树链剖分(〃>目<)
小声吐槽:如果不是拍了200000组没问题后瞪眼瞪出来了,我才不写呢
Decribe:
给定一棵 \(n\) 个节点的树,初始时该树的根为 \(1\) 号节点,每个节点有一个给定的权值。下面依次进行 \(m\) 个操作,操作分为如下五种类型:
-
换根:将一个指定的节点设置为树的新根。
-
修改路径权值:给定两个节点,将这两个节点间路径上的所有节点权值(含这两个节点)增加一个给定的值。
-
修改子树权值:给定一个节点,将以该节点为根的子树内的所有节点权值增加一个给定的值。
-
询问路径:询问某条路径上节点的权值和。
-
询问子树:询问某个子树内节点的权值和。
Solution:
讲讲树剖这个东西。树链剖分又分重链剖分、长链剖分、实链剖分。这里只讲重链剖分(下文所讲的树链剖分即重链剖分)。
当遇到树上的区间操作时,尤其是复杂操作,树链剖分绝对是一个不错的选择。它本质上就是把一棵树分割成许多区间,再拼到一起,就可以再套上各种区间数据结构,线段树、ST 表等皆可食用。此外,这玩意常数极小,上界很少能达到,常常创造卡常奇迹,特别香。
好了好了,正式开讲吧,不吹了。首先,对于一棵普普通通的树,一个节点可能会有很多儿子,在区间操作时就不知道要向那个儿子走才是正确的方向,所以一般是让区间的两头向上跳到最近公共祖先,方便统计。但是如何在向上跳的同时计算区间贡献呢?
树链剖分对于每个节点,选择一个子树节点最多的儿子作为重儿子(若有一样多的就随便挑一个,不会有影响),其他儿子作为轻儿子。然后再分割成一条条重链,每条重链的最浅的节点一定是这条链中层数最低的,并且其他节点一定都是重儿子。
比如说这棵树:
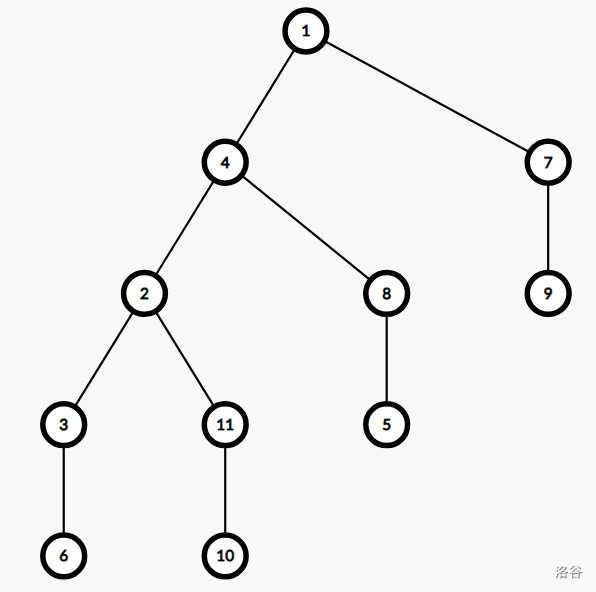
\(1\) 的重儿子就是 \(4\) ,以 \(1\) 为链头的一条可能重链为 $ 1 \to 4 \to 2 \to 3 \to 6 $。所有重链组成的区间就可能是这样的:\(1-4-2-3-6-11-10-8-5-7-9\),其中 \(1 \to 4 \to 2 \to 3 \to 6\),\(11\to 10\),\(8\to 5\),\(7\to 9\) 为重链。
对于每个节点,我们需要记录以下信息:
- \(fa\):节点的父亲。
- \(dep\):节点的层数。
- \(son\):节点的重儿子。
- \(siz\):以该节点为根的子树节点数。
- \(dfn\):节点对应区间的位置编号。
- \(top\):节点所在重链的链头。
用以实现后面的操作。
将每条重链按一定的顺序拼接起来,就可以用区间数据结构维护了。这样的分链的树有一些有趣的性质:
- 每下到一个轻儿子,子树节点数至少减少 \(\lceil \cfrac{size}{2} \rceil\)。
这条很简单,如果该儿子的子树节点数超过了 $ \cfrac{size}{2}$,那这个儿子的子树节点数一定比其他儿子的子树节点数多,因而成为重儿子,这与轻儿子的定义不符。
- 每个子树都在一段连续的区间上。
这两个性质决定了路径操作和子树操作的时间复杂度。第一个性质决定了路径操作不会超过 \(O(\log n)\) 的时间查询路径,第二个性质决定了子树操作是 \(O(1)\) 的。
这里证明一下路径操作不会超过 \(O(\log n)\) 的时间查询路径:
对于路径上左右端点,如果在重链上,可以直接对链头至节点做区间操作。若是不在,则对该链做一次区间操作,并跳到重链头的父亲这个位置,子树节点数因为第一条性质至少增加了 \(\lceil \cfrac{size}{2} \rceil\),至多能够增加 \(\log n\) 次,因此复杂度为 \(O(\log n)\)。
对于区间修改和查询,随便套个线段树就可以。但 loj 的模板不是一般的恶心。可以看到,题目中还有换根操作,然而树链剖分只能处理静态树,每次换根重分链时间会爆炸的。
实际上,我们并不需要真的换根,只需要处理换根造成的影响即可。
首先,对于路径显然换根是不会有任何影响的。对于子树,我们需要分类讨论。
-
根在该子树根上。
——那显然是在查询整棵树,对区间 $1 \sim n $ 操作即可。 -
根在该子树内。
——那就需要查询除根所在的子树内的区间的整个区间,所以我们需要找到根在哪个儿子的子树上。这里就还需要再分类讨论。
一、根在重儿子所在子树上。那直接将重儿子所在子树的影响去除即可。
二、根在轻儿子所在子树上。那就从根开始不断跳到重链头,直到父亲是该节点为止。显然同查询路径一样,不会超过 \(O(\log n)\)。 -
根在该子树外。
——那没有影响,直接对 \(dfn \sim dfn+siz-1\) 这个区间操作即可。
Code:
bool _Start;
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
namespace IO
{
#define TP template<typename T>
#define TP_ template<typename T,typename ... T_>
#ifdef DEBUG
#define gc() (getchar())
#else
char buf[1<<20],*p1,*p2;
#define gc() (p1==p2&&(p2=(p1=buf)+fread(buf,1,1<<20,stdin),p1==p2)?EOF:*p1++)
#endif
#ifdef DEBUG
void pc(const char &c)
{
putchar(c);
}
#else
char pbuf[1<<20],*pp=pbuf;
void pc(const char &c)
{
if(pp-pbuf==1<<20)
fwrite(pbuf,1,1<<20,stdout),pp=pbuf;
*pp++=c;
}
struct IO{~IO(){fwrite(pbuf,1,pp-pbuf,stdout);}}_;
#endif
TP void read(T &x)
{
x=0;static int f;f=0;static char ch;ch=gc();
for(;ch<'0'||ch>'9';ch=gc())ch=='-'&&(f=1);
for(;ch>='0'&&ch<='9';ch=gc())x=(x<<1)+(x<<3)+(ch^48);
f&&(x=-x);
}
TP void write(T x)
{
if(x<0)
pc('-'),x=-x;
static T sta[35],top;top=0;
do
sta[++top]=x%10,x/=10;
while(x);
while(top)
pc(sta[top--]^48);
}
TP_ void read(T &x,T_&...y){read(x);read(y...);}
TP void writeln(const T x){write(x);pc('\n');}
TP void writesp(const T x){write(x);pc(' ');}
TP_ void writeln(const T x,const T_ ...y){writesp(x);writeln(y...);}
TP void debugsp(const T x){fprintf(stderr,"%d ",x);}
TP void debug(const T x){fprintf(stderr,"%d\n",x);}
TP_ void debug(const T x,const T_...y){debugsp(x);debug(y...);}
TP inline T max(const T &a,const T &b){return a>b?a:b;}
TP_ inline T max(const T &a,const T_&...b){return max(a,max(b...));}
TP inline T min(const T &a,const T &b){return a<b?a:b;}
TP_ inline T min(const T &a,const T_&...b){return min(a,min(b...));}
TP inline void swap(T &a,T &b){static T t;t=a;a=b;b=t;}
TP inline T abs(const T &a){return a>0?a:-a;}
#undef TP
#undef TP_
}
using namespace IO;
using std::cerr;
using LL=long long;
constexpr int N=1e5+10;
struct edge
{
int y,pre;
}
a[N];int alen,last[N];
void ins(int x,int y)
{
a[++alen]=edge{y,last[x]};
last[x]=alen;
}
namespace Chain
{
struct trnode
{
int fa,dep,son,siz,dfn,top,end;LL val;//这里 end 就是 dfn+siz-1。
}tr[N];
void prepare(int x,int fa)
{
tr[x]={fa,tr[fa].dep+1,0,1,0,0,0,tr[x].val};
for(int k=last[x];k;k=a[k].pre)
{
int y=a[k].y;
if(y==fa)
continue;
prepare(y,x);
tr[x].siz+=tr[y].siz;
if(tr[tr[x].son].siz<tr[y].siz)
tr[x].son=y;
}
}
int num,b[N];
void dfs_chain(int x,int tp)
{
b[tr[x].dfn=++num]=x;
tr[x].top=tp;
if(tr[x].son)
dfs_chain(tr[x].son,tp);
for(int k=last[x];k;k=a[k].pre)
{
int y=a[k].y;
if(y==tr[x].fa||y==tr[x].son)
continue;
dfs_chain(y,y);
}
tr[x].end=num;
}
}
namespace Segtree
{
struct trnode
{
int l,r,lc,rc;LL sum;
LL lazy;
}
tr[N<<1];int trlen;
#define lc tr[now].lc
#define rc tr[now].rc
void Plus(int now,LL c)
{
tr[now].sum+=(tr[now].r-tr[now].l+1)*c;
tr[now].lazy+=c;
}
void pushup(int now)
{
tr[now].sum=tr[lc].sum+tr[rc].sum;
}
void pushdown(int now)
{
if(tr[now].lazy)
{
Plus(lc,tr[now].lazy);
Plus(rc,tr[now].lazy);
tr[now].lazy=0;
}
}
void build(int l,int r)
{
int now=++trlen;
tr[now]={l,r};
if(l==r)
tr[now].sum=Chain::tr[Chain::b[l]].val;
else
{
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
lc=trlen+1;build(l,mid);
rc=trlen+1;build(mid+1,r);
pushup(now);
}
}
void modify(int now,int l,int r,LL c)
{
if(l<=tr[now].l&&tr[now].r<=r)
return Plus(now,c);
pushdown(now);
int mid=(tr[now].r+tr[now].l)>>1;
if(l<=mid)
modify(lc,l,r,c);
if(r>=mid+1)
modify(rc,l,r,c);
pushup(now);
}
LL query(int now,int l,int r)
{
if(l<=tr[now].l&&tr[now].r<=r)
return tr[now].sum;
pushdown(now);
LL ans=0;int mid=(tr[now].r+tr[now].l)>>1;
if(l<=mid)
ans+=query(lc,l,r);
if(r>=mid+1)
ans+=query(rc,l,r);
return ans;
}
#undef lc
#undef rc
}
int rt=1;
void modify_route(int x,int y,LL c)
{
using namespace Chain;
using Segtree::modify;
while(tr[x].top!=tr[y].top)
{
if(tr[tr[x].top].dep>tr[tr[y].top].dep)
swap(x,y);
modify(1,tr[tr[y].top].dfn,tr[y].dfn,c);
y=tr[tr[y].top].fa;
}
if(tr[x].dep>tr[y].dep)
swap(x,y);
modify(1,tr[x].dfn,tr[y].dfn,c);
}
void modify_subtree(int x,LL c)
{
using namespace Chain;
using Segtree::modify;
if(tr[x].dfn>tr[rt].dfn||tr[x].end<tr[rt].dfn)
return modify(1,tr[x].dfn,tr[x].end,c);
modify(1,1,num,c);
if(tr[tr[x].son].dfn<=tr[rt].dfn&&tr[tr[x].son].end>=tr[rt].dfn)
return modify(1,tr[tr[x].son].dfn,tr[tr[x].son].end,-c);
else if(tr[x].dfn<tr[rt].dfn&&tr[x].end>=tr[rt].dfn)
{
int tmp=tr[rt].top;
while(tr[tmp].fa!=x)
tmp=tr[tr[tmp].fa].top;
return modify(1,tr[tmp].dfn,tr[tmp].end,-c);
}
}
LL query_route(int x,int y)
{
using namespace Chain;
using Segtree::query;
LL ans=0;
while(tr[x].top!=tr[y].top)
{
if(tr[tr[x].top].dep>tr[tr[y].top].dep)
swap(x,y);
ans+=query(1,tr[tr[y].top].dfn,tr[y].dfn);
y=tr[tr[y].top].fa;
}
if(tr[x].dep>tr[y].dep)
swap(x,y);
ans+=query(1,tr[x].dfn,tr[y].dfn);
return ans;
}
LL query_subtree(int x)
{
using namespace Chain;
using Segtree::query;
if(tr[x].dfn>tr[rt].dfn||tr[x].end<tr[rt].dfn)
return query(1,tr[x].dfn,tr[x].end);
LL ans=0;
ans+=query(1,1,num);
if(tr[tr[x].son].dfn<=tr[rt].dfn&&tr[tr[x].son].end>=tr[rt].dfn)
return ans-=query(1,tr[tr[x].son].dfn,tr[tr[x].son].end);
else if(tr[x].dfn<tr[rt].dfn&&tr[x].end>=tr[rt].dfn)
{
int tmp=tr[rt].top;
while(tr[tmp].fa!=x)
tmp=tr[tr[tmp].fa].top;
return ans-=query(1,tr[tmp].dfn,tr[tmp].end);
}
return ans;
}
bool _End;
int main()
{
// fprintf(stderr,"%.2 MBlf\n",(&_End-&_Start)/1048576.0);
int n;read(n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
read(Chain::tr[i].val);
for(int i=2,x;i<=n;i++)
read(x),ins(x,i);
Chain::prepare(rt,0);
Chain::dfs_chain(rt,rt);
Segtree::build(1,Chain::num);
int q;read(q);
while(q--)
{
int op;read(op);
switch(op)
{
case 1:
{
read(rt);
break;
}
case 2:
{
int x,y;LL c;
read(x,y,c);
modify_route(x,y,c);
break;
}
case 3:
{
int x;LL c;
read(x,c);
modify_subtree(x,c);
break;
}
case 4:
{
int x,y;
read(x,y);
writeln(query_route(x,y));
break;
}
case 5:
{
int x;read(x);
writeln(query_subtree(x));
break;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
2024.5.23 update:
长链剖分
几乎与重链剖分一致,只是把重儿子的定义换成了所有子树中深度最深的,其他没什么改变,但查询路径的时间变为了 \(O(\sqrt n)\)。
所以,我一开始看到这个东西是觉得没有应用场景的。直到······
长链剖分优化 dp
当 dp 数组中有一维是深度的时候,可以利用长链剖分优化内存和时间,将这一维均摊为 \(O(1)\)。
具体来说,沿用重链剖分其他的定义,设 \(f_{x,i}\) 为 \(x\) 节点向下 \(i\) 深度的节点的贡献。那么显然有 \(f_{x,i}=f_{son,i-1}\)。那就可以让这两个数组指向同一块内存,实现重链中同时修改,这可以用指针实现,具体实现看代码。而轻儿子的贡献直接暴力计算即可。由于每个节点实际上只有作为轻儿子时向上做出了贡献,所以时间复杂度为 \(O(n)\)。
那么内存实际时与重链节点数相关的,而所有重链节点数加起来显然应是整棵树的节点数,所以只需要多开一块 \(O(n)\) 的内存即可。
例题:
CF1009F Dominant Indices
板子题。不多说,上代码。
bool _Start;//
// #define DEBUG
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
namespace IO
{
#define TP template<typename T>
#define TP_ template<typename T,typename ... T_>
#ifdef DEBUG
#define gc() (getchar())
#else
char buf[1<<20],*p1,*p2;
#define gc() (p1==p2&&(p2=(p1=buf)+fread(buf,1,1<<20,stdin),p1==p2)?EOF:*p1++)
#endif
#ifdef DEBUG
void pc(const char &c)
{
putchar(c);
}
#else
char pbuf[1<<20],*pp=pbuf;
inline void pc(const char &c)
{
if(pp-pbuf==1<<20)
fwrite(pbuf,1,1<<20,stdout),pp=pbuf;
*pp++=c;
}
struct IO{~IO(){fwrite(pbuf,1,pp-pbuf,stdout);}}_;
#endif
TP inline void read(T &x)
{
x=0;static int f;f=0;static char ch;ch=gc();
for(;ch<'0'||ch>'9';ch=gc())ch=='-'&&(f=1);
for(;ch>='0'&&ch<='9';ch=gc())x=(x<<1)+(x<<3)+(ch^48);
f&&(x=-x);
}
TP void write(T x)
{
if(x<0)
pc('-'),x=-x;
static T sta[35],top;top=0;
do
sta[++top]=x%10,x/=10;
while(x);
while(top)
pc(sta[top--]^48);
}
TP_ inline void read(T &x,T_&...y){read(x);read(y...);}
TP void writeln(const T x){write(x);pc('\n');}
TP void writesp(const T x){write(x);pc(' ');}
TP_ void writeln(const T x,const T_ ...y){writesp(x);writeln(y...);}
void writest(const std::string &a){for(int i=0;a[i];i++)pc(a[i]);}
TP inline T max(const T &a,const T &b){return a>b?a:b;}
TP_ inline T max(const T &a,const T_&...b){return max(a,max(b...));}
TP inline T min(const T &a,const T &b){return a<b?a:b;}
TP_ inline T min(const T &a,const T_&...b){return min(a,min(b...));}
TP inline void swap(T &a,T &b){static T t;t=a;a=b;b=t;}
TP inline T abs(const T &a){return a>0?a:-a;}
#undef TP
#undef TP_
}
using namespace IO;
using std::cerr;
using LL=long long;
constexpr int N=1e6+10;
constexpr int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
LL ans;
namespace graph
{
std::vector<int>g[N];
inline void ins(int x,int y)
{
g[x].push_back(y);
}
}
namespace Long_chain
{
int len[N],son[N],tmp[N],*f[N],*id=tmp,ans[N];
using namespace graph;
void prepare(int x,int fa)
{
for(int y:g[x])
{
if(y==fa)
continue;
prepare(y,x);
if(len[y]>len[son[x]])
son[x]=y;
}
len[x]=len[son[x]]+1;
}
void dp_chain(int x,int fa)
{
f[x][0]=1;
if(son[x])
{
f[son[x]]=f[x]+1;//f[son[x]] 所指向的内存储存的信息与 f[x][1] 是一致的
dp_chain(son[x],x);
ans[x]=ans[son[x]]+1;
}
for(int y:g[x])
{
if(y==fa||y==son[x])
continue;
f[y]=id;id+=len[y];//留下 len[y] 的空间给 y 所在的长链使用
dp_chain(y,x);
for(int j=1;j<=len[y];j++)
{
f[x][j]+=f[y][j-1];// 暴力转移
if((j<ans[x]&&f[x][j]>=f[x][ans[x]])||(j>ans[x]&&f[x][j]>f[x][ans[x]]))
ans[x]=j;
}
}
if(f[x][0]>=f[x][ans[x]])
ans[x]=0;
}
void solve()
{
prepare(1,0);
f[1]=id;id+=len[1];
dp_chain(1,0);
}
}
namespace Lofty
{
int n;
void work()
{
read(n);
for(int i=1,x,y;i<n;i++)
{
read(x,y);
graph::ins(x,y);
graph::ins(y,x);
}
Long_chain::solve();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
writeln(Long_chain::ans[i]);
}
}
bool _End;
int main()
{
// fprintf(stderr,"%.2lf MB\n",(&_End-&_Start)/1048576.0);
Lofty::work();
return 0;
}
//
P5904 [POI2014] HOT-Hotels 加强版
什么叫懒,这就叫懒。
bool _Start;//
// #define DEBUG
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
namespace IO
{
#define TP template<typename T>
#define TP_ template<typename T,typename ... T_>
#ifdef DEBUG
#define gc() (getchar())
#else
char buf[1<<20],*p1,*p2;
#define gc() (p1==p2&&(p2=(p1=buf)+fread(buf,1,1<<20,stdin),p1==p2)?EOF:*p1++)
#endif
#ifdef DEBUG
void pc(const char &c)
{
putchar(c);
}
#else
char pbuf[1<<20],*pp=pbuf;
inline void pc(const char &c)
{
if(pp-pbuf==1<<20)
fwrite(pbuf,1,1<<20,stdout),pp=pbuf;
*pp++=c;
}
struct IO{~IO(){fwrite(pbuf,1,pp-pbuf,stdout);}}_;
#endif
TP inline void read(T &x)
{
x=0;static int f;f=0;static char ch;ch=gc();
for(;ch<'0'||ch>'9';ch=gc())ch=='-'&&(f=1);
for(;ch>='0'&&ch<='9';ch=gc())x=(x<<1)+(x<<3)+(ch^48);
f&&(x=-x);
}
TP void write(T x)
{
if(x<0)
pc('-'),x=-x;
static T sta[35],top;top=0;
do
sta[++top]=x%10,x/=10;
while(x);
while(top)
pc(sta[top--]^48);
}
TP_ inline void read(T &x,T_&...y){read(x);read(y...);}
TP void writeln(const T x){write(x);pc('\n');}
TP void writesp(const T x){write(x);pc(' ');}
TP_ void writeln(const T x,const T_ ...y){writesp(x);writeln(y...);}
void writest(const std::string &a){for(int i=0;a[i];i++)pc(a[i]);}
TP inline T max(const T &a,const T &b){return a>b?a:b;}
TP_ inline T max(const T &a,const T_&...b){return max(a,max(b...));}
TP inline T min(const T &a,const T &b){return a<b?a:b;}
TP_ inline T min(const T &a,const T_&...b){return min(a,min(b...));}
TP inline void swap(T &a,T &b){static T t;t=a;a=b;b=t;}
TP inline T abs(const T &a){return a>0?a:-a;}
#undef TP
#undef TP_
}
using namespace IO;
using std::cerr;
using LL=long long;
constexpr int N=1e5+10;
constexpr int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
namespace graph
{
std::vector<int>g[N];
inline void ins(int x,int y)
{
g[x].push_back(y);
}
}
namespace Long_chain
{
int len[N],son[N];
LL tmp[N*3],*dp[N],*id,*f[N],ans;
using namespace graph;
void prepare(int x,int fa)
{
for(int y:g[x])
{
if(y==fa)
continue;
prepare(y,x);
if(len[y]>len[son[x]])
son[x]=y;
}
len[x]=len[son[x]]+1;
}
void dp_chain(int x,int fa)
{
dp[x][0]=1;
if(son[x])
{
dp[son[x]]=dp[x]+1;
f[son[x]]=f[x]-1;
dp_chain(son[x],x);
}
ans+=f[x][0];
for(int y:g[x])
{
if(y==fa||y==son[x])
continue;
dp[y]=id;id+=len[y]<<1;
f[y]=id;id+=len[y];
dp_chain(y,x);
for(int i=0;i<len[y];i++)
{
if(i)
ans+=f[y][i]*dp[x][i-1];
ans+=f[x][i+1]*dp[y][i];
}
for(int i=0;i<len[y];i++)
{
if(i)
f[x][i-1]+=f[y][i];
f[x][i+1]+=dp[x][i+1]*dp[y][i];
dp[x][i+1]+=dp[y][i];
}
}
}
void solve()
{
id=tmp;
prepare(1,0);
dp[1]=id;id+=len[1]<<1;
f[1]=id;id+=len[1];
dp_chain(1,0);
writeln(ans);
}
}
namespace Lofty
{
int n;
void work()
{
read(n);
for(int i=1,x,y;i<n;i++)
{
read(x,y);
graph::ins(x,y);
graph::ins(y,x);
}
Long_chain::solve();
}
}
bool _End;
int main()
{
// fprintf(stderr,"%.2lf MB\n",(&_End-&_Start)/1048576.0);
Lofty::work();
return 0;
}
//


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号