Introduction
Divide-and-Conquer的三个步骤:
Divide the problem into a number of subproblems that are smaller instances of the
same problem.
Conquer the subproblems by solving them recursively. If the subproblem sizes are
small enough, however, just solve the subproblems in a straightforward manner.
Combine the solutions to the subproblems into the solution for the original problem.
简单来说,就是将原问题分解成性质相同的子问题,到子问题小到能够直接解决的时候再将子问题递归式的合为原问题,这种方法不一定能降低问题的复杂度,但它在一定程度上使问题变得更直观简洁,并且此类方法很容易分析复杂度。
一些简单的名词解释,what is recursive case and what is base case?一般来说,base case就是能够直接解决的子问题,除了这些子问题都是recursive case。
recurrences
recurrences在这里的意思是递归式。递归和Divide-and-Conquer有什么关系?但我们想要用Divide-and-Conquer的时候,用递归来实现其实是一个很自然的过程。而且借助recurrences能帮助我们用(后面会讲的)master method分析整个算法的运行时间。
例如,下面就是一个recurrences。

A recurrence of the form in equation (4.2) characterizes a divideand-conquer algorithm that creates a subproblems, each of which is 1=b the
size of the original problem, and in which the divide and combine steps together take f(n) time.
对于上述的recurrences,我们可以这样解读:它将原问题分成了a个子问题,每个子问题的规模是原问题的1/b,并且每一次拆分和组合的过程需要f(n)的时间。
Technicalities in recurrences
关于recurrences有一些细节需要注意:
1.When we state and solve recurrences, we often omit floors, ceilings, and boundary conditions.
对于某些recurrences来说会带有向上取整/向下取整等符号,在我们计算复杂度等的时候可以忽略这些符号。
2.sometimes we ignore the (if n=1) case,The reason is that although changing
the value of T(1) changes the exact solution to the recurrence, the solution typically doesn’t change by more than a constant factor, and so the order of growth is
unchanged. 有时候我们写一个recurrences的时候会自动省略它的base case的情况,因为这类情况通常不会对
算法的复杂度造成影响。
Maximum-subarray problem
给出这样一个问题,解决它的算法有哪些?
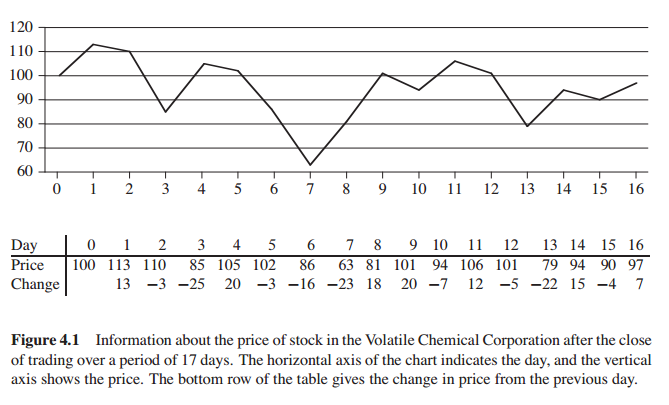
Brute-force solution
俗称“暴力破解法”,匹配每一对日子,并比较profit的最大值得出答案。
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
int size=prices.size();
int profit=INT_MIN;
for(int cnt=0;cnt<size;cnt++){
for(int i=cnt;i<size;i++){
profit=max(profit,prices[i]-prices[cnt]);
}
}
return profit;
}
};
太简单也就不提了。
My solution
其实这道题我在leetcode见过,#121. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock
有一个很清晰也很简单的解决办法,这个问题其实是要我们做到“低价买,高价卖”,
所以我们只需要知道每一个price后面的max-price即可,
先从数组尾端开始遍历一遍得到每个price后面的max-price,再遍历一遍比较即可,time complexity:O(n), space complexity:O(n)。
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
if(prices.size()<=0) return 0;
int sold=INT_MIN;//尽量大
vector<int> inverse_max=prices;
for(auto end=inverse_max.end()-1;end>=inverse_max.begin();end--)
sold=*end=max(sold,*end);
int profit=0;
for(int cnt=0;cnt<prices.size();cnt++){
profit=max(inverse_max[cnt]-prices[cnt],profit);
}
return profit;
}
};
Divide-and-Conquer solution
刚开始看到这个卖股票的时候我懵逼了,因为实在想不到它为什么能用Divide-and-Conquer做,直到书上
告诉我这里有一个tranformation我才恍然大悟。所谓的transformation,就是不用原来的prices数据,而是
用价格的变化作为处理对象。由此,此问题就变成了Maximum-subarray problem。
对于最大子数组这个问题,其实也有更为简洁粗暴的解决方案:
//leetcode #53. Maximum Subarray
class Solution {
public:
int maxSubArray(vector<int>& nums) {
int result = INT_MIN, f = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i) {
f = max(f + nums[i], nums[i]);
result = max(result, f);
}
return result;
}
};
书上为了介绍Divide-and-Conquer,就强行用了Divide-and-Conquer做。
整体思路是:将原数组分为左右两个数组,此数组的Maximum-subarray要么全部在左边,要么全部在右边,
要么一部分在左边一部分在右边,只需比较这三种情况下的Maximum-subarray,就能得到答案,算法的伪代码是:
Algorithm:FIND_MAX_CROSSING_SUBARRAY(A,low,mid,high)
left_sum=INT_MIN
sum=0
for i=mid downto low
sum+=A[i]
if sum>left_sum
left_sum=sum
max_left=i
right_sum=INT_MIN
sum=0
for j=mid+1 to high
sum+=A[j]
if sum>right_sum
right_sum=sum
max_right=i
return(max_left,max_right,left_sum+right_sum)
Algorithm:FIND_MAXIMUM_SUBARRAY(A,low,high)
if high==low
return(low,high,A[low]) //base case:only one element
else mid=(low+high)/2
(left_low,left_high,left_sum)=FIND_MAXIMUM_SUBARRAY(A,low,mid)
(right_low,right_high,right_sum)=FIND_MAXIMUM_SUBARRAY(A,mid+1,high)
(cross_low,cross_high,cross_sum)=FIND_MAX_CROSSING_SUBARRAY(A,low,mid,high)
return max(left,right,cross)
而对于这个Divide-and-Conquer算法来说,它的recurrences是:
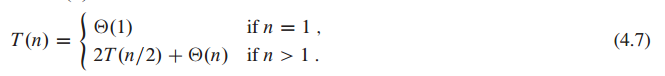
与merge-sort的recurrences相同,可以得知,这个算法的时间复杂度是:O(nlogn)
Exercises
4.1-1
What does FIND-MAXIMUM-SUBARRAY return when all elements of A are negative?
I think the algorithm will return the maximum negative number in the array.
4.1-2
Write pseudocode for the brute-force method of solving the maximum-subarray
problem. Your procedure should run in O(n^2) time.
Too easy to write, I think.
4.1-4
Suppose we change the definition of the maximum-subarray problem to allow the
result to be an empty subarray, where the sum of the values of an empty subarray is 0. How would you change any of the algorithms that do not allow empty
subarrays to permit an empty subarray to be the result?
Solution: Check all of the return value, if the value is negative then return zero.
4.1-5
Use the following ideas to develop a nonrecursive, linear-time algorithm for the
maximum-subarray problem. Start at the left end of the array, and progress toward
the right, keeping track of the maximum subarray seen so far. Knowing a maximum
subarray of A[1..j], extend the answer to find a maximum subarray ending at index j+1 by
using the following observation: a maximum subarray of A[1..j+1]
is either a maximum subarray of A[1..j] or a subarray A[i..j+1], for some
i belongs to [1,j+1]. Determine a maximum subarray of the form A[i..j+1] in
constant time based on knowing a maximum subarray ending at index j.
class Solution {
public:
int maxSubArray(vector<int>& nums) {
//遍历nums
//遇到一个数将其加入temp_subarray,若temp_sum+nums[cnt]>0,则保持,若其<=0,比较sum和temp_sum
//若sum小,则sum=temp_sum,且subarray=temp_subarray,sum大,则无视
//然后令temp_subarray的首尾都等于cnt+1
int temp_sum=0;
int sum=INT_MIN;
vector<int> temp_subArray,subArray;
for(int cnt=0;cnt<nums.size();cnt++){
temp_subArray.push_back(nums[cnt]);//遇到一个数先将其加入temp_subArray
temp_sum+=nums[cnt];
if(temp_sum<=0){
if(temp_subArray.size()==1){//是为了避免连着两个负数的情况,比如{-1,-2},没有加这个条件就AC不了}
if(nums[cnt]>sum){
sum=temp_sum;
temp_subArray.pop_back();
}
temp_subArray.erase(temp_subArray.begin(),temp_subArray.end());
temp_sum=0;
}
else{
if(temp_sum-nums[cnt]>sum){
//找到新子串
sum=temp_sum;
temp_subArray.pop_back();
}
temp_subArray.erase(temp_subArray.begin(),temp_subArray.end());
temp_sum=0;
}
}
else{
sum=temp_sum>sum?temp_sum:sum;
}
}
return sum;
}
};
关于这道题,上面是我在做Leetcode那道题的时候第一次用的解法,时间复杂度也是O(n),但是有可能不符合这道题的思路,这道题给出的思路我其实有点想不通,
如果有人觉得自己了解那个思路具体是怎么做的,麻烦在评论区留言,请不吝赐教!



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号