precision = thresholds[np.argmax(precisions >= 0.90)]
threshold_90_precision # 3370.0194991439557
y_train_pred_90 = (y_scores >= threshold_90_precision)
precision_score(y_train_5, y_train_pred_90) # 0.9000345901072293
recall_score(y_train_5, y_train_pred_90) # 0.4799852425751706
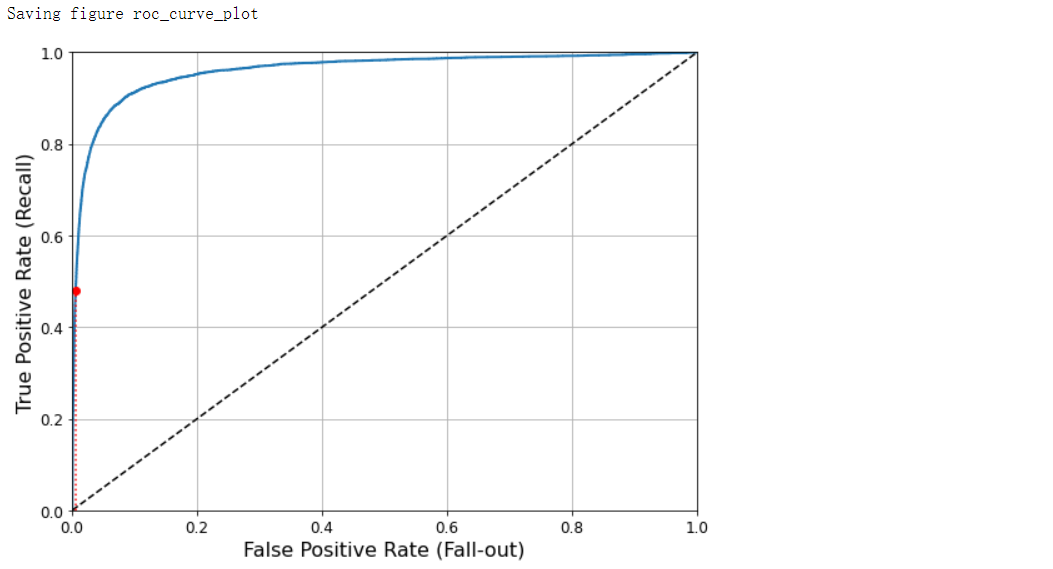
ROC曲线#
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve
fpr, tpr, thresholds = roc_curve(y_train_5, y_scores)
def plot_roc_curve(fpr, tpr, label=None):
plt.plot(fpr, tpr, linewidth=2, label=label)
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], 'k--')
plt.axis([0, 1, 0, 1])
plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate (Fall-out)', fontsize=16)
plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate (Recall)', fontsize=16)
plt.grid(True)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plot_roc_curve(fpr, tpr)
fpr_90 = fpr[np.argmax(tpr >= recall_90_precision)]
plt.plot([fpr_90, fpr_90], [0.0, recall_90_precision], 'r:')
plt.plot([0.0, fpr_90], [recall_90_precision, recall_90_precision], 'r:')
plt.plot([fpr_90], [recall_90_precision], 'ro')
save_fig('roc_curve_plot')
plt.show()
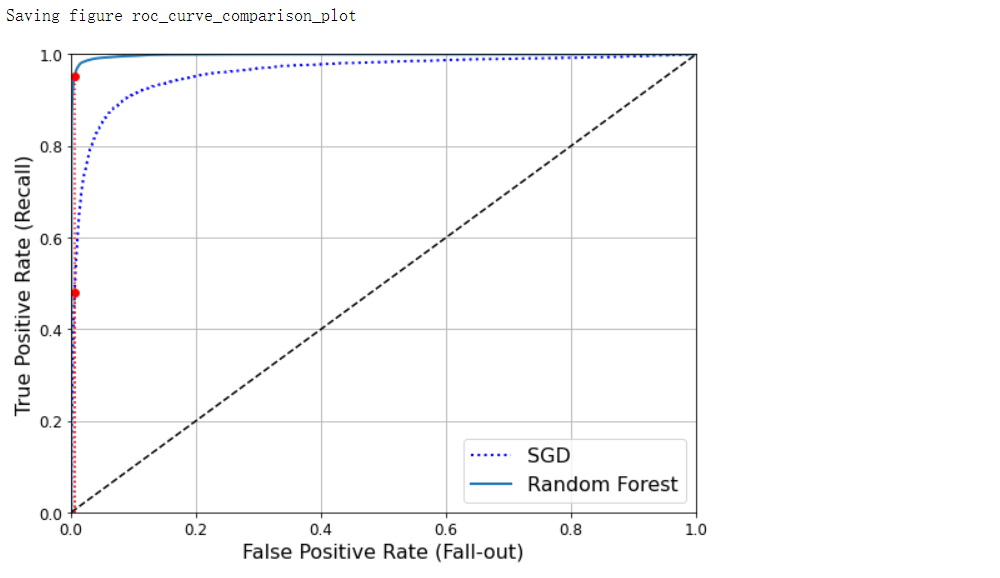
AUC#
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
roc_auc_score(y_train_5, y_scores)
forest_clf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, random_state=42)
y_probas_forest = cross_val_predict(forest_clf, X_train, y_train_5, cv=3, method='predict_proba')
# 得分为预测为正例的概率
y_score_forest = y_probas_forest[:, 1]
fpr_forest, tpr_forest, thresholds_forest = roc_curve(y_train_5, y_score_forest)
recall_for_forest = tpr_forest[np.argmax(fpr_forest >= fpr_90)]
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.plot(fpr, tpr, 'b:', linewidth=2, label='SGD')
plot_roc_curve(fpr_forest, tpr_forest, 'Random Forest')
plt.plot([fpr_90, fpr_90], [0.0, recall_90_precision], 'r:')
plt.plot([0.0, fpr_90], [recall_90_precision, recall_90_precision], 'r:')
plt.plot([fpr_90], [recall_90_precision], 'ro')
plt.plot([fpr_90, fpr_90], [0.0, recall_for_forest], 'r:')
plt.plot([fpr_90], [recall_for_forest], 'ro')
plt.grid(True)
plt.legend(loc='lower right', fontsize=16)
save_fig('roc_curve_comparison_plot')
plt.show()
roc_auc_score(y_train_5, y_score_forest) # 0.9983436731328145
y_train_pred_forest = cross_val_predict(forest_clf, X_train, y_train_5, cv=3)
precision_score(y_train_5, y_train_pred_forest) # 0.9905083315756169
recall_score(y_train_5, y_train_pred_forest) # 0.8662608374838591
多分类#
from sklearn.multiclass import OneVsRestClassifier
ovr_clf = OneVsRestClassifier(SVC(gamma='auto', random_state=42))
ovr_clf.fit(X_train[:1000], y_train[:1000])
ovr_clf.predict([some_digit])
len(ovr_clf.estimators_) # 10
标准化提升准确率#
cross_val_score(sgd_clf, X_train, y_train, cv=3, scoring='accuracy') # array([0.87365, 0.85835, 0.8689 ])
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
scaler = StandardScaler()
X_train_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X_train.astype(np.float64))
cross_val_score(sgd_clf, X_train_scaled, y_train, cv=3, scoring='accuracy') # array([0.8983, 0.891 , 0.9018])
错误分析#
y_train_pred = cross_val_predict(sgd_clf, X_train_scaled, y_train, cv=3)
conf_mx = confusion_matrix(y_train, y_train_pred)
conf_mx
'''
array([[5577, 0, 22, 5, 8, 43, 36, 6, 225, 1],
[ 0, 6400, 37, 24, 4, 44, 4, 7, 212, 10],
[ 27, 27, 5220, 92, 73, 27, 67, 36, 378, 11],
[ 22, 17, 117, 5227, 2, 203, 27, 40, 403, 73],
[ 12, 14, 41, 9, 5182, 12, 34, 27, 347, 164],
[ 27, 15, 30, 168, 53, 4444, 75, 14, 535, 60],
[ 30, 15, 42, 3, 44, 97, 5552, 3, 131, 1],
[ 21, 10, 51, 30, 49, 12, 3, 5684, 195, 210],
[ 17, 63, 48, 86, 3, 126, 25, 10, 5429, 44],
[ 25, 18, 30, 64, 118, 36, 1, 179, 371, 5107]])
'''
# 彩色&colorbar
def plot_confusion_matrix(matrix):
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
cax = ax.matshow(matrix)
fig.colorbar(cax)
plt.matshow(conf_mx, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
save_fig('confusion_matrix_plot', tight_layout=False)
plt.show()
row_sums = conf_mx.sum(axis=1, keepdims=True)
norm_conf_mx = conf_mx / row_sums
# 预测为数字8的错误较多
np.fill_diagonal(norm_conf_mx, 0)
plt.matshow(norm_conf_mx, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
save_fig('confusion_matrix_errors_plot', tight_layout=False)
plt.show()
多标签分类#
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
y_train_large = (y_train >= 7)
y_train_odd = (y_train % 2 == 1)
y_multilabel = np.c_[y_train_large, y_train_odd]
knn_clf = KNeighborsClassifier()
knn_clf.fit(X_train, y_multilabel)
knn_clf.predict([some_digit]) # array([[False, True]])
y_train_knn_pred = cross_val_predict(knn_clf, X_train, y_multilabel, cv=3)
f1_score(y_multilabel, y_train_knn_pred, average='macro') # 0.976410265560605
多输出分类#
noise = np.random.randint(0, 100, (len(X_train), 784))
X_train_mod = X_train + noise
noise = np.random.randint(0, 100, (len(X_test), 784))
X_test_mod = X_test + noise
y_train_mod = X_train # 一个y是一个输出系列
y_test_mod = X_test
some_index = 0
plt.subplot(121); plot_digit(X_test_mod[some_index])
plt.subplot(122); plot_digit(y_test_mod[some_index])
save_fig('noisy_digit_example_plot')
plt.show()
knn_clf.fit(X_train_mod, y_train_mod)
clean_digit = knn_clf.predict([X_test_mod[some_index]])
plot_digit(clean_digit)
save_fig('cleaned_digit_example_plot')
作者:lotuslaw
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/lotuslaw/p/15533057.html
版权:本作品采用「署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际」许可协议进行许可。








【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧