@
目录
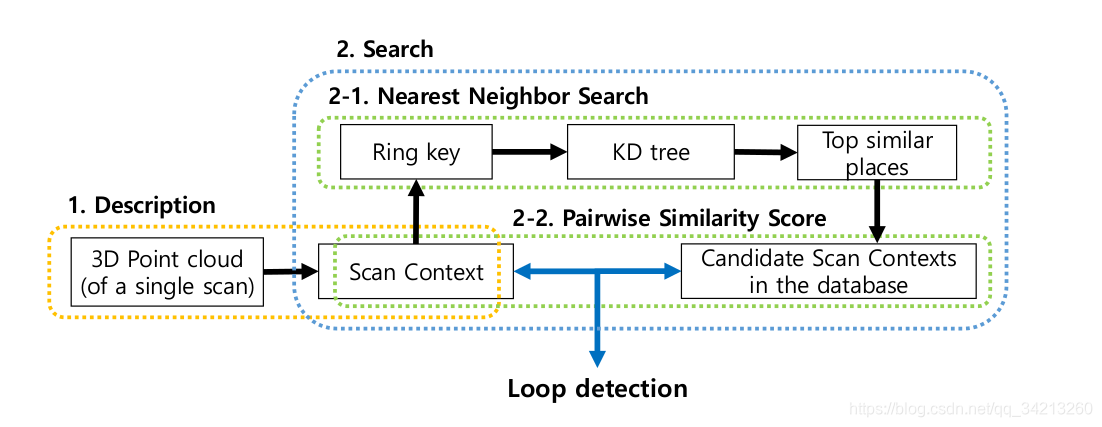
Scan Context: Egocentric Spatial Descriptor for Place Recognition within 3D Point Cloud Map(IROS2018)
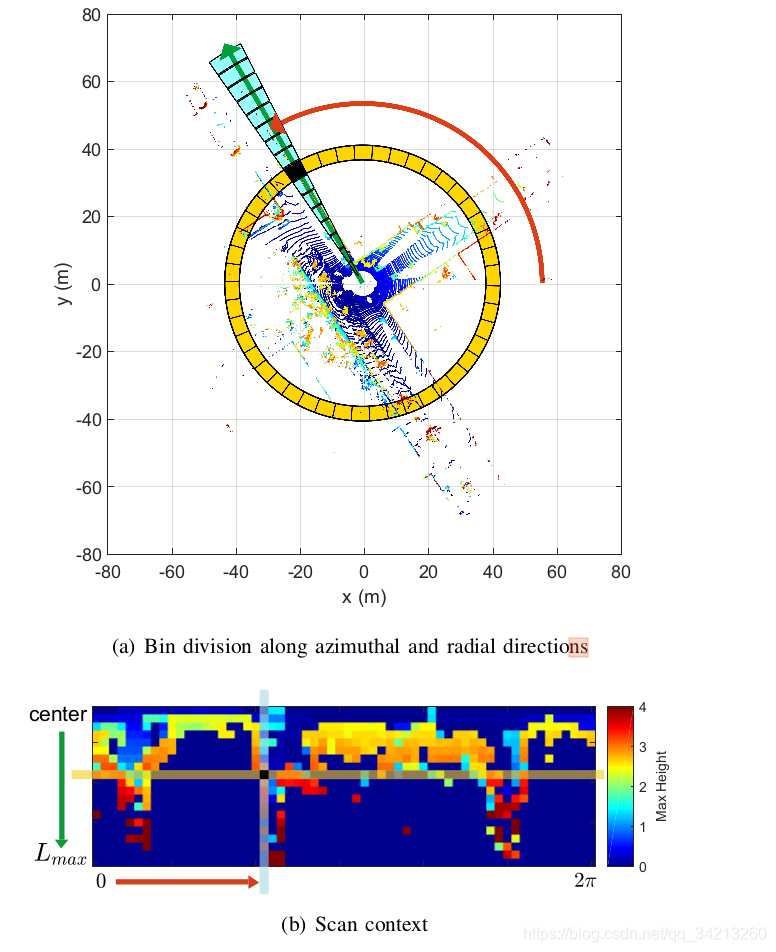
一、构建Scan Context
 \(N_r\):ring分成多少份
\(N_r\):ring分成多少份
\(N_s\): sectors分成多少份

// 制作Scancontext
MatrixXd SCManager::makeScancontext( pcl::PointCloud<SCPointType> & _scan_down )
{
TicToc t_making_desc;
int num_pts_scan_down = _scan_down.points.size();
// main
// 初始化desc=Scancontext
const int NO_POINT = -1000;
MatrixXd desc = NO_POINT * MatrixXd::Ones(PC_NUM_RING, PC_NUM_SECTOR);
SCPointType pt;
float azim_angle, azim_range; // 极坐标wihtin 2d plane
int ring_idx, sctor_idx; //Scancontext中的索引,注意是从1开始的
for (int pt_idx = 0; pt_idx < num_pts_scan_down; pt_idx++)
{
pt.x = _scan_down.points[pt_idx].x;
pt.y = _scan_down.points[pt_idx].y;
pt.z = _scan_down.points[pt_idx].z + LIDAR_HEIGHT; // naive adding is ok (all points should be > 0).
// xyz to ring, sector
azim_range = sqrt(pt.x * pt.x + pt.y * pt.y);
azim_angle = xy2theta(pt.x, pt.y);
// if range is out of roi, pass
// 超出范围的去掉
if( azim_range > PC_MAX_RADIUS )
continue;
ring_idx = std::max( std::min( PC_NUM_RING, int(ceil( (azim_range / PC_MAX_RADIUS) * PC_NUM_RING )) ), 1 );
sctor_idx = std::max( std::min( PC_NUM_SECTOR, int(ceil( (azim_angle / 360.0) * PC_NUM_SECTOR )) ), 1 );
// taking maximum z
// 获取每个bin中的z最大值
if ( desc(ring_idx-1, sctor_idx-1) < pt.z ) // -1 means cpp starts from 0
desc(ring_idx-1, sctor_idx-1) = pt.z; // update for taking maximum value at that bin
}
// reset no points to zero (for cosine dist later)
// 没有点的bin=0
for ( int row_idx = 0; row_idx < desc.rows(); row_idx++ )
for ( int col_idx = 0; col_idx < desc.cols(); col_idx++ )
if( desc(row_idx, col_idx) == NO_POINT )
desc(row_idx, col_idx) = 0;
t_making_desc.toc("PolarContext making");
return desc;
} // SCManager::makeScancontext
二、计算Scan Context的每一行的均值作为RingKey
//Scancontext每一行的均值作为Ringkey
MatrixXd SCManager::makeRingkeyFromScancontext( Eigen::MatrixXd &_desc )
{
/*
* summary: rowwise mean vector
*/
Eigen::MatrixXd invariant_key(_desc.rows(), 1);
for ( int row_idx = 0; row_idx < _desc.rows(); row_idx++ )
{
Eigen::MatrixXd curr_row = _desc.row(row_idx);
invariant_key(row_idx, 0) = curr_row.mean();
}
return invariant_key;
} // SCManager::makeRingkeyFromScancontext
三、将所有历史帧的RingKey构建Kd-tree查找候选关键帧
四、遍历候选关键帧,选择距离最近的帧作为匹配帧。
计算距离的步骤
- 计算每一帧的Sectorkey
- 使用Sectorkey,计算当前帧和闭环帧的偏移量shfit
- 使用偏移量对齐两帧
- 计算两帧的每一列距离的平均值作为总的距离值
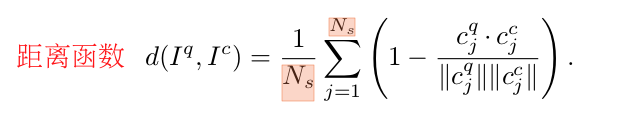
- 距离最小且满足阈值的候选关键帧即为闭环关键帧返回索引id
五、再用icp匹配
优缺点
优点
- 速度快
- 旋转不变性
缺点
- 只保留z的最大值丢失了信息
- 个人认为距离只相差几米时应该就会导致相似度很低而失效,比如车道很宽,原来靠左现在靠右可能都会失效
打赏
码字不易,如果对您有帮助,就打赏一下吧O(∩_∩)O
支付宝

微信



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号