30.1 HashSet存储自定义对象 未去重解决
问题:
package day30_HashSet; import java.util.HashSet; /* * 通过hashset存储自定义对象,没有进行去重。 * * */ public class HashSetSutdentDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建集合对象 HashSet<Student> hs = new HashSet<Student>(); //创建元素对象 Student st = new Student("aa",20); Student st2 = new Student("bb",18); Student st3 = new Student("bb",18); //添加元素对象 hs.add(st); hs.add(st2); hs.add(st3); //遍历集合对象 for (Student s : hs) { System.out.println(s); } } } class Student { String name; int age; public Student(String name,int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { //默认输出的是student的地址值,重写tostring方法 return "Student{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } }
输出
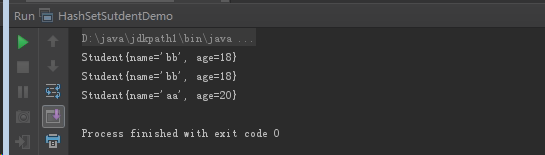
解决:
HashSet 的 add方法使用的是 hashcode 和equals进行比较
需要重写hashcode 和equals
package day30_HashSet; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Objects; /* * 使用HashSet存储自定义对象并遍历 * 通过查看源码发现: * HashSet的add()方法,首先会使用当前集合中的每一个元素和新添加的元素进行hash值比较, * 如果hash值不一样,则直接添加新的元素 * 如果hash值一样,比较地址值或者使用equals方法进行比较 * 比较结果一样,则认为是重复不添加 * 所有的比较结果都不一样则添加 */ public class HashSetStudentDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { HashSet<Student2> hs = new HashSet<Student2>(); //创建元素对象 Student2 s = new Student2("zhangsan",18); Student2 s2 = new Student2("lisi",19); Student2 s3 = new Student2("lisi",19); //添加元素对象 hs.add(s); hs.add(s2); hs.add(s3); //遍历集合对象 for (Student2 student : hs) { System.out.println(student); } } } class Student2 { String name; int age; public Student2(String name,int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student2{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (this == o) return true; if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false; Student2 student2 = (Student2) o; return age == student2.age && Objects.equals(name, student2.name); } @Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(name, age); } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号