浅记 ctf linux内核程序逆向
这里以ACTF的一道题为例
题目是给出了这三个文件
1、bzImage文件
1、文件bzImage是压缩编译的内核镜像文件 2、有的题目会直接给出vmlinux文件(未被压缩的镜像文件),主要目的就是找gadget。。。vmlinux是一个包含linux kernel的静态链接的可执行文件,文件类型是linux接受的可执行文件格式之一(ELF、COFF或a.out)。 3、我们也可以直接从bzImage.sh脚本中直接提取出vmlinux文件 sh脚本如下: #!/bin/sh # SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-2.0-only # ---------------------------------------------------------------------- # extract-vmlinux - Extract uncompressed vmlinux from a kernel image # # Inspired from extract-ikconfig # (c) 2009,2010 Dick Streefland <dick@streefland.net> # # (c) 2011 Corentin Chary <corentin.chary@gmail.com> # # ---------------------------------------------------------------------- check_vmlinux() { # Use readelf to check if it's a valid ELF # TODO: find a better to way to check that it's really vmlinux # and not just an elf readelf -h $1 > /dev/null 2>&1 || return 1 cat $1 exit 0 } try_decompress() { # The obscure use of the "tr" filter is to work around older versions of # "grep" that report the byte offset of the line instead of the pattern. # Try to find the header ($1) and decompress from here for pos in `tr "$1\n$2" "\n$2=" < "$img" | grep -abo "^$2"` do pos=${pos%%:*} tail -c+$pos "$img" | $3 > $tmp 2> /dev/null check_vmlinux $tmp done } # Check invocation: me=${0##*/} img=$1 if [ $# -ne 1 -o ! -s "$img" ] then echo "Usage: $me <kernel-image>" >&2 exit 2 fi # Prepare temp files: tmp=$(mktemp /tmp/vmlinux-XXX) trap "rm -f $tmp" 0 # That didn't work, so retry after decompression. try_decompress '\037\213\010' xy gunzip try_decompress '\3757zXZ\000' abcde unxz try_decompress 'BZh' xy bunzip2 try_decompress '\135\0\0\0' xxx unlzma try_decompress '\211\114\132' xy 'lzop -d' try_decompress '\002!L\030' xxx 'lz4 -d' try_decompress '(\265/\375' xxx unzstd # Finally check for uncompressed images or objects: check_vmlinux $img # Bail out: echo "$me: Cannot find vmlinux." >&2
之后直接 xxx.sh '/home/tlsn/Desktop/ACTF/bzImage' > vmlinux 即可
2、launch.sh启动脚本
文件打开后如下
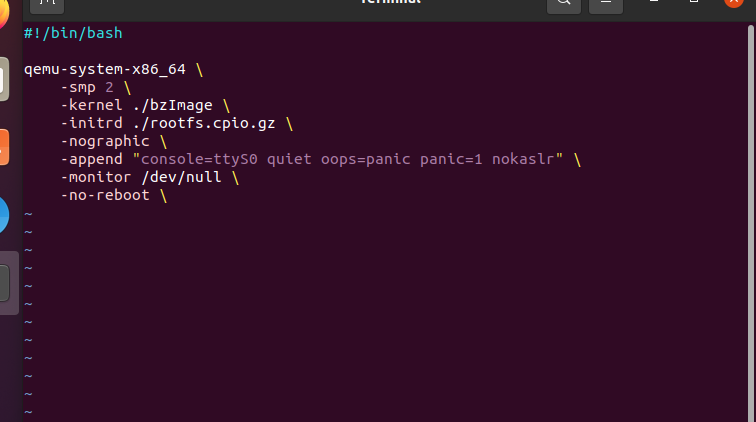

类似于这样的文件功能如下
#!/bin/bash qemu-system-x86_64 \ -initrd rootfs.cpio \ # 指定使用rootfs.cpio作为初始RAM磁盘。可以使用cpio 命令提取这个cpio文件,提取出里面的需要的文件,比如init脚本和babydriver.ko的驱动文件。提取操作的命令放在下面的操作步骤中 -kernel bzImage \ # 使用当前目录的bzImage作为内核镜像 -append 'console=ttyS0 root=/dev/ram oops=panic panic=1' \ # 使用后面的字符串作为内核命令行 -enable-kvm \ # 启用加速器 -monitor /dev/null \ # 将监视器重定向到字符设备/dev/null -m 64M \ # 参数设置RAM大小为64M --nographic \ # 参数禁用图形输出并将串行I/O重定向到控制台 -smp cores=1,threads=1 \ # 参数将CPU设置为1核心1线程 -cpu kvm64,+smep # 参数选择CPU为kvm64,开启了smep保护,无法在ring 0级别执行用户代码
3、.cpio文件
这是初始化的文件系统,我们可以解压得到文件系统
其中得到的Init文件
4、Init文件
它决定启动哪些程序,比如执行某些脚本和启动shell
命令如下:
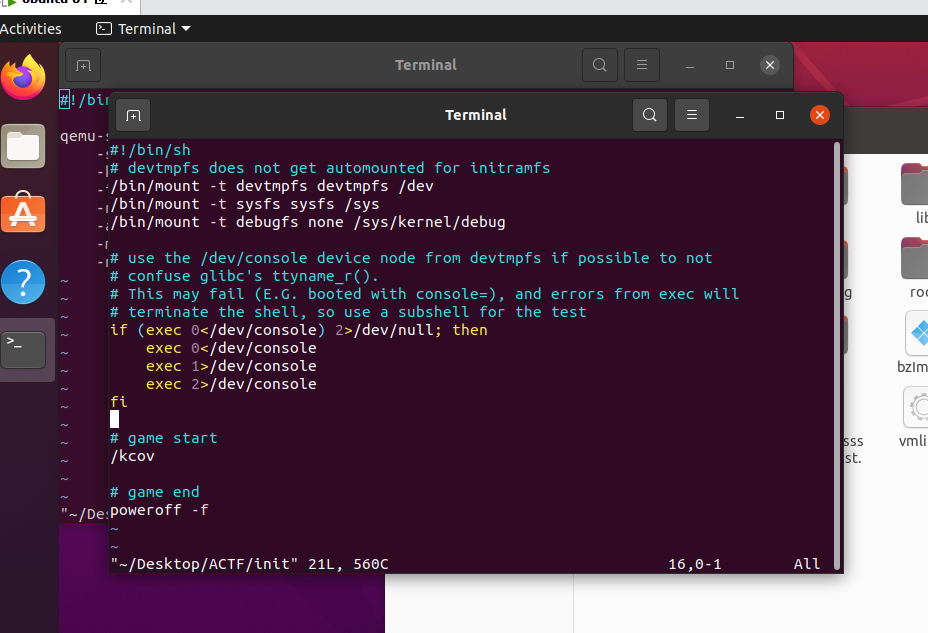
一般的init文件都会加载一个.ko的驱动文件,pwn手的主要战场就在那里


