队列详解包含测试过的完整代码
文章目录
零.前言
栈和队列都是顺序表或者链表的特殊结构,栈由于是尾插尾删,所以我们使用顺序表来实现;而队列使用尾插头删,如果我们使用顺序表的话则正中其缺点,即插入删除数据的时候需要进行数据的挪动,所以我们使用链表来进行队列的实现。
1.队列的结构
1.逻辑结构
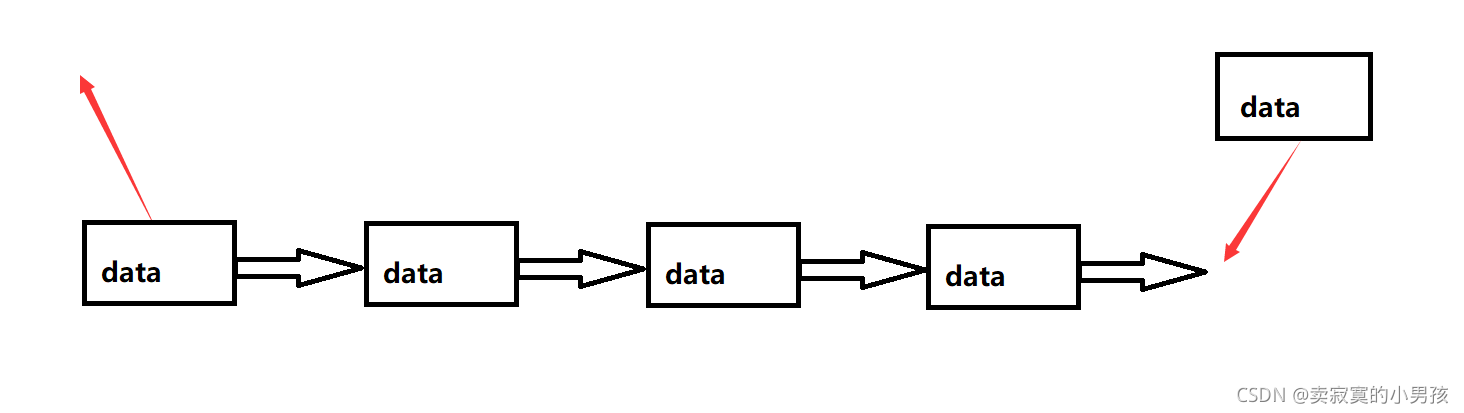
即先进先出,头删尾插。
物理结构
物理结构与链表是相同的,这里就不画了。
2.实现队列的基本操作
1.队列的建立
typedef struct QueueNode {
struct QueueNode* next;
DataType x;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head;
QNode* tail;
}Queue;
这里使用了两个结构体来进行队列的实现,第一个结构体表示队列的一个节点,第二个结构体表示一个队列的头指针和尾指针。第二个结构体用头指针和尾指针抽象表示一个队列。
2.队列的初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = NULL;
pq->tail = NULL;//将pq队列的head和tail都置为空
}
建立一个队列pq,将它的头指针和尾指针都指向空。
3.队列的销毁
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;//遍历队列,由于释放cur之后无法再找到cur->next了,所以定义一个next先存起来
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
和链表一样,在进行队列的销毁时,也需要遍历整个序列,然后依次销毁空间,最后指针别忘记指空。
4.判断队列是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head == NULL;//当head为空则为空返回TRUE
}
我们用bool类型来接收结果,如果为空返回True,不为空返回False。
5.计算队列的大小
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
int n = 0;
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
n++;
cur = cur->next;//利用cur进行遍历
}
return n;
}
遍历队列,只到找到空指针,每一次对n加一。
3.队列的插入与删除
1.队列的插入
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, DataType x)
{
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
newnode->x = x;
newnode->next = NULL;//初始化一个节点
if (pq->head == NULL)
{
pq->head =pq->tail= newnode;//当只有一个节点的时候将head和tail赋值为newnode
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
pq->tail = newnode;//将newnode作为新的尾指针
}
}
队列采用的是尾插,即在tail后插入,如果队列为空,则插入的元素就为头元素,若不为空则在尾部插入,然后将节点作为新的尾。
2.队列的删除
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
Queue* next = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;//首先定义一个next接收head->next
if (pq->head == NULL)
{
pq->tail = NULL;
}//当只有一个元素时删除后要将pq的尾指针赋值为空
}
对队列进行删除,需要先断言判断队列是否为空,不为空则从头部开始删除,然后将第二个元素作为头部。
4.得到队列的头尾
1.得到队列的头
int QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
return pq->head->x;
}
2.得到队列的尾
int QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
return pq->tail->x;
}
5.全部文件
1.queue.h文件
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#define DataType int
typedef struct QueueNode {
struct QueueNode* next;
DataType x;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head;
QNode* tail;
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, DataType x);
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
int QueueFront(Queue* pq);
int QueueBack(Queue* pq);
void QueuePrint(Queue* pq);
2.queue.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"queue.h"
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = NULL;
pq->tail = NULL;//将pq队列的head和tail都置为空
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;//遍历队列,由于释放cur之后无法再找到cur->next了,所以定义一个next先存起来
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, DataType x)
{
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
newnode->x = x;
newnode->next = NULL;//初始化一个节点
if (pq->head == NULL)
{
pq->head =pq->tail= newnode;//当只有一个节点的时候将head和tail赋值为newnode
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
pq->tail = newnode;//将newnode作为新的尾指针
}
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
Queue* next = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;//首先定义一个next接收head->next
if (pq->head == NULL)
{
pq->tail = NULL;
}//当只有一个元素时删除后要将pq的尾指针赋值为空
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head == NULL;//当head为空则为空返回TRUE
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
int n = 0;
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
n++;
cur = cur->next;//利用cur进行遍历
}
return n;
}
int QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
return pq->head->x;
}
int QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
return pq->tail->x;
}
void QueuePrint(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
printf("%d ", cur->x);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
3.test.c文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"queue.h"
void menu()
{
printf("****1.入队*******2.出队****\n");
printf("****3.队首*******4.队尾****\n");
printf("****5.是否为空***6.大小****\n");
printf("****0.删除队列*************\n");
}
int main()
{
Queue pq;
QueueInit(&pq);
QueuePush(&pq, 1);
QueuePush(&pq, 2);
QueuePush(&pq, 3);
QueuePush(&pq, 4);
QueuePush(&pq, 5);
QueuePrint(&pq);
//printf("write by lonely little boy\n");
int input = 0;
do{
menu();
int x;
int y;
scanf("%d", &input);
switch (input)
{
case 1:scanf("%d", &x);
QueuePush(&pq, x);
QueuePrint(&pq);
break;
case 2:QueuePop(&pq);
QueuePrint(&pq);
break;
case 3:y = QueueFront(&pq);
printf("%d\n", y);
break;
case 4:y = QueueBack(&pq);
printf("%d\n", y);
break;
case 5:y = QueueEmpty(&pq);
if (y == 1)
{
printf("empty!\n");
}
else
{
printf("not empty\n");
}
break;
case 6:y = QueueSize(&pq);
printf("%d\n", y);
break;
case 0:QueueDestroy(&pq);
break;
default:printf("wrong type!\n");
break;
}
} while (input);
return 0;
}
6.测试
插入:成功
删除至空报错:成功
判断为空:成功
计算大小为空为0:成功
取头取尾空时报错:成功
退出:成功
综上代码测试成功
7.总结
队列是建立起来和别的不一样的存在,需要定义两个结构体,定义了头尾指针方便了我们进行对队列的操作,最近也做了一些栈和队列的题目,发现其实很多用C++编写会相对简单一些,C语言不是那么太适合刷题,但是要了解一些最最基本的结构实现的话,C语言是最好的选择,我认为原理还是最重要的内容,如果不了解原理是没有办法进行创新的。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 全程不用写代码,我用AI程序员写了一个飞机大战
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· MongoDB 8.0这个新功能碉堡了,比商业数据库还牛
· .NET10 - 预览版1新功能体验(一)