ChaCha20加密 与 Salsa20加密
一、简介
Chacha20流密码经常和Poly1305消息认证码结合使用,被称为ChaCha20-Poly1305,由Google公司率先在Andriod移动平台中的Chrome中代替RC4使用,由于其算法精简、安全性强、兼容性强等特点,目前Google致力于全面将其在移动端推广
二、初始化矩阵
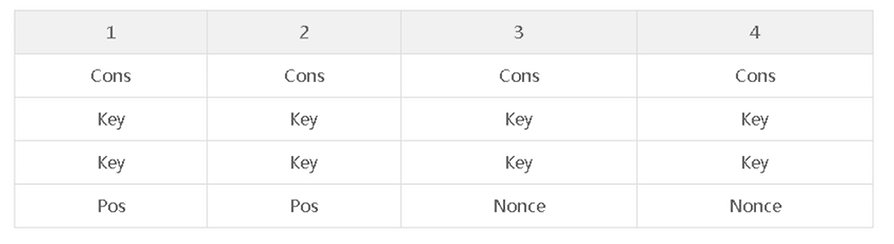
ChaCha20加密的初始状态包括了包括了
1、一个128位常量(Constant)
常量的内容为0x61707865,0x3320646e,0x79622d32,0x6b206574.)
2、一个256位密钥(Key)
3、一个64位计数(Counter)
4、一个64位随机数(Nonce)
一共64字节其排列成4 * 4的32位字矩阵如下所示:(实际运算为小端)
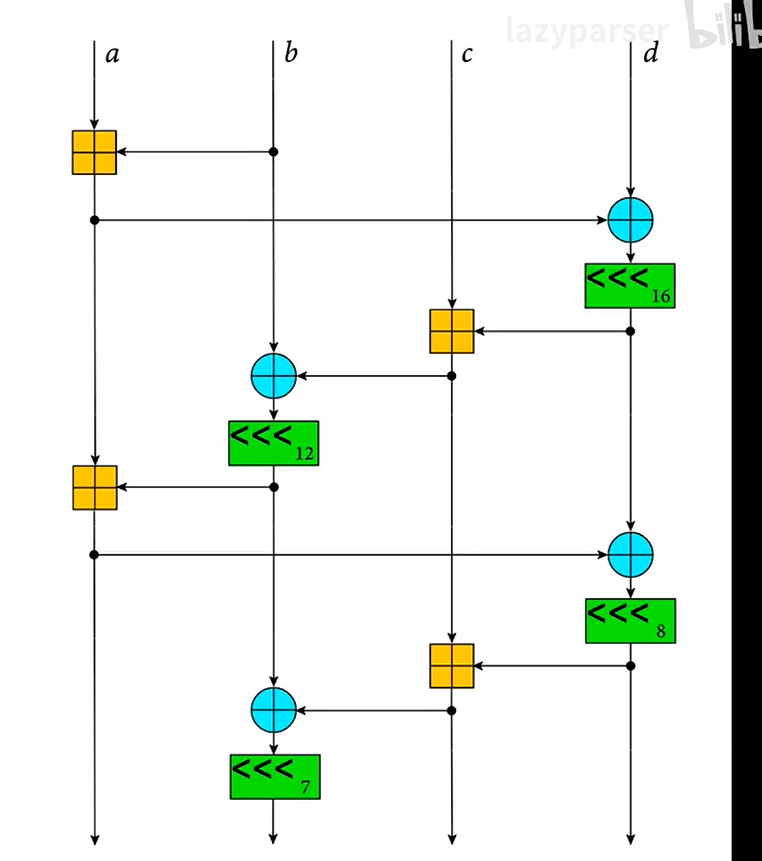
三、1/4 轮操作
在ChaCha20算法当中, 一个基础的操作即为1/4轮运算, 它主要操作4个32位的无符号整数,具体操作如下:
QR(a,b,c,d)
代码如下:
static void chacha20_quarterround(uint32_t *x, int a, int b, int c, int d) { x[a] += x[b]; x[d] = rotl32(x[d] ^ x[a], 16); x[c] += x[d]; x[b] = rotl32(x[b] ^ x[c], 12); x[a] += x[b]; x[d] = rotl32(x[d] ^ x[a], 8); x[c] += x[d]; x[b] = rotl32(x[b] ^ x[c], 7); }
四、块函数
这个块函数输入是之前所生成的状态矩阵, 最终输出64bit的"随机化"的字节
块函数加密时分两种情况,一种是计数为奇数时,进行行变换,如下:
为偶数的时候进行列变换,如下:
代码实现如下:
static void chacha20_block(uint32_t in[16], uint8_t out[64], int num_rounds) { // num_rounds 一般为20 int i; uint32_t x[16]; memcpy(x, in, sizeof(uint32_t) * 16); for (i = num_rounds; i > 0; i -= 2) { //odd round // 奇数行变换 chacha20_quarterround(x, 0, 4, 8, 12); chacha20_quarterround(x, 1, 5, 9, 13); chacha20_quarterround(x, 2, 6, 10, 14); chacha20_quarterround(x, 3, 7, 11, 15); //even round // 偶数列变换 chacha20_quarterround(x, 0, 5, 10, 15); chacha20_quarterround(x, 1, 6, 11, 12); chacha20_quarterround(x, 2, 7, 8, 13); chacha20_quarterround(x, 3, 4, 9, 14); } for (i = 0; i < 16; i++) { x[i] += in[i]; } chacha20_serialize(x, out); }
五、ChaCha20总代码如下
1、C语言实现
编译器:Dev-C++
chacha20.cpp
#include <stdint.h> #include <string.h> #include "chacha20.h" static inline void u32t8le(uint32_t v, uint8_t p[4]) { p[0] = v & 0xff; p[1] = (v >> 8) & 0xff; p[2] = (v >> 16) & 0xff; p[3] = (v >> 24) & 0xff; } static inline uint32_t u8t32le(uint8_t p[4]) { uint32_t value = p[3]; value = (value << 8) | p[2]; value = (value << 8) | p[1]; value = (value << 8) | p[0]; return value; } static inline uint32_t rotl32(uint32_t x, int n) { // http://blog.regehr.org/archives/1063 return x << n | (x >> (-n & 31)); } // https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7539#section-2.1 static void chacha20_quarterround(uint32_t *x, int a, int b, int c, int d) { x[a] += x[b]; x[d] = rotl32(x[d] ^ x[a], 16); x[c] += x[d]; x[b] = rotl32(x[b] ^ x[c], 12); x[a] += x[b]; x[d] = rotl32(x[d] ^ x[a], 8); x[c] += x[d]; x[b] = rotl32(x[b] ^ x[c], 7); } static void chacha20_serialize(uint32_t in[16], uint8_t output[64]) { int i; for (i = 0; i < 16; i++) { u32t8le(in[i], output + (i << 2)); } } static void chacha20_block(uint32_t in[16], uint8_t out[64], int num_rounds) { // num_rounds 一般为20 int i; uint32_t x[16]; memcpy(x, in, sizeof(uint32_t) * 16); for (i = num_rounds; i > 0; i -= 2) { //odd round chacha20_quarterround(x, 0, 4, 8, 12); chacha20_quarterround(x, 1, 5, 9, 13); chacha20_quarterround(x, 2, 6, 10, 14); chacha20_quarterround(x, 3, 7, 11, 15); //even round chacha20_quarterround(x, 0, 5, 10, 15); chacha20_quarterround(x, 1, 6, 11, 12); chacha20_quarterround(x, 2, 7, 8, 13); chacha20_quarterround(x, 3, 4, 9, 14); } for (i = 0; i < 16; i++) { x[i] += in[i]; } chacha20_serialize(x, out); } // https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7539#section-2.3 static void chacha20_init_state(uint32_t s[16], uint8_t key[32], uint32_t counter, uint8_t nonce[12]) { int i; // refer: https://dxr.mozilla.org/mozilla-beta/source/security/nss/lib/freebl/chacha20.c // convert magic number to string: "expand 32-byte k" s[0] = 0x61707865; s[1] = 0x3320646e; s[2] = 0x79622d32; s[3] = 0x6b206574; for (i = 0; i < 8; i++) { s[4 + i] = u8t32le(key + i * 4); } s[12] = counter; for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) { s[13 + i] = u8t32le(nonce + i * 4); } } void ChaCha20XOR(uint8_t key[32], uint32_t counter, uint8_t nonce[12], uint8_t *in, uint8_t *out, int inlen) { int i, j; uint32_t s[16]; uint8_t block[64]; chacha20_init_state(s, key, counter, nonce); for (i = 0; i < inlen; i += 64) { chacha20_block(s, block, 20); s[12]++; for (j = i; j < i + 64; j++) { if (j >= inlen) { break; } out[j] = in[j] ^ block[j - i]; } } }
chacha20.h
#ifndef __CHACHA20_H #define __CHACHA20_H #include <stdint.h> void ChaCha20XOR(uint8_t key[32], uint32_t counter, uint8_t nonce[12], uint8_t *input, uint8_t *output, int inputlen); #endif
main.cpp
#include <stdio.h> #include "chacha20.h" int main(int argc, char **argv) { int i; uint8_t key[] = { 0x00, 0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x05, 0x06, 0x07, 0x08, 0x09, 0x0a, 0x0b, 0x0c, 0x0d, 0x0e, 0x0f, 0x10, 0x11, 0x12, 0x13, 0x14, 0x15, 0x16, 0x17, 0x18, 0x19, 0x1a, 0x1b, 0x1c, 0x1d, 0x1e, 0x1f }; uint8_t nonce[] = { // 随机数 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x4a, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00 }; uint8_t input[114] = { 0x4c, 0x61, 0x64, 0x69, 0x65, 0x73, 0x20, 0x61, 0x6e, 0x64, 0x20, 0x47, 0x65, 0x6e, 0x74, 0x6c, 0x65, 0x6d, 0x65, 0x6e, 0x20, 0x6f, 0x66, 0x20, 0x74, 0x68, 0x65, 0x20, 0x63, 0x6c, 0x61, 0x73, 0x73, 0x20, 0x6f, 0x66, 0x20, 0x27, 0x39, 0x39, 0x3a, 0x20, 0x49, 0x66, 0x20, 0x49, 0x20, 0x63, 0x6f, 0x75, 0x6c, 0x64, 0x20, 0x6f, 0x66, 0x66, 0x65, 0x72, 0x20, 0x79, 0x6f, 0x75, 0x20, 0x6f, 0x6e, 0x6c, 0x79, 0x20, 0x6f, 0x6e, 0x65, 0x20, 0x74, 0x69, 0x70, 0x20, 0x66, 0x6f, 0x72, 0x20, 0x74, 0x68, 0x65, 0x20, 0x66, 0x75, 0x74, 0x75, 0x72, 0x65, 0x2c, 0x20, 0x73, 0x75, 0x6e, 0x73, 0x63, 0x72, 0x65, 0x65, 0x6e, 0x20, 0x77, 0x6f, 0x75, 0x6c, 0x64, 0x20, 0x62, 0x65, 0x20, 0x69, 0x74, 0x2e }; uint8_t encrypt[114]; uint8_t decrypt[114]; ChaCha20XOR(key, 1, nonce, input, encrypt, 114); //1 就是conter ChaCha20XOR(key, 1, nonce, encrypt, decrypt, 114); printf("\nkey:"); for (i = 0; i < 32; i++) { if (!(i % 16)) { printf("\n"); } printf("%02x ", key[i]); } printf("\n\nnonce:\n"); for (i = 0; i < 12; i++) { printf("%02x ", nonce[i]); } printf("\n\nplaintext:"); for (i = 0; i < 114; i++) { if (!(i % 16)) { printf("\n"); } printf("%02x ", input[i]); } printf("\n\nencrypted:"); for (i = 0; i < 114; i++) { if (!(i % 16)) { printf("\n"); } printf("%02x ", encrypt[i]); } printf("\n\ndecrypted:"); for (i = 0; i < 114; i++) { if (!(i % 16)) { printf("\n"); } printf("%02x ", decrypt[i]); } printf("\n"); return 0; }
2、Python实现
def main(): runtests() def chacha20_decrypt(key, counter, nonce, ciphertext): return chacha20_encrypt(key, counter, nonce, ciphertext) def chacha20_encrypt(key, counter, nonce, plaintext): byte_length = len(plaintext) full_blocks = byte_length//64 remainder_bytes = byte_length % 64 encrypted_message = b'' for i in range(full_blocks): key_stream = serialize(chacha20_block(key, counter + i, nonce)) plaintext_block = plaintext[i*64:i*64+64] encrypted_block = [plaintext_block[j] ^ key_stream[j] for j in range(64)] encrypted_message += bytes(encrypted_block) if remainder_bytes != 0: key_stream = serialize(chacha20_block(key, counter + full_blocks, nonce)) plaintext_block = plaintext[full_blocks*64:byte_length] encrypted_block = [plaintext_block[j] ^ key_stream[j] for j in range(remainder_bytes)] encrypted_message += bytes(encrypted_block) return encrypted_message # returns a list of 16 32-bit unsigned integers def chacha20_block(key, counter, nonce): BLOCK_CONSTANTS = [0x61707865, 0x3320646e, 0x79622d32, 0x6b206574] init_state = BLOCK_CONSTANTS + key + [counter] + nonce current_state = init_state[:] for i in range(10): inner_block(current_state) for i in range(16): current_state[i] = add_32(current_state[i], init_state[i]) return current_state def inner_block(state): # columns quarterround(state, 0, 4, 8, 12) quarterround(state, 1, 5, 9, 13) quarterround(state, 2, 6, 10, 14) quarterround(state, 3, 7, 11, 15) # diagonals quarterround(state, 0, 5, 10, 15) quarterround(state, 1, 6, 11, 12) quarterround(state, 2, 7, 8, 13) quarterround(state, 3, 4, 9, 14) def xor_32(x, y): return (x ^ y) & 0xffffffff def add_32(x, y): return (x + y) & 0xffffffff def rot_l32(x, n): return ((x << n) | (x >> (32 - n))) & 0xffffffff def quarterround(state, i1, i2, i3, i4): a = state[i1] b = state[i2] c = state[i3] d = state[i4] a = add_32(a, b); d = xor_32(d, a); d = rot_l32(d, 16) c = add_32(c, d); b = xor_32(b, c); b = rot_l32(b, 12) a = add_32(a, b); d = xor_32(d, a); d = rot_l32(d, 8) c = add_32(c, d); b = xor_32(b, c); b = rot_l32(b, 7) state[i1] = a state[i2] = b state[i3] = c state[i4] = d def serialize(block): return b''.join([(word).to_bytes(4, 'little') for word in block]) # Test Vectors from RFC 8439 def runtests(): key = [0x2519EB0A, 0x909CE82E, 0xD6C085EC, 0x545ACF07, 0x24124049, 0x1E1353E7, 0x14AD4F2F, 0xE98FF6DE] plaintext = b"\x8e\x91\x9e\xbe\x6a\x6c\x64\xc1\x02\x02\xf8\xda\xc4\xc8\xd6\x14\xa0\xa3\x9c\x0e\x62\x64\x70\x6d\x02\x02\x0c\x9d\xd2\xd6\xc6\xa8" nonce = [0x7369C667, 0xEC4AFF51, 0xABBACD29] init_counter = 0x00000001 ciphertext = chacha20_encrypt(key, init_counter, nonce, plaintext) for i in range(len(ciphertext)): print(hex(ciphertext[i])[2:],end = " ") assert(chacha20_decrypt(key, init_counter, nonce, ciphertext) == plaintext) print("All tests passed!") main();
参考:
六、Salsa20加密
其实Salsa20加密和ChaCha20特别相似,ChaCha20是对Salsa20上稍微做了调整,数据bit扩散更快。每一个1/4 round会修改一个字两次,每一个输入字也会影响到输出字
两种加密算法只有四分之一论操作有一点点不同
ChaCha20是这样的:
static inline uint32_t rotl32(uint32_t x, int n) { // http://blog.regehr.org/archives/1063 return x << n | (x >> (-n & 31)); } // https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7539#section-2.1 static void chacha20_quarterround(uint32_t *x, int a, int b, int c, int d) { x[a] += x[b]; x[d] = rotl32(x[d] ^ x[a], 16); x[c] += x[d]; x[b] = rotl32(x[b] ^ x[c], 12); x[a] += x[b]; x[d] = rotl32(x[d] ^ x[a], 8); x[c] += x[d]; x[b] = rotl32(x[b] ^ x[c], 7); }
Salsa20则是这样的:
#define quarter(a,b,c,d) do {\ b ^= R(d+a, 7);\ c ^= R(a+b, 9);\ d ^= R(b+c, 13);\ a ^= R(c+d, 18);\ } while (0)
七、Salsa20代码实现
1、C语言实现
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdint.h> // we use 32-bit words // rotate x to left by n bits, the bits that go over the left edge reappear on the right #define R(x,n) (((x) << (n)) | ((x) >> (32-(n)))) // addition wraps modulo 2^32 // the choice of 7,9,13,18 "doesn't seem very important" (spec) #define quarter(a,b,c,d) do {\ b ^= R(d+a, 7);\ c ^= R(a+b, 9);\ d ^= R(b+c, 13);\ a ^= R(c+d, 18);\ } while (0) void salsa20_words(uint32_t *out, uint32_t in[16]) { // chacha20_quarterround(x, 0, 4, 8, 12); //chacha20_quarterround(x, 1, 5, 9, 13); //chacha20_quarterround(x, 2, 6, 10, 14); //chacha20_quarterround(x, 3, 7, 11, 15); ////even round //chacha20_quarterround(x, 0, 5, 10, 15); //chacha20_quarterround(x, 1, 6, 11, 12); //chacha20_quarterround(x, 2, 7, 8, 13); //chacha20_quarterround(x, 3, 4, 9, 14); 其实这俩的置换是一模一样的 uint32_t x[4][4]; int i; for (i=0; i<16; ++i) x[i/4][i%4] = in[i]; for (i=0; i<10; ++i) { // 10 double rounds = 20 rounds // column round: quarter round on each column; start at ith element and wrap quarter(x[0][0], x[1][0], x[2][0], x[3][0]); quarter(x[1][1], x[2][1], x[3][1], x[0][1]); quarter(x[2][2], x[3][2], x[0][2], x[1][2]); quarter(x[3][3], x[0][3], x[1][3], x[2][3]); // row round: quarter round on each row; start at ith element and wrap around quarter(x[0][0], x[0][1], x[0][2], x[0][3]); quarter(x[1][1], x[1][2], x[1][3], x[1][0]); quarter(x[2][2], x[2][3], x[2][0], x[2][1]); quarter(x[3][3], x[3][0], x[3][1], x[3][2]); } for (i=0; i<16; ++i) out[i] = x[i/4][i%4] + in[i]; } // inputting a key, message nonce, keystream index and constants to that transormation void salsa20_block(uint8_t *out, uint8_t key[32], uint64_t nonce, uint64_t index) { static const char c[16] = "expand 32-byte k"; // arbitrary constant #define LE(p) ( (p)[0] | ((p)[1]<<8) | ((p)[2]<<16) | ((p)[3]<<24) ) uint32_t in[16] = {LE(c), LE(key), LE(key+4), LE(key+8), LE(key+12), LE(c+4), nonce&0xffffffff, nonce>>32, index&0xffffffff, index>>32, LE(c+8), LE(key+16), LE(key+20), LE(key+24), LE(key+28), LE(c+12)}; uint32_t wordout[16]; salsa20_words(wordout, in); int i; for (i=0; i<64; ++i) out[i] = 0xff & (wordout[i/4] >> (8*(i%4))); } // enc/dec: xor a message with transformations of key, a per-message nonce and block index void salsa20(uint8_t *message, uint64_t mlen, uint8_t key[32], uint64_t nonce) { int i; uint8_t block[64]; for (i=0; i<mlen; i++) { if (i%64 == 0) salsa20_block(block, key, nonce, i/64); message[i] ^= block[i%64]; } } //Set 2, vector# 0: // key = 00000000000000000000000000000000 // 00000000000000000000000000000000 // IV = 0000000000000000 // stream[0..63] = 9A97F65B9B4C721B960A672145FCA8D4 // E32E67F9111EA979CE9C4826806AEEE6 // 3DE9C0DA2BD7F91EBCB2639BF989C625 // 1B29BF38D39A9BDCE7C55F4B2AC12A39 int main () { uint8_t key[32] = {0}; uint64_t nonce = 0; uint8_t msg[64] = {0}; // 密文 salsa20(msg, sizeof(msg), key, nonce); int i; for (i=0; i<sizeof(msg); ++i) printf("%02X ", msg[i]); printf("\n"); printf("\n%d\n",i); return 0; }
抄自github
2、Python实现
class Salsa: def __init__(self,r=20): assert r >= 0 self._r = r # number of rounds self._mask = 0xffffffff # 32-bit mask def __call__(self,key=[0]*32,nonce=[0]*8,block_counter=[0]*8): assert len(key) == 32 assert len(nonce) == 8 assert len(block_counter) == 8 # init state k = [self._littleendian(key[4*i:4*i+4]) for i in range(8)] n = [self._littleendian(nonce[4*i:4*i+4]) for i in range(2)] b = [self._littleendian(block_counter[4*i:4*i+4]) for i in range(2)] c = [0x61707865, 0x3320646e, 0x79622d32, 0x6b206574] s = [c[0], k[0], k[1], k[2], k[3], c[1], n[0], n[1], b[0], b[1], c[2], k[4], k[5], k[6], k[7], c[3]] # the state self._s = s[:] for i in range(self._r): self._round() # add initial state to the final one self._s = [(self._s[i] + s[i]) & self._mask for i in range(16)] return self._s def _littleendian(self,b): assert len(b) == 4 return b[0] ^ (b[1] << 8) ^ (b[2] << 16) ^ (b[3] << 24) def _round(self): # quarterround 1 self._s[ 4] ^= self._rotl32((self._s[ 0] + self._s[12]) & self._mask, 7) self._s[ 8] ^= self._rotl32((self._s[ 0] + self._s[ 4]) & self._mask, 9) self._s[12] ^= self._rotl32((self._s[ 4] + self._s[ 8]) & self._mask,13) self._s[ 0] ^= self._rotl32((self._s[ 8] + self._s[12]) & self._mask,18) # quarterround 2 self._s[ 9] ^= self._rotl32((self._s[ 1] + self._s[ 5]) & self._mask, 7) self._s[13] ^= self._rotl32((self._s[ 5] + self._s[ 9]) & self._mask, 9) self._s[ 1] ^= self._rotl32((self._s[ 9] + self._s[13]) & self._mask,13) self._s[ 5] ^= self._rotl32((self._s[ 1] + self._s[13]) & self._mask,18) # quarterround 3 self._s[14] ^= self._rotl32((self._s[ 6] + self._s[10]) & self._mask, 7) self._s[ 2] ^= self._rotl32((self._s[10] + self._s[14]) & self._mask, 9) self._s[ 6] ^= self._rotl32((self._s[ 2] + self._s[14]) & self._mask,13) self._s[10] ^= self._rotl32((self._s[ 2] + self._s[ 6]) & self._mask,18) # quarterround 4 self._s[ 3] ^= self._rotl32((self._s[11] + self._s[15]) & self._mask, 7) self._s[ 7] ^= self._rotl32((self._s[ 3] + self._s[15]) & self._mask, 9) self._s[11] ^= self._rotl32((self._s[ 3] + self._s[ 7]) & self._mask,13) self._s[15] ^= self._rotl32((self._s[ 7] + self._s[11]) & self._mask,18) # transpose self._s = [self._s[ 0], self._s[ 4], self._s[ 8], self._s[12], self._s[ 1], self._s[ 5], self._s[ 9], self._s[13], self._s[ 2], self._s[ 6], self._s[10], self._s[14], self._s[ 3], self._s[ 7], self._s[11], self._s[15]] def _rotl32(self,w,r): # rotate left for 32-bits return ( ( ( w << r ) & self._mask) | ( w >> ( 32 - r ) ) ) if __name__ == '__main__': salsa20 = Salsa() # vectors = [ # [ [0]*32, [3,1,4,1,5,9,2,6], [7,0,0,0,0,0,0,0], # 这里就是参数!!! # [ 0xb9a205a3,0x0695e150,0xaa94881a,0xadb7b12c, # 0x798942d4,0x26107016,0x64edb1a4,0x2d27173f, # 0xb1c7f1fa,0x62066edc,0xe035fa23,0xc4496f04, # 0x2131e6b3,0x810bde28,0xf62cb407,0x6bdede3d ] ] ] vectors = [ [ [0]*32, [0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0], [0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]]] # 这里就是参数!!! for i in range(len(vectors)): v = vectors[i] print(f"v[0] => {v[0]}") print(f"v[1] => {v[1]}") print(f"v[2] => {v[2]}") s = salsa20(v[0],v[1],v[2]) stream_key = [] # for i in s: # print(hex(i),end = " ") for i in range(len(s)): stream_key.append(s[i] & 0xff) stream_key.append((s[i] & 0xff00) >> 8) stream_key.append((s[i] & 0xff0000) >>16 ) stream_key.append((s[i] & 0xff000000) >>24 ) print() for i in stream_key: print(hex(i),end = " ") # 得到的是密钥流
__EOF__

本文作者:_TLSN
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/lordtianqiyi/articles/16822639.html
关于博主:评论和私信会在第一时间回复。或者直接私信我。
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
声援博主:如果您觉得文章对您有帮助,可以点击文章右下角【推荐】一下。您的鼓励是博主的最大动力!
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/lordtianqiyi/articles/16822639.html
关于博主:评论和私信会在第一时间回复。或者直接私信我。
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
声援博主:如果您觉得文章对您有帮助,可以点击文章右下角【推荐】一下。您的鼓励是博主的最大动力!





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 25岁的心里话
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 按钮权限的设计及实现