Java中的IO流之输出流|乐字节
大家好,乐字节小乐又来了。上一篇给大家带来的是:Java中的IO流之输入流|乐字节,本文将继续讲述IO流之输出流。

一、输出流
1、抽象类:OutputStream 和 Writer
OutputStream和Writer也非常相似。
在OutputStream 里包含如下方法:
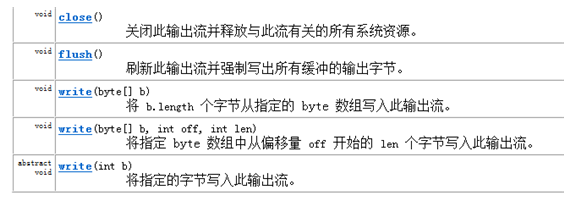
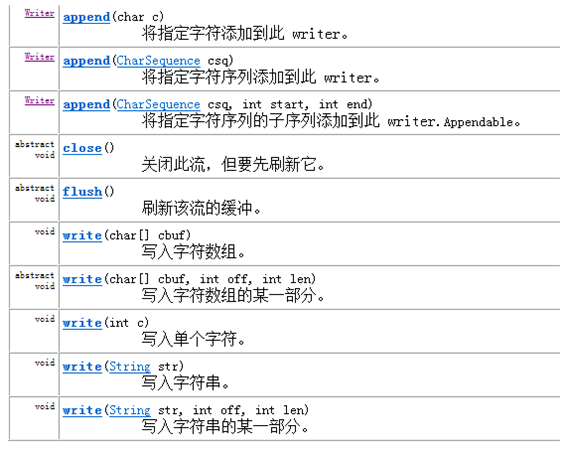
在 Writer 中, 因为字符流直接以字符作为操作单位,所以 Writer 可以用字符串来代替字符数组,即以String对象来作为参数。 包含如下方法:
2、文件节点类: FileOutputStream 和 FileWriter
FileOutputStream 和 FileWriter,它们都是节点流,直接和指定文件关联。
public class WriteFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1、建立联系 File对象 源头 目的地
File dest=new File("c:/IO/print.txt");
//2、选择流 文件输出流 OutputStream FileOutputStream
OutputStream out=null;
//以追加形式写出文件 必须为true 否则会覆盖
try {
out=new FileOutputStream(dest,true);
//3、操作
String str="shsxt is very good \r\n good good good";
//字符串转成字节数组
byte[] data=str.getBytes();
out.write(data,0,data.length);
out.flush();//强制刷新出去
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("文件未找到");
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("文件写出失败");
}finally{
try {
if(out!=null){
out.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("关闭输出流失败");
}
}
}
}
//1、创建源
File dest=new File("f:/IO/char.txt");
//2、选择流
Writer wr=new FileWriter(dest,true);
//3、写出
String str="锄禾日当午\r\n码农真辛苦\r\n一本小破书\r\n一读一上午";
wr.write(str);
//追加内容
wr.append("我就是追加进去的");
wr.flush();//强制刷出
//4、关闭资源
wr.close();
结合输入输出流,可以实现文件拷贝
public static void copyFile(String srcPath, String destPath) throws FileNotFoundException,IOException{
// 1、建立联系 源(存在且为文件) 目的地(文件可以不存在)
File src = new File(srcPath);
File dest = new File(destPath);
if(!src.isFile()){//不是文件或者为null时抛出异常
System.out.println("只能拷贝文件");
throw new IOException("只能拷贝文件");
}
// 2、选择流
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(src);
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(dest);
// 3、操作
byte[] flush = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
// 读取
while (-1 != (len = in.read(flush))) {
// 写出
out.write(flush, 0, len);
}
out.flush();// 强制刷出
// 关闭流 先打开的后关闭
out.close();
in.close();
}
3、缓冲处理流:BufferedOutputStream 和 BufferedWriter
缓冲流提升性能,BufferedWriter存在新增方法newLine(),不能发生多态
public static void copyFile(String srcPath, String destPath) throws FileNotFoundException,IOException{
// 1、建立联系 源(存在且为文件) 目的地(文件可以不存在)
File src = new File(srcPath);
File dest = new File(destPath);
if(!src.isFile()){//不是文件或者为null时抛出异常
System.out.println("只能拷贝文件");
throw new IOException("只能拷贝文件");
}
// 2、选择流
InputStream in = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(src));
OutputStream out =new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dest));
// 3、操作
byte[] flush = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
// 读取
while (-1 != (len = in.read(flush))) {
// 写出
out.write(flush, 0, len);
}
out.flush();// 强制刷出
// 关闭流 先打开的后关闭
out.close();
in.close();
}
}
//1、创建源 仅限于 字符的纯文本
File src=new File("f:/char.txt");
File dest=new File("f:/testIO/char.txt");
//2、选择流
BufferedReader reader=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(src));
BufferedWriter wr=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(dest,true));pend(msg2);
//3、新增方法操作
String line=null;
while(null!=(line=reader.readLine())){
wr.write(line);
//wr.append("\r\n");
//换行符号
wr.newLine();
}
wr.flush();//强制刷出
// 4、关闭流 先打开的后关闭
out.close();
in.close();
4、转换处理流:OutputStreamWriter
可以处理文件的字符集,即将文件按指定字符集进行编码存储 。
//写出文件 编码
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(
new OutputStreamWriter(
new BufferedOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream(
new File("f:/testIO/char.txt")
)
),"utf-8"
)
);
String info=null;
while(null!=(info=br.readLine())){
bw.write(info);
bw.newLine();
}
bw.flush();
bw.close();
5、字节数组节点类: ByteArrayOutputStream
/**
* 字节数组输出流:操作与文件输出流有些不同,有新增方法,所以不可以使用多态
* @throws IOException
*/
public static byte[] write() throws IOException{
//目的地 字节数组
byte[]dest;
//选择流 不同点:不需要将目的地放入new ByteArrayOutputStream()
ByteArrayOutputStream bos=new ByteArrayOutputStream();
//操作 写出, 可以当作将本地的内容通过字节数组写入服务器
String msg="字节数组输入流:操作与文件输入流操作一致";
byte[]info=msg.getBytes();
//将内容写入bos
bos.write(info,0,info.length);
//不同点:获取数据 toByteArray():是将字节数组输出流转为字节数组
dest=bos.toByteArray();
//释放资源
bos.close();//由于bos在jvm中,所以关闭与否不影响
return dest;
}
再来看几个作业题,大家不妨思考思考。
1、Reader和Writer的基本特点是?
2、FileReader和FileWriter的作用是?
3、BufferedReader和BufferedWriter的作用是?
4、word文档能使用字符流操作吗?为什么?
5、使用BufferedReader和BufferedWriter实现文本文件的拷贝
6、什么情况下可以使用字符流拷贝文件夹?什么情况下不能?拷贝文件夹应该使用字符流还是字节流?
7、拷贝文件 使用哪些流?
8、InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter的作用。
9、ByteArrayInputStream与 ByteArrayOutputStream的数据源是什么?
10、为什么ByteArrayOutputStream 不推荐使用匿名?
11、将”坚信没有学不会的知识,只有不想学的知识”写出到字节数组中。
12、从上述的 字节数组中,读取字符串。
13、DataInputStream和DataOutputStream的特点是?
14、将3.14 写出到字节数组中,再进行读取
15、序列化和反序列化指的是什么?
16、想序列化某个类的对象,该类必须实现Serializable接口吗?
17、说说Serializable接口的特点。
18、transient的作用是?
19、使用ObjectInputstream和ObjectOutputStream实现将某个对象存储到硬盘上,然后再读到程序中。
20、PrintStream打印流经常用于什么情况?




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号