
















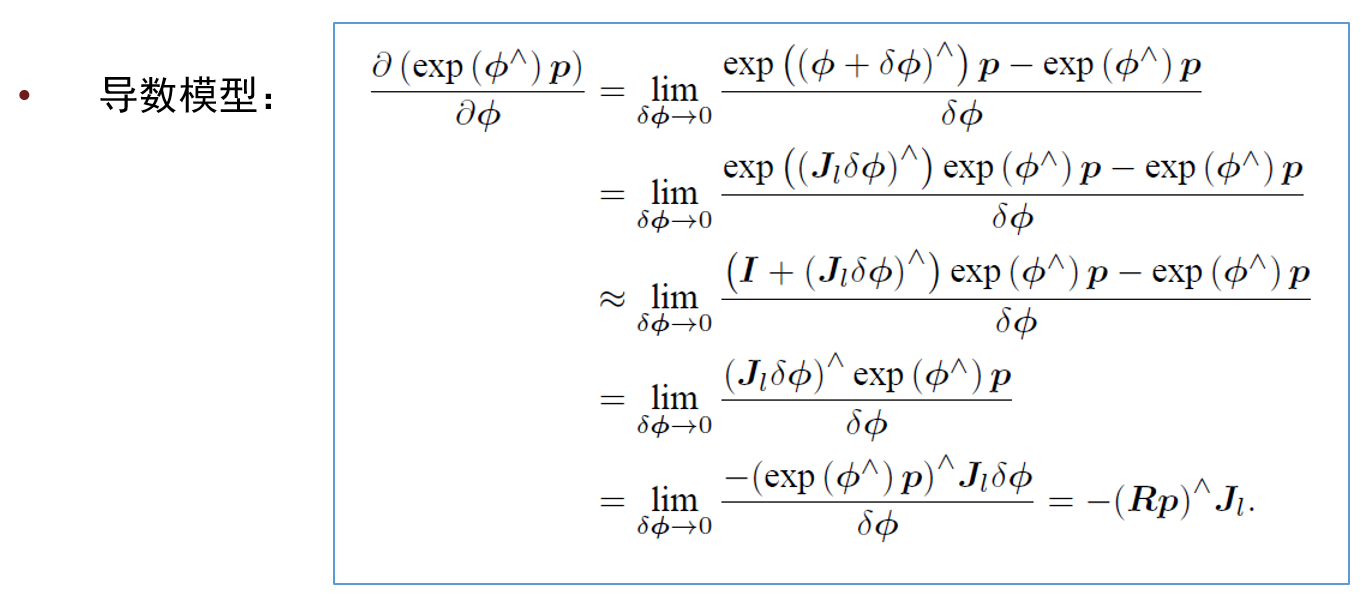
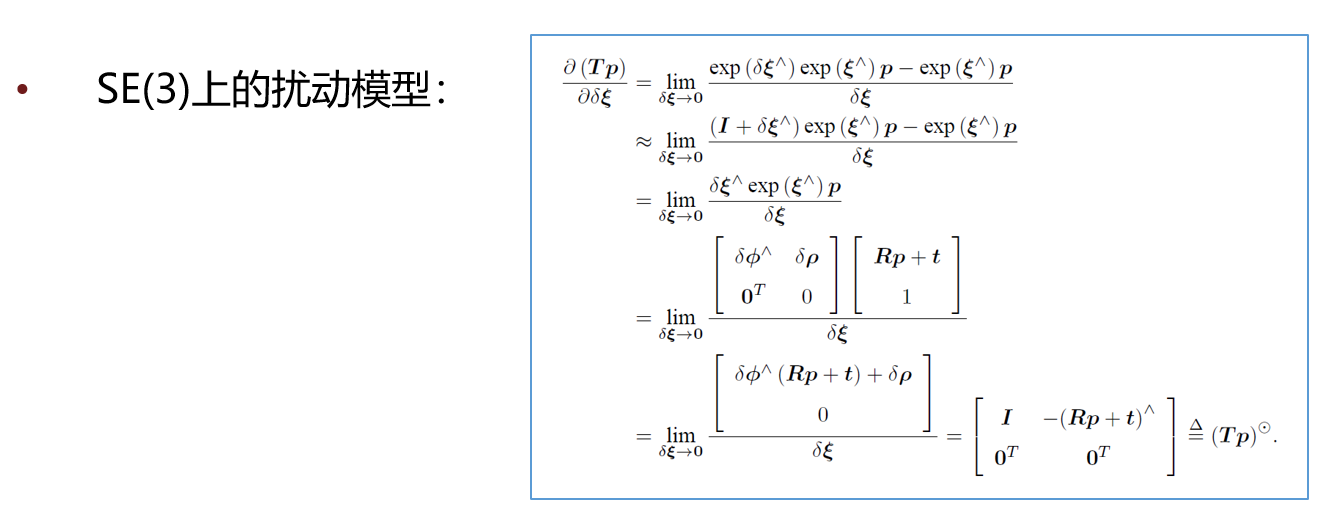
注意:!!!!!看书本,这里的导数是旋转之后点的坐标相对于旋转的导数 !!!!!

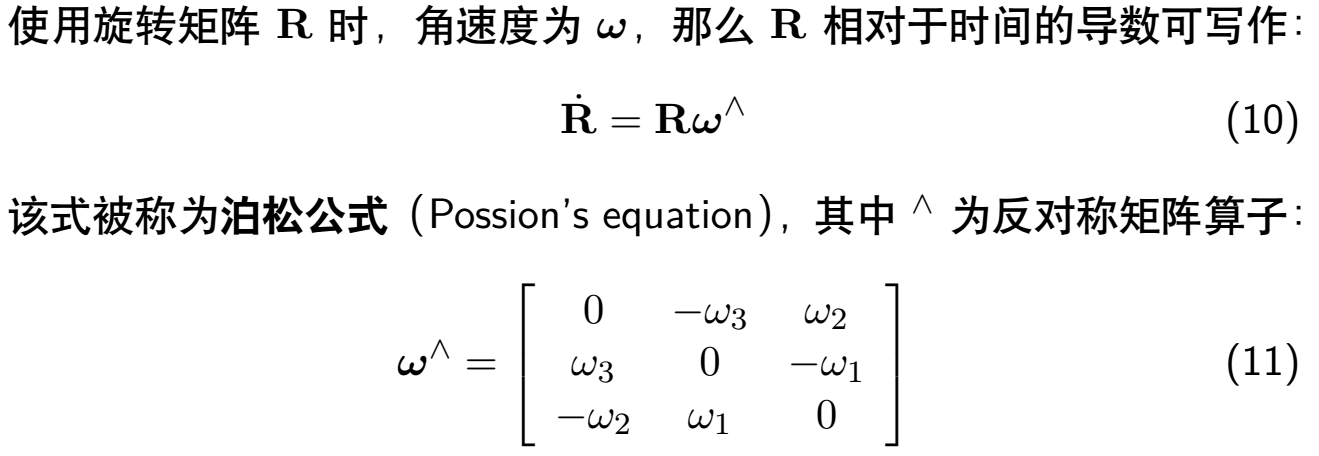
旋转矩阵对时间的导数应为

#include <iostream> #include <cmath> #include <Eigen/Core> #include <Eigen/Geometry> #include "sophus/se3.hpp" using namespace std; using namespace Eigen; /// 本程序演示sophus的基本用法 int main(int argc, char **argv) { // 沿Z轴转90度的旋转矩阵 Matrix3d R = AngleAxisd(M_PI / 2, Vector3d(0, 0, 1)).toRotationMatrix(); // 或者四元数 Quaterniond q(R); Sophus::SO3d SO3_R(R); // Sophus::SO3d可以直接从旋转矩阵构造 Sophus::SO3d SO3_q(q); // 也可以通过四元数构造 // 二者是等价的 cout << "SO(3) from matrix:\n" << SO3_R.matrix() << endl; cout << "SO(3) from quaternion:\n" << SO3_q.matrix() << endl; cout << "they are equal" << endl; // 使用对数映射获得它的李代数 Vector3d so3 = SO3_R.log(); cout << "so3 = " << so3.transpose() << endl; // hat 为向量到反对称矩阵 cout << "so3 hat=\n" << Sophus::SO3d::hat(so3) << endl; // 相对的,vee为反对称到向量 cout << "so3 hat vee= " << Sophus::SO3d::vee(Sophus::SO3d::hat(so3)).transpose() << endl; // 增量扰动模型的更新 Vector3d update_so3(1e-4, 0, 0); //假设更新量为这么多 Sophus::SO3d SO3_updated = Sophus::SO3d::exp(update_so3) * SO3_R; cout << "SO3 updated = \n" << SO3_updated.matrix() << endl; cout << "*******************************" << endl; // 对SE(3)操作大同小异 Vector3d t(1, 0, 0); // 沿X轴平移1 Sophus::SE3d SE3_Rt(R, t); // 从R,t构造SE(3) Sophus::SE3d SE3_qt(q, t); // 从q,t构造SE(3) cout << "SE3 from R,t= \n" << SE3_Rt.matrix() << endl; cout << "SE3 from q,t= \n" << SE3_qt.matrix() << endl; // 李代数se(3) 是一个六维向量,方便起见先typedef一下 typedef Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 1> Vector6d; Vector6d se3 = SE3_Rt.log(); cout << "se3 = " << se3.transpose() << endl; // 观察输出,会发现在Sophus中,se(3)的平移在前,旋转在后. // 同样的,有hat和vee两个算符 cout << "se3 hat = \n" << Sophus::SE3d::hat(se3) << endl; cout << "se3 hat vee = " << Sophus::SE3d::vee(Sophus::SE3d::hat(se3)).transpose() << endl; // 最后,演示一下更新 Vector6d update_se3; //更新量 update_se3.setZero(); update_se3(0, 0) = 1e-4d; Sophus::SE3d SE3_updated = Sophus::SE3d::exp(update_se3) * SE3_Rt; cout << "SE3 updated = " << endl << SE3_updated.matrix() << endl; return 0; }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号