组合数
1、求组合数,从a中选b个数的方案:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; const int N = 2001, mod = 1e9 + 7; int c[N][N]; void init() { for(int i = 0;i < N;i++) for(int j = 0; j <= i; j++) if(!j) c[i][j] = 1; else c[i][j] = (c[i-1][j] + c[i-1][j-1]) % mod; } int main() { init(); int n; cin>>n; while(n--) { int a, b; cin>>a>>b; cout<<c[a][b]<<endl; } }
从a中选b个的方案 = 假如先拿出一个,然后剩下的a-1个选b个的方案(不包含拿出的这个数,所以要选b个) + 剩下的a-1个选b-1个的方案(包含拿出的这一个数,所以要选b-1个)之和。
首先预处理出所有的方案数,时间复杂度为2000 * 2000 = 4e6;
注意边界c[i][0] (0 <= i <= N) c[i][0] = 1;
1)n<=1e5, 1<=a,b<=2000 用的是递推c[a][b] = c[a-1][b] + c[a-1][b-1];
2)n<=1e4, 1<=a,b<=1e5, 预处理 Cab = a! / b! * (a - b)!, fact[i] = i! mod 1e9+7; a / b mod p != a mod p / b mod p, 用逆元来算,把除法变成乘法。
预处理初阶乘的逆元:infact[i] = i!^-1 mod 1e9 + 7;
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; const int N = 100010, mod = 1e9 + 7; int fact[N], infact[N]; LL quickPow(int a, int k, int p) { LL res = 1; while(k) { if(k & 1) res = res * a % p; k >>= 1; a = (LL)a * a % p; } return res; } int main() { fact[0] = infact[0] = 1; for(int i = 1; i < N;i++) { fact[i] = (LL) fact[i-1] * i % mod; infact[i] = (LL)infact[i-1] * quickPow(i, mod-2,mod) % mod; } int n; cin>>n; while(n--) { int a, b; cin>>a>>b; cout<<(LL)fact[a] * infact[a-b] % mod * infact[b] % mod<<endl; } }
也就是说逆元就是把除法改成乘法了b /a ,那么1 / a就是a的逆元了。求逆元的方法费马定理:b * b^-1 ≡ 1 ( mod p) 那么逆元就是b^(p-2) 也就是说infact[i] = infact[i-1] * i^-1, 因为i^-1 * i ≡ 1 (mod p), 所以i^-1 = i^(p-2).
3) 如果a,b<=10^18 那么就要用Lucas定理。

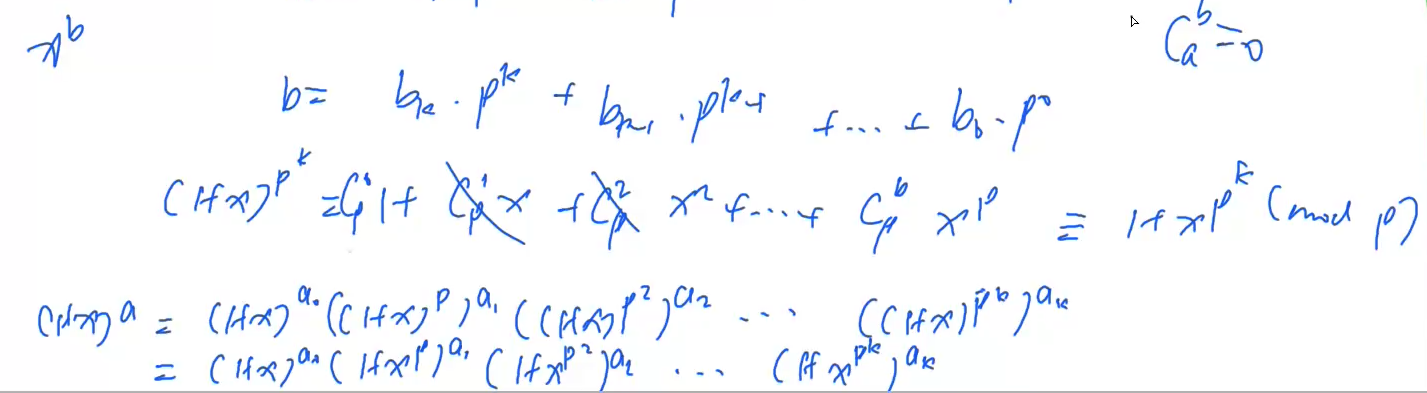
lucas定理:
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; typedef unsigned long long LL; int p; int quickPow(int a, int k) { int res = 1; while(k) { if(k & 1) res = (LL)res * a % p; a = (LL)a * a % p; k >>= 1; } return res; } int C(LL a, LL b) { LL res = 1; for(LL i = 1, j = a; i <= b; i++, j--) { res = (LL)res * j % p; res = (LL)res * quickPow(i, p - 2) % p; } return res; } int lucas(LL a, LL b) { if(a < p && b < p) return C(a,b); return (LL) C(a % p, b % p) * lucas(a / p, b / p) % p; } int main() { int n; cin>>n; while(n--) { LL a, b; cin>>a>>b>>p; cout<<lucas(a,b)<<endl; } return 0; }

最后用高精度求解完整组合数,没有取模。
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <vector> const int N = 5010; using namespace std; int primes[N], cnt; int sum[N]; bool st[N]; //线性筛质数 void get_primes(int n) { for(int i = 2;i <= n; i++) { if(!st[i]) primes[cnt++] = i; for(int j = 0; primes[j] <= n / i;j++) { st[primes[j] * i] = true; if(i % primes[j] == 0) break; } } } //n!包含质数p,p^2,p^3...p^k的个数 int get(int n, int p) { int res = 0; while(n) { res += n / p; n /= p; } return res; } vector<int> mul(vector<int> a, int b) { vector<int> c; int t = 0; for(int i = 0; i < a.size(); i++) { t += a[i] * b; c.push_back(t % 10); t /= 10; } while(t) { c.push_back(t % 10); t /= 10; } return c; } int main() { int a,b; cin>>a>>b; get_primes(a); for(int i = 0;i < cnt; i++) { int p = primes[i]; sum[i] = get(a, p) - get(b, p) - get(a - b, p); } vector<int> res; res.push_back(1); for(int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) for(int j = 0; j < sum[i]; j ++) res = mul(res, primes[i]);//高精度乘法的模板 for(int i = res.size() - 1; i >= 0; i --) printf("%d",res[i]); puts(""); return 0; }
高精度乘法这里比较妙:第一重循环:质数的个数,第二重循环:每个质数的个数,这样就把有的每个质数都乘进来。
for(int i = 0; i < a.size(); i++)
{
t += a[i] * b;
c.push_back(t % 10);
t /= 10;
}
while(t)
{
c.push_back(t % 10);
t /= 10;
}
还有一个是求a!中质数的个数方法也很是巧妙:
int res = 0;
while(n)
{
res += n / p;
n /= p;
}
比如5!质数2的个数:res = 2 + 1 = 3, 5 * 4 * 3 * 2 * 1 = 2 ^ 3 * 30,质数2确实是是3个。
5!质数3的个数: res = 5 / 3 + 1 / 3 = 1个。
再然后是非常好用的线性筛模板:
void get_primes(int n) { for(int i = 2; i <= n;i++) { if(!st[i]) primes[cnt++] = i; for(int j = 0; j <= n / i; j++) { st[primes[j] * i] = true; if(i % primes[j] == 0) break; } } }
//卡特兰数:每种数列可以转化为一条路径,同样每个路径也可以转化为一种01排列。0:向右,1:向上,那么要使得前缀中0的个数大于等于1个
//就要使得路径都在所有的{(0,0),(6,6)}即 y = x这条对角线的下面,同时也要使得我们的路径不得经过 y = x - 1;
//总的方案数C12^6 - 经过y = x - 1的方案数 = 不经过的方案数。不合法的路径一定是(0,0)到(5,7) C2n^n - C2n^n-1


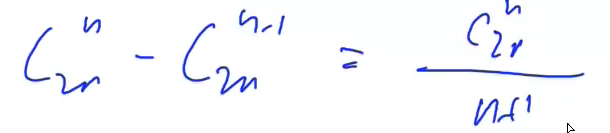
如果取模的数是质数,那么就可以用快速幂来计算逆元,但是如果不是的话,那么只能用扩展欧几里得来求逆元
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int mod = 1e9 + 7; typedef long long LL; int quickPow(int a, int k) { int res = 1; while(k) { if(k & 1) res = (LL)res * a % mod; k >>= 1; a = (LL)a * a % mod; } return res; } int main() { int n; cin>>n; int a = 2 * n, b = n; int res = 1; for(int i = a; i > a - b; i--) res = (LL) res * i % mod; //(2n - n + 1)! for(int i = 1; i <= b; i++) res = (LL) res * quickPow(i, mod - 2) % mod; res = (LL) res * quickPow(n + 1, mod - 2) % mod; cout<<res<<endl; return 0; }





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?