pytorch基础(一)
关于Pytorch的一些笔记
Tensor
numpy数组与torch tensor的互相转换
np_data = np.arange(6).reshape((2, 3))
torch_data = torch.from_numpy(np_data)
tensor2array = torch_data.numpy()
print(
'\nnumpy array:', np_data, # [[0 1 2], [3 4 5]]
'\ntorch tensor:', torch_data, # 0 1 2 \n 3 4 5 [torch.LongTensor of size 2x3]
'\ntensor to array:', tensor2array, # [[0 1 2], [3 4 5]]
)
torch中常用的数学操作
- torch.abs(tensor)
- torch.sin(tensor)
- torch.mean(tensor)
- torch.mm(tensor, tensor) ——矩阵乘法
关于矩阵乘法,需要注意的是:
# matrix multiplication
data = [[1,2], [3,4]]
tensor = torch.FloatTensor(data) # 32-bit floating point
# correct method
print(
'\nmatrix multiplication (matmul)',
'\nnumpy: ', np.matmul(data, data), # [[7, 10], [15, 22]]
'\ntorch: ', torch.mm(tensor, tensor) # [[7, 10], [15, 22]]
)
# incorrect method
data = np.array(data)
print(
'\nmatrix multiplication (dot)',
'\nnumpy: ', data.dot(data), # [[7, 10], [15, 22]]
'\ntorch: ', tensor.dot(tensor) # this will convert tensor to [1,2,3,4], you'll get 30.0
)
Variable
- 这部分内容涉及到DNN基础,可参考:深度学习之前馈神经网络
- 关于Variable的作用,可参考:Pytorch笔记01-Variable和Function
import torch
from torch.autograd import Variable
tensor = torch.FloatTensor([[1,2],[3,4]]) # build a tensor
variable = Variable(tensor, requires_grad=True) # build a variable, usually for compute gradients
print(tensor) # [torch.FloatTensor of size 2x2]
print(variable) # [torch.FloatTensor of size 2x2]
梯度:
t_out = torch.mean(tensor*tensor) # x^2
v_out = torch.mean(variable*variable) # x^2
print(t_out)
print(v_out) # 7.5
v_out.backward() # backpropagation from v_out
# v_out = 1/4 * sum(variable*variable)
# the gradients w.r.t the variable, d(v_out)/d(variable) = 1/4*2*variable = variable/2
print(variable.grad)
'''
0.5000 1.0000
1.5000 2.0000
'''
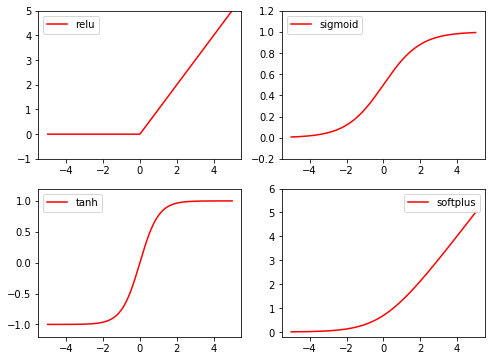
激活函数
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.autograd import Variable
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# fake data
x = torch.linspace(-5, 5, 200) # x data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
x = Variable(x)
x_np = x.data.numpy() # numpy array for plotting
# following are popular activation functions
y_relu = torch.relu(x).data.numpy()
y_sigmoid = torch.sigmoid(x).data.numpy()
y_tanh = torch.tanh(x).data.numpy()
y_softplus = F.softplus(x).data.numpy() # there's no softplus in torch
# y_softmax = torch.softmax(x, dim=0).data.numpy() softmax is a special kind of activation function, it is about probability
# plt to visualize these activation function
plt.figure(1, figsize=(8, 6))
plt.subplot(221)
plt.plot(x_np, y_relu, c='red', label='relu')
plt.ylim((-1, 5))
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.subplot(222)
plt.plot(x_np, y_sigmoid, c='red', label='sigmoid')
plt.ylim((-0.2, 1.2))
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.subplot(223)
plt.plot(x_np, y_tanh, c='red', label='tanh')
plt.ylim((-1.2, 1.2))
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.subplot(224)
plt.plot(x_np, y_softplus, c='red', label='softplus')
plt.ylim((-0.2, 6))
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
回归
神经网络将通过torch.nn包进行构建
nn包依赖autograd包来定义模型并求导.一个nn.Module包含各个层和一个forward(input)方法,该方法返回output
神经网络的典型训练过程如下:
- 定义神经网络模型,它有一些可学习的参数(或者权重);
- 在数据集上迭代;
- 通过神经网络处理输入;
- 计算损失(输出结果和正确值的差距大小)
- 将梯度反向传播至网络的参数;
- 更新网络的参数,主要使用如下简单的更新原则:
weight = weight - learning_rate * gradient
用于回归的数据:
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible
x = torch.unsqueeze(torch.linspace(-1, 1, 100), dim=1) # 增加1个维度:x data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
y = x.pow(2) + 0.2*torch.rand(x.size()) # noisy y data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
# plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())
# plt.show()
使用torch.nn.Module来搭建网络:
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_feature, n_hidden, n_output):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.hidden = torch.nn.Linear(n_feature, n_hidden) # hidden layer
self.predict = torch.nn.Linear(n_hidden, n_output) # output layer
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.hidden(x)) # activation function for hidden layer
x = self.predict(x) # linear output
return x
net = Net(n_feature=1, n_hidden=10, n_output=1) # define the network
print(net) # net architecture
训练网络并测试结果:
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.2)
loss_func = torch.nn.MSELoss() # this is for regression mean squared loss
plt.ion() # something about plotting
for t in range(200):
prediction = net(x) # input x and predict based on x
loss = loss_func(prediction, y) # must be (1. nn output, 2. target)
optimizer.zero_grad() # clear gradients for next train
loss.backward() # backpropagation, compute gradients
optimizer.step() # apply gradients
if t % 5 == 0:
# plot and show learning process
plt.cla()
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())
plt.plot(x.data.numpy(), prediction.data.numpy(), 'r-', lw=5)
plt.text(0.5, 0, 'Loss=%.4f' % loss.data.numpy(), fontdict={'size': 20, 'color': 'red'})
plt.pause(0.1)
plt.ioff()
plt.show()
分类
导包,构造数据:
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible
# make fake data
n_data = torch.ones(100, 2)
x0 = torch.normal(2*n_data, 1) # class0 x data (tensor), shape=(100, 2)
y0 = torch.zeros(100) # class0 y data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
x1 = torch.normal(-2*n_data, 1) # class1 x data (tensor), shape=(100, 2)
y1 = torch.ones(100) # class1 y data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
x = torch.cat((x0, x1), 0).type(torch.FloatTensor) # shape (200, 2) FloatTensor = 32-bit floating
y = torch.cat((y0, y1), ).type(torch.LongTensor) # shape (200,) LongTensor = 64-bit integer
# plt.scatter(x.data.numpy()[:, 0], x.data.numpy()[:, 1], c=y.data.numpy(), s=100, lw=0, cmap='RdYlGn')
# plt.show()
构建网络:
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_feature, n_hidden, n_output):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.hidden = torch.nn.Linear(n_feature, n_hidden) # hidden layer
self.out = torch.nn.Linear(n_hidden, n_output) # output layer
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.hidden(x)) # activation function for hidden layer
x = self.out(x)
return x
net = Net(n_feature=2, n_hidden=10, n_output=2) # define the network
print(net) # net architecture
训练与测试:
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.02)
loss_func = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # the target label is NOT an one-hotted
plt.ion() # something about plotting
for t in range(100):
out = net(x) # input x and predict based on x
loss = loss_func(out, y) # must be (1. nn output, 2. target), the target label is NOT one-hotted
optimizer.zero_grad() # clear gradients for next train
loss.backward() # backpropagation, compute gradients
optimizer.step() # apply gradients
if t % 2 == 0:
# plot and show learning process
plt.cla()
prediction = torch.max(out, 1)[1]
pred_y = prediction.data.numpy()
target_y = y.data.numpy()
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy()[:, 0], x.data.numpy()[:, 1], c=pred_y, s=100, lw=0, cmap='RdYlGn')
accuracy = float((pred_y == target_y).astype(int).sum()) / float(target_y.size)
plt.text(1.5, -4, 'Accuracy=%.2f' % accuracy, fontdict={'size': 20, 'color': 'red'})
plt.pause(0.1)
plt.ioff()
plt.show()
参考资料


