集合源码分析[3]-ArrayList 源码分析
介绍
ArrayList是一个数组队列,相当于动态数组,与Java的数组对比,他的容量可以动态改变。
继承关系
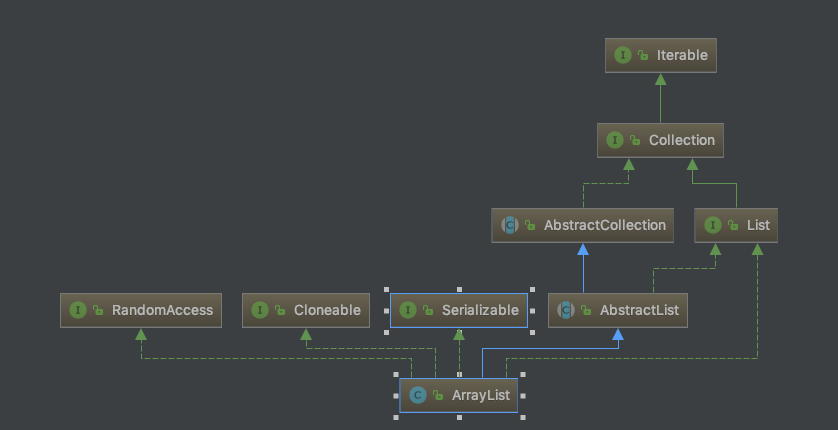
- ArrayList继承AbstractList
- 实现了
List,RandomAccess,Cloneable,Serializable接口
特点
- 基于数组实现速度快
- 实现了
RandomAccess接口,提供了随机访问功能 - 实现了
Cloneable接口,能被克隆 - 实现了
Serializable接口,支持序列化传输 - 非线程安全(ps:线程安全类:CopyOnWriteArrayList)
- 适用于频繁查询和获取数据
- 查询效率在众多List中效率还是非常不错
构造函数以及常用的方法
构造函数
public ArrayList();//无元素默认为0,有元素初始化默认容量为10
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c);//默认为c这个集合的list(浅拷贝)
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity);//设置一个初始化为initialCapacity集合
注意点
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
//解决bug问题,由于其c.toArray()可能出现返回值不为Object[]的错误,所以采用如下方法
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
//使用数组拷贝来进行
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
} else {
// replace with empty array.
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}
在这个方法中出现if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)这样一组判断,查阅资料发现,这是一个bug才这么判断的地址,改问题已经在JDK9已经进行了修复了。
成员变量
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L;
/**
* 默认初始化容量10
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
/**
* 共享的空数据容器
*/
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* 共享空数据容器
*/
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* 缓存数据集合
*/
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
/**
* 容器数据集大小
*
* @serial
*/
private int size;
/**
* 该容器能够承受的最大容量
* 为什么是Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
* 因为有些VM虚拟机会在一个数组中存储一些头部信息,所以采用这个值
* The maximum size of array to allocate.
* Some VMs reserve some header words in an array.
* Attempts to allocate larger arrays may result in
* OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit
*/
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
值得注意的点:
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE设置为Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8是因为有些VM虚拟机会在数组中存储一些头部信息,从而占用一些空间,所以-8
常用方法

值得注意的方法
trimToSize():
缩小容器大小让容器释放多余的空间,会触发一次数组的变化
/**
* 缩小容器大小
* 例如当你一开始创建了一个100个的List但是你只使用了10个,想将这个容器缩减为10个
*/
public void trimToSize() {
//这个参数和我们并发控制的时候version一个味道,用于判断是否并发修改的标志1
modCount++;
if (size < elementData.length) {
elementData = (size == 0)
? EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
: Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
}
}
clone():
返回数据的浅克隆的实例
/**
* 返回数据的浅克隆的实例
*
* @return a clone of this <tt>ArrayList</tt> instance
*/
public Object clone() {
try {
//调用父类的克隆方法->Object的克隆方法
ArrayList<?> v = (ArrayList<?>) super.clone();
//拷贝数组,注意是直接通过Arrays的copyOf所以为浅克隆
v.elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
//设置并发version
v.modCount = 0;
return v;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
//克隆异常则抛出error
// this shouldn't happen, since we are Cloneable
throw new InternalError(e);
}
}
toArray():
同样为浅拷贝,拷贝出来的数组还是会被改变的,该方法返回的为Object[]数组
/**
* 同样为浅拷贝,拷贝出来的数组还是会被改变的
* 将List转换成数组
* Demo[] cloneArr = (Demo[]) demos.toArray(); //ERROR
*
* @return an array containing all of the elements in this list in
* proper sequence
*/
public Object[] toArray() {
return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
}
add方法
/**
* 追加一个元素在列表的最后面
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
//这里会导致其并发版本+1,
// 因为需要先确认容器大小操作,并确定是否需要扩容。
//对数据有修改,因而其并发版本也就会+1
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
//设置值
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
/**
* 在index位置后插入元素,并移动后面元素的位置
* 1. 需要对index后面的所有的元素index+1,需要拷贝工作产生
* 2. 如果你的List中有大量的这样的插入工作建议采用
* @see LinkedList
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
//校验index
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
//确定扩容权限
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
//数组拷贝,耗时工作
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
//赋值
elementData[index] = element;
//长度
size++;
}
- 该方法每次都要确定容器大小,会导致并发版本的count+1
- add 方法有两个
- add(E e):直接将数据插入到List的尾部
- add(int index,E e):将数据插入到index后面
- 如果是插入,则会导致数组进行复制操作,由于ArrayList基于数组,所以会导致数组复制,而数组复制必定是一个耗时的操作
remove()
public E remove(int index) {
//校验
rangeCheck(index);
//并发参数+1
modCount++;
//获取旧值
E oldValue = elementData(index);
//移动的长度为=数组长度-需要删除元素下标-1
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
//让gc回收这个数据的内存
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
//返回旧值
return oldValue;
}
- 同样删除会导致数组复制
subList
该方法主要用于将数组进行分割,对于数组分割后,其实该数组为浅拷贝操作,如果在该SubList中操作相关数据,将会导致ArrayList中的数据改变!!
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size);
return new SubList(this, 0, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
ArrayList扩容机制
规则
- 如果其数组需要进行扩容,则会扩容为原数组的1.5倍
- 如果用户指定了容器的大小,且用于指定的数值大于容器的最小容量,则将用于容量作为该容器容量
- 如果容器容量扩容后大于
Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8,则会尝试扩容为Integer.MAX_VALUE大小
解析
-
确定minCapacity值是否比容器中的数据容量大
-
如果大则扩容,否则什么也不做
-
扩容
-
如果minCapacity比newCapacity小则直接使用minCapacity作为扩容容量
-
如果其数组个数大于最大的数组的长度,则尝试使用Integer.MAX_VALUE作为数组的容器大小
-
源码解析
/**
* 1.确定minCapacity值是否比容器中的数据容量大
* 2.如果大则扩容,否则什么也不做
* @param minCapacity
*/
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
/**
* Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the
* number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument.
* 扩容
* 1. 如果minCapacity比newCapacity小则直接使用minCapacity作为扩容容量
* 2. 如果其数组个数大于最大的数组的长度,则尝试使用Integer.MAX_VALUE作为数组的容器大小
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
//新容器容量扩容为现在容器的容量的1.5倍
//eg 旧10个->新15个
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
//看看谁大
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
//如果min比new小则直接复制min
newCapacity = minCapacity;
//如果新的容器比最大的数组大小还要打
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
//只能复制为最大容器大小,但是可能会抛出oom
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
/**
* 大数组容器扩容
* @param minCapacity
* @return
*/
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
//校验参数合法性
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
List的序列化操作
由于Java默认序列化以及反序列化的时候回分别调用对应的writeObject方法以及readObject()方法,所以以下将对这两个方法进行分析。
6.1 为什么需要自定义序列化规则
由于在ArrayList中的elementData数组中可能存在一些空的元素(由于ArrayList扩容机制)
6.2 源码分析
- 序列化操作:
- ArrayList内部存储数据元素为
transient不会被序列化
- ArrayList内部存储数据元素为
/**
* 缓存数据集合
*/
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
-
如何支持序列化操作
1. 序列化数量 2. 获取数据数组,然后使用for循环一个一个序列化该对象到数据中。/** * Save the state of the <tt>ArrayList</tt> instance to a stream (that * is, serialize it). * 保证其可以被序列化到对象中 * * @serialData The length of the array backing the <tt>ArrayList</tt> * instance is emitted (int), followed by all of its elements * (each an <tt>Object</tt>) in the proper order. */ private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) throws java.io.IOException{ // Write out element count, and any hidden stuff //数据被序列化的数量 int expectedModCount = modCount; //使用默认的模式进行序列化,只序列化非静态化变量以及非transient修饰的数据 s.defaultWriteObject(); // Write out size as capacity for behavioural compatibility with clone() //写入长度 s.writeInt(size); // Write out all elements in the proper order. for (int i=0; i<size; i++) { //写入每一个object数据 s.writeObject(elementData[i]); } //如果发现序列化的modCount与expectedModCount可能是并发导致 if (modCount != expectedModCount) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } -
如何进行的反序列化
- 重新创建List,然后读取长度以及多个对象对对象进行相关赋值操作
/** * Reconstitute the <tt>ArrayList</tt> instance from a stream (that is, * deserialize it). * 反序列化数据 */ private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException { //设置默认的数组长度为空数组长度 elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; // Read in size, and any hidden stuff //使用默认的模式进行序列化,只序列化非静态化变量以及非transient修饰的数据 s.defaultReadObject(); // Read in capacity //读取list长度 s.readInt(); // ignored if (size > 0) { // be like clone(), allocate array based upon size not capacity //开始计算并克隆 int capacity = calculateCapacity(elementData, size); SharedSecrets.getJavaOISAccess().checkArray(s, Object[].class, capacity); //确定数组长度是否够 ensureCapacityInternal(size); //进行数据读取 Object[] a = elementData; // Read in all elements in the proper order. for (int i=0; i<size; i++) { a[i] = s.readObject(); } } }
JDK1.8新增的方法
forEach()
lambda循环方法
/**
* JDK新增方法 ForEach方法
* @param action
*/
@Override
public void forEach(Consumer<? super E> action) {
//校验lambda不为空
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
//并发version版本统计
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
final E[] elementData = (E[]) this.elementData;
final int size = this.size;
//循环每次判断一下并发参数是否进行了修改,如果进行了修改则直接退出for循环
for (int i=0; modCount == expectedModCount && i < size; i++) {
action.accept(elementData[i]);
}
//并抛出并发异常
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
spliterator
该方法用于返回进行并发计算时候的分割器
/**
* Creates a <em><a href="Spliterator.html#binding">late-binding</a></em>
* and <em>fail-fast</em> {@link Spliterator} over the elements in this
* list.
*
* <p>The {@code Spliterator} reports {@link Spliterator#SIZED},
* {@link Spliterator#SUBSIZED}, and {@link Spliterator#ORDERED}.
* Overriding implementations should document the reporting of additional
* characteristic values.
* 并发分割方法
* 懒加载加入,只有当数据
* @return a {@code Spliterator} over the elements in this list
* @since 1.8
*/
@Override
public Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
/**
* 1. 参数1 this
* 2. origin
* 3. fence 当使用的时候才进行初始化
* 4. 并发参数
*/
return new ArrayListSpliterator<>(this, 0, -1, 0);
}
removeIf方法
lambda 移除符合某个规则的方法
/**
* liambad方法移除元素
* @param filter
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {
Objects.requireNonNull(filter);
// figure out which elements are to be removed
// any exception thrown from the filter predicate at this stage
// will leave the collection unmodified
int removeCount = 0;
//使用这玩意来统计存在的位置
final BitSet removeSet = new BitSet(size);
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
final int size = this.size;
for (int i=0; modCount == expectedModCount && i < size; i++) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
final E element = (E) elementData[i];
if (filter.test(element)) {
removeSet.set(i);
removeCount++;
}
}
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
// shift surviving elements left over the spaces left by removed elements
final boolean anyToRemove = removeCount > 0;
if (anyToRemove) {
//新数组的大小为之前的数组长度-需要移除元素的个数
final int newSize = size - removeCount;
//执行清除工作
for (int i=0, j=0; (i < size) && (j < newSize); i++, j++) {
i = removeSet.nextClearBit(i);
elementData[j] = elementData[i];
}
//释放gc
for (int k=newSize; k < size; k++) {
elementData[k] = null; // Let gc do its work
}
this.size = newSize;
//并发version检查
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
//并发值+1
modCount++;
}
return anyToRemove;
}
ArrayListSpliterator
其为并发分割器,用于我们使用并发调用parallelStream方法时候调用该方法
static final class ArrayListSpliterator<E> implements Spliterator<E> {
private final ArrayList<E> list;
private int index; // current index, modified on advance/split
private int fence; // -1 until used; then one past last index
private int expectedModCount; // initialized when fence set
/** Create new spliterator covering the given range */
ArrayListSpliterator(ArrayList<E> list, int origin, int fence,
int expectedModCount) {
this.list = list; // OK if null unless traversed
this.index = origin;
this.fence = fence;
this.expectedModCount = expectedModCount;
}
/**
* 当获取的时候才进行fence的初始化操作
* @return
*/
private int getFence() { // initialize fence to size on first use
int hi; // (a specialized variant appears in method forEach)
ArrayList<E> lst;
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
//之前的数组为空则说明没有进行分割,则从0开始
if ((lst = list) == null)
hi = fence = 0;
else {
//否则则
expectedModCount = lst.modCount;
//则将该值赋值为lst的长度
hi = fence = lst.size;
}
}
return hi;
}
/**
* 尝试分割
* 1、总长度为数组长度
* 2、分割成两份
* 3、二分法分割
* 3、中间值为数组长度+分割后的数组长度,就是二分法啦
* @return
*/
public ArrayListSpliterator<E> trySplit() {
int hi = getFence(), lo = index, mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
return (lo >= mid) ? null : // divide range in half unless too small
new ArrayListSpliterator<E>(list, lo, index = mid,
expectedModCount);
}
/**
* 并发执行操作
* @param action
* @return
*/
public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super E> action) {
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int hi = getFence(), i = index;
//如果没有超过这个分割的长度则继续操作否则返回false
if (i < hi) {
index = i + 1;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E)list.elementData[i];
action.accept(e);
//如果出现了并发改变,则抛出异常
if (list.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 并发ForEach输出
* @param action
*/
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
int i, hi, mc; // hoist accesses and checks from loop
ArrayList<E> lst; Object[] a;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if ((lst = list) != null && (a = lst.elementData) != null) {
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
mc = lst.modCount;
hi = lst.size;
}
else
mc = expectedModCount;
if ((i = index) >= 0 && (index = hi) <= a.length) {
for (; i < hi; ++i) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) a[i];
action.accept(e);
}
if (lst.modCount == mc)
return;
}
}
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
public long estimateSize() {
return (long) (getFence() - index);
}
public int characteristics() {
return Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.SUBSIZED;
}
}
ArrayList遍历
8.1 使用迭代器进行遍历
Iterator<Double> iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
Double next = iterator.next();
System.out.println(next);
}
使用fori进行遍历
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
8.3 使用for进行遍历
for (Double next : list) {
System.out.println(next);
}
8.4 使用流进行访问(JDK1.8)
list.forEach(System.out::println);
8.5 以上几种模式的效率比较
测试代码如下
package cn.lonecloud;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.time.Instant;
import java.util.*;
/**
* @author lonecloud
* @version v1.0
* @date 2019/4/3 19:56
*/
public class ListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int len=20000000;
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>(len);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
list.add(i);
}
test(list);
}
public static void test(List<Integer> list){
long itrBegin = System.currentTimeMillis();
//1. 使用迭代器
Iterator<Integer> iterator = list.iterator();
Integer a=0;
while (iterator.hasNext()){
Integer next = iterator.next();
a=next;
}
long itrEnd=System.currentTimeMillis();
long foriStart=System.currentTimeMillis();
//2. fori
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
a=list.get(i);
}
long foriEnd=System.currentTimeMillis();
long forStart=System.currentTimeMillis();
//3. for
for (Integer next : list) {
a=next;
}
long forEnd=System.currentTimeMillis();
long streamstart=System.currentTimeMillis();
//4. stream
list.forEach((value)->{
Integer b=value;
});
long streamEnd=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("迭代器时间:"+(itrEnd-itrBegin));
System.out.println("fori时间:"+(foriEnd-foriStart));
System.out.println("for时间:"+(forEnd-forStart));
System.out.println("stream时间:"+(streamEnd-streamstart));
}
}
结果:
迭代器时间:31
fori时间:32
for时间:32
stream时间:74
总结:
效率:
-
fori和for和迭代器大致相同,由于事先了RandomAccess
-
stream时间高一些,原因是需要进行更多的方法调用产生的时间
使用到的设计模式
- 迭代器设计模式
- 模板设计模式
总结
-
ArrayList是基于数组的集合,适合循环迭代多的场景,不适合修改多的场景
-
在使用ArrayList时候需要注意在创建的时候(预估一下你需要的容器大小)
由于如果你在使用的时候超过了初始化容量(10),这将会导致容器进行一次(容器扩容),而数组复制是一件非常耗时的操作
-
ArrayList中的clone()方法以及copy方法,都是浅克隆的。
-
在一般情况下,如果集合容器出现容量不足需要扩容的时候,其集合会扩容为原集合的1.5倍大小
-
如果需要将List转换成数组,推荐使用泛型方法
T[] toArray(T[] a)而不是Object[] toArray()方法 -
如果涉及在指定位置上插入指定元素的操作,如果这种操作比较多,推荐使用LinkedList而不是使用ArrayList,因为你每次在指定的位置上插入元素会导致数组拷贝操作。
-
如果List涉及到频繁修改的时候,建议使用LinkedList,而不是使用ArrayList。
-
ArrayList是一个非线程安全类,如果需要设计到线程安全,请使用并发包相关的类
-
subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex)方法返回的SubList类,其中如果你对该List操作时候,原集合也会改变


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号