Mybatis思
站在巨人的肩膀上,感谢!
mybatis源码分析之Mapper代理实现分析
版权声明:欢迎转载,如有不足之处,恳请斧正。如果有错误,欢迎指出。 https://blog.csdn.net/huangshanchun/article/details/78597789
0 概述
使用过mybatis框架的人都知道,我们只是写了一个个mapper接口但是没有写它的实现类,但是我们可以直接使用它调用其对应的接口执行相应的sql语句。其实很容易想到它是使用代理来实现的,那么究竟是怎么实现的呢?本文主要来揭开这一神秘面纱。
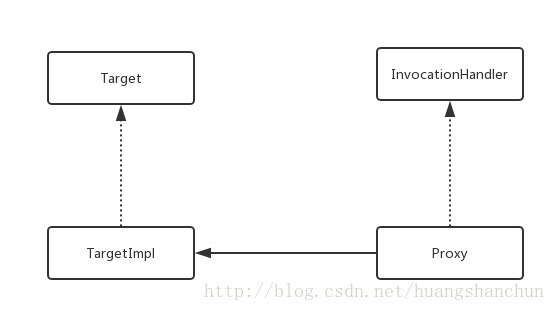
1 代理模式
之前写过一篇代理模式的简介,一般使用代理方式如下,有个Target接口以及其实现类,Proxy中会调用具体Target实现类。具体实例可见:代理模式
2 Mapper接口代理实现的源码分析
我们知道Mapper接口是没有具体的实现类,那么是怎么个代理法?其实是一种约定,但是正是因为这种约定可以大大的简化开发。约定Mapper接口XML文件一一对应,这样在invoke方法中就可以通过相应的类名、方法名获取到相应的xml文件配置的sql语句,从而执行对应的sql语句。
如下面实例,不难发现mapper类名和xml 中namespace对应上,mapper中方法名和对应的id对应上。
package com.hsc.dao;
import com.hsc.entity.Book;
/**
* Created by hsc on 17/7/22.
*/
public interface BookMapper {
int insert(Book book);
}
对应xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.hsc.dao.BookMapper">
<sql id="Base_Column_List">
`id`,`name`
</sql>
<insert id="insert" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id"
parameterType="com.hsc.entity.Book">
insert into book(name)
values(
#{name})
</insert>
</mapper>MapperProxyFactory 工厂类
/**
* @author Lasse Voss
*/
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {
//Mapper接口
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<Method, MapperMethod>();
public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
public Class<T> getMapperInterface() {
return mapperInterface;
}
public Map<Method, MapperMethod> getMethodCache() {
return methodCache;
}
//返回接口的代理对象,基于JDK的原生的代理方式
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
}MapperProxy 是实现InvocationHandler接口,重点关注下invoke方法的实现
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6424540398559729838L;
private final SqlSession sqlSession;
//mapper 接口
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache;
public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
this.methodCache = methodCache;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
// 这里是为了做兼容,因为MapperProxyFactory生成的代理对象其祖先也是Object,比如代理对象调用toString方法就会默认调用Object类中的
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) {
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
//根据配置找到对应执行方法(进行包装)
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
//执行
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
MapperMethod mapperMethod = methodCache.get(method);
if (mapperMethod == null) {
mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration());
methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod);
}
return mapperMethod;
}
@UsesJava7
private Object invokeDefaultMethod(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable {
final Constructor<MethodHandles.Lookup> constructor = MethodHandles.Lookup.class
.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, int.class);
if (!constructor.isAccessible()) {
constructor.setAccessible(true);
}
final Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
return constructor
.newInstance(declaringClass,
MethodHandles.Lookup.PRIVATE | MethodHandles.Lookup.PROTECTED
| MethodHandles.Lookup.PACKAGE | MethodHandles.Lookup.PUBLIC)
.unreflectSpecial(method, declaringClass).bindTo(proxy).invokeWithArguments(args);
}
/**
* Backport of java.lang.reflect.Method#isDefault()
*/
private boolean isDefaultMethod(Method method) {
return ((method.getModifiers()
& (Modifier.ABSTRACT | Modifier.PUBLIC | Modifier.STATIC)) == Modifier.PUBLIC)
&& method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface();
}
}3 小结
mybatis通过这种约定以及使用代理模式这种巧妙的设计方式是值得我们思考和学习的。
没有什么比每天有成长进步更高兴的事情