Codeforces Round #361 (Div. 2) A. Mike and Cellphone
While swimming at the beach, Mike has accidentally dropped his cellphone into the water. There was no worry as he bought a cheap replacement phone with an old-fashioned keyboard. The keyboard has only ten digital equal-sized keys, located in the following way:
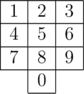
Together with his old phone, he lost all his contacts and now he can only remember the way his fingers moved when he put some number in. One can formally consider finger movements as a sequence of vectors connecting centers of keys pressed consecutively to put in a number. For example, the finger movements for number "586" are the same as finger movements for number "253":
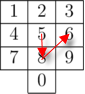
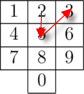
Mike has already put in a number by his "finger memory" and started calling it, so he is now worrying, can he be sure that he is calling the correct number? In other words, is there any other number, that has the same finger movements?
The first line of the input contains the only integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 9) — the number of digits in the phone number that Mike put in.
The second line contains the string consisting of n digits (characters from '0' to '9') representing the number that Mike put in.
If there is no other phone number with the same finger movements and Mike can be sure he is calling the correct number, print "YES" (without quotes) in the only line.
Otherwise print "NO" (without quotes) in the first line.
3
586
NO
2
09
NO
9
123456789
YES
3
911
YES
You can find the picture clarifying the first sample case in the statement above.
智商不够,暴力来凑_(:з」∠)_
#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <iostream> #include <map> #include <utility> #define MP(x, y) make_pair(x, y); using namespace std; char num[10]; map< int, pair<int, int> > mp; vector< pair<int, int> > vec; map< pair<int, int>, pair<int, int> > mp2; bool check(int x, int y) { if((x >= 1 && x <= 3 && y >= 1 && y <= 3) || (x == 2 && y == 4)) return true; return false; } int main() { int n; int cnt = 0; for(int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) { for(int j = 1; j <= 3; j++) { ++cnt; mp[cnt] = MP(i, j); } } mp[0] = MP(4, 2); for(int i = 0; i <= 9; i++) { for(int j = 0; j <= 9; j++) { pair<int, int> p; pair<int, int> p2; p = MP(i, j); p2 = make_pair(mp[j].first - mp[i].first, mp[j].second - mp[i].second); mp2[p] = p2; } } while(~scanf("%d", &n)) { scanf("%s", num); int len = strlen(num); for(int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) { int tmpa = num[i] - '0'; int tmpb = num[i + 1] - '0'; pair<int, int> p; p = MP(tmpa, tmpb); vec.push_back(mp2[p]); } int cnt = 0; for(int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) { for(int j = 1; j <= 3; j++) { int flag = 1; int nowx = j, nowy = i; for(int k = 0; k < vec.size(); k++) { if(!check(nowx, nowy)) { flag = 0; break; } nowy += vec[k].first; nowx += vec[k].second; if(!check(nowx, nowy)) { flag = 0; break; } } if(flag) cnt++; } } if(cnt >= 2) puts("NO"); else puts("YES"); } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号