【转】基础知识系列4--队列
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/mcgrady/p/3221672.html
上一篇讲了栈,这一篇要总结的是我们常用的队列,我想从以下几个方面进行总结。
1,什么是队列?
2,队列的存储结构?
3,队列的常用操作及实现代码?
1.什么是队列
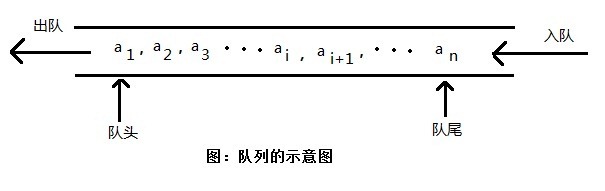
1,首先,队列也是一种特殊的线性表,它是一种操作受限的线性表。它只允许在表的一端进行元素插入,而在另一端进行元素删除。允许插入的一端称为队尾(rear),允许删除的一端称为队头(font)。
2,对于队列,与现实生活中的排队类似,新加入的成员总是在队尾,而排在队列最前面的总是最先离开队列,即先进先出,因此队列也称为先进先出表(FIFO)。
2.队列的存储结构
3.队列的常见操作和代码实现
1,初始化队列
思路:构造一个空队列,即将头指针head和尾指针rear都设置为0。
2,入队
思路:若队列不满,则将数据x插入到尾指针rear指向的位置,然后再将rear加1。
3,出队
思路:若队列不空,则将头指针head加1,并返回被删除的元素。
4,取队头
思路:若队列不空,则返回队头元素。
5,取队长
思路:即尾指针rear-头指针head。
6,判队空
思路:只需要判断头指针head与尾指针是否相等即可
7,判队满
思路:只需判断尾指针与MaxSize是否相等即可
注:在一个非空队列中,头指针始终指向队头元素,而尾指针始终指向队尾元素的下一个位置。
原代码实现用一个数组,但是没有固定队列头,head和rear指针一直在加,即使固定了队列头,每次把队列头推出去也要移动数组,用循环数组可以不用移动,感觉用链表会更加灵活方便,于是我就自己写了一个demo。
循环数组实现队列:
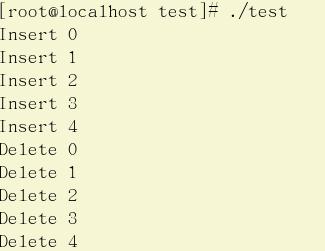
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 #define OK 0 5 #define ERROR -1 6 #define N 5 7 8 typedef int Status; 9 typedef int ElemType; 10 typedef struct queue 11 { 12 ElemType data[N]; 13 int head,rear; 14 }Queue; 15 16 void Init(Queue *q) 17 { 18 q->head=q->rear=0; 19 } 20 21 Status InQueue(Queue *q,ElemType e) 22 { 23 printf("Insert %d to queue\n",e); 24 if((q->rear+1)%N == q->head) 25 { 26 printf("queue is full\n"); 27 return ERROR; 28 } 29 q->data[q->rear] = e; 30 q->rear = (q->rear+1)%N; 31 32 return OK; 33 } 34 35 Status DeleteQueue(Queue *q,ElemType *e) 36 { 37 if(q->head == q->rear) 38 { 39 printf("queue is empty\n"); 40 return ERROR; 41 } 42 *e = q->data[q->head]; 43 printf("delete %d\n",*e); 44 q->head = (q->head+1)%N; 45 return OK; 46 } 47 48 void Display(Queue *q) 49 { 50 int i=0; 51 printf("Queue is :"); 52 while((q->head+i)%N != q->rear) 53 { 54 printf("%d ",q->data[(q->head+i)%N]); 55 i++; 56 } 57 printf("\n"); 58 } 59 60 int main(void) 61 { 62 int i; 63 ElemType e; 64 Queue *q = (Queue*)malloc(sizeof(Queue)); 65 66 Init(q); 67 for(i=0;i<10;i++) 68 { 69 InQueue(q,i); 70 Display(q); 71 } 72 while(q->head != q->rear) 73 { 74 DeleteQueue(q,&e); 75 Display(q); 76 } 77 78 return 0; 79 }
运行结果

链表实现队列:
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 4 typedef struct list 5 { 6 int data; 7 struct list*next; 8 }List; 9 typedef struct queue 10 { 11 List*front; 12 List*rear; 13 }Queue; 14 15 void init_queue(Queue*q) 16 { 17 q->front=q->rear=NULL; 18 } 19 20 void inqueue(Queue *q,int data) 21 { 22 List*newnode=(List*)malloc(sizeof(List)); 23 newnode->next=NULL; 24 newnode->data=data; 25 if(q->front==NULL && q->rear==NULL)//如果是空队列 26 { 27 q->front=q->rear=newnode; 28 } 29 else//如果队列非空 30 { 31 q->rear->next=newnode; 32 q->rear=newnode; 33 } 34 printf("Insert %d\n",data); 35 } 36 int dequeue(Queue*q) 37 { 38 List*temp=NULL; 39 int result; 40 //如果队列为空 41 if(q->front==NULL && q->rear==NULL) 42 { 43 printf("queue is empty,out of queue failed\n"); 44 return -1; 45 } 46 //如果最后一个元素出队列 47 else if(q->front==q->rear) 48 { 49 temp=q->front; 50 result=temp->data; 51 q->front=q->rear=NULL; 52 free(temp); 53 return result; 54 } 55 //非最后元素出队列 56 else 57 { 58 temp=q->front; 59 result=temp->data; 60 q->front=q->front->next; 61 free(temp); 62 return result; 63 } 64 } 65 int queue_isEmpty(Queue*q) 66 { 67 if(q->front==q->rear && q->front==NULL) 68 return 1; 69 else 70 return 0; 71 } 72 73 int main() 74 { 75 int i; 76 Queue*q=(Queue*)malloc(sizeof(Queue)); 77 init_queue(q); 78 for(i=0;i<5;i++) 79 inqueue(q,i); 80 while(!queue_isEmpty(q)) 81 { 82 printf("Delete %d\n",dequeue(q)); 83 } 84 }
运行结果
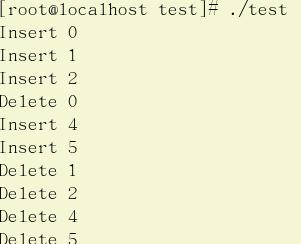
栈实现队列:
思路是:首先开辟两个栈,如果进队列,则体现得是进栈A
如果出队列,体现的是:如果栈B空(之前的元素全部弹出去了),则A全部出队列,再全部进栈B,然后栈B出栈一个元素;
如果栈B不空,则栈B出栈一个元素
代码:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 #define OK 0 5 #define ERROR 1 6 7 typedef int ElemType; 8 typedef int Status; 9 10 typedef struct list 11 { 12 ElemType data; 13 struct list *next; 14 }List; 15 16 typedef struct stack 17 { 18 List* top; 19 }Stack; 20 21 Stack *A,*B; 22 23 void InitStack(Stack *s) 24 { 25 s->top =NULL; 26 } 27 28 void Push(Stack *s,ElemType e) 29 { 30 List *p = (List*)malloc(sizeof(List)); 31 p->data = e; 32 p->next = s->top; 33 s->top = p; 34 } 35 36 Status Pop(Stack *s) 37 { 38 ElemType temp; 39 List *p; 40 if(s->top == NULL) 41 return ERROR; 42 p = s->top; 43 s->top = s->top->next; 44 temp = p->data; 45 free(p); 46 return temp; 47 } 48 49 void InitQueue() 50 { 51 A = (Stack*)malloc(sizeof(Stack)); 52 B = (Stack*)malloc(sizeof(Stack)); 53 InitStack(A); 54 InitStack(B); 55 } 56 57 void InQueue(ElemType e) 58 { 59 Push(A,e); 60 } 61 62 Status QueueIsEmpty() 63 { 64 if(A->top == NULL && B->top == NULL) 65 return 1; 66 return 0; 67 } 68 69 Status DeleteQueue() 70 { 71 if(B->top == NULL) 72 { 73 while(A->top != NULL) 74 Push(B,Pop(A)); 75 } 76 printf("Delete %d\n",Pop(B)); 77 } 78 79 int main(void) 80 { 81 int i; 82 InitQueue(); 83 for(i=0;i<3;i++) 84 { 85 printf("Insert %d\n",i); 86 InQueue(i); 87 } 88 DeleteQueue(); 89 printf("Insert 4\n"); 90 InQueue(4); 91 printf("Insert 5\n"); 92 InQueue(5); 93 while(!QueueIsEmpty()) 94 DeleteQueue(); 95 96 return 0; 97 }
运行结果: