无源汇有上下界可行流
Describe:
\(n\) 个点,\(m\) 条边,每条边 \(e\) 有一个流量下界 \(\text{lower}(e)\) 和流量上界 \(\text{upper}(e)\),求一种可行方案满足流量守恒的同时满足每条边的限制条件。
Solution:
可以先考虑满足所有边的最低条件,获得一个初始的流量网络。
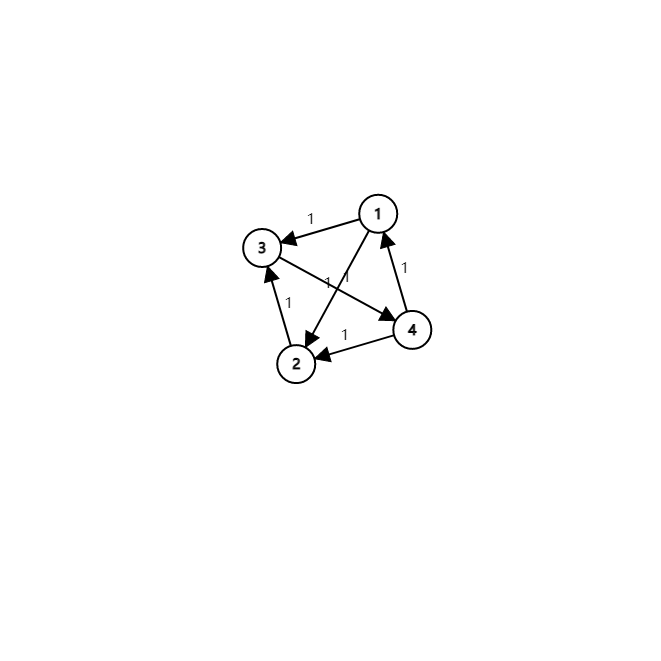
这时各个点是不一定满足流量守恒的。可能会有多余的流量无处可走,也可能会有流量不足以流出。因此可以建立一个源点,补充不足的流量,同时也建立一个汇点,汇入多余的流量。
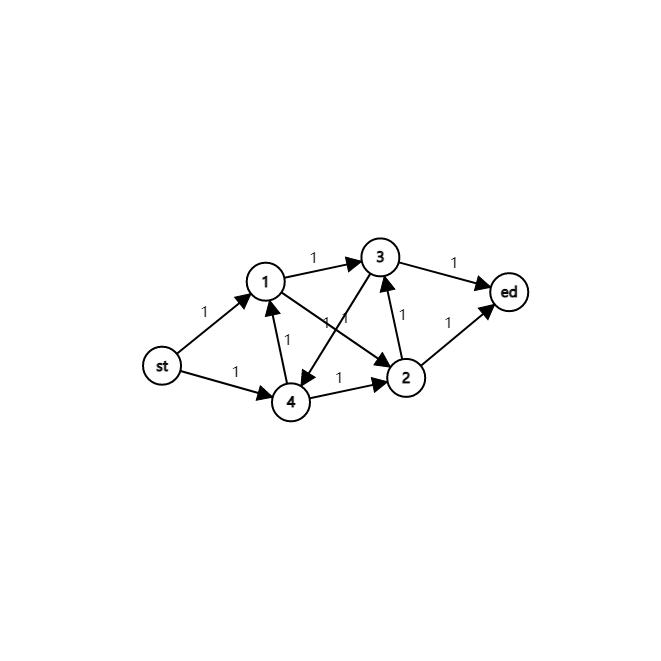
如果能在满足所有边的条件下从源点全部流入汇点,显然就是一个可行流。
因此可以建立一个残量网络,每条边的流量改为 \(\text{upper}(e) - \text{lower}(e)\),跑一个最大流。判断一下最大流是否等于源点的流量即可。每条边的实际流量就是最低流量加残量网络中每条边流出的流量。
Code:
bool _Start;
#include<deque>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
namespace IO
{
#define TP template<typename T>
#define TP_ template<typename T,typename ... T_>
#ifdef DEBUG
#define gc() (getchar())
#else
char buf[1<<20],*p1,*p2;
#define gc() (p1==p2&&(p2=(p1=buf)+fread(buf,1,1<<20,stdin),p1==p2)?EOF:*p1++)
#endif
#ifdef DEBUG
void pc(const char &c)
{
putchar(c);
}
#else
char pbuf[1<<20],*pp=pbuf;
void pc(const char &c)
{
if(pp-pbuf==1<<20)
fwrite(pbuf,1,1<<20,stdout),pp=pbuf;
*pp++=c;
}
struct IO{~IO(){fwrite(pbuf,1,pp-pbuf,stdout);}}_;
#endif
TP void read(T &x)
{
x=0;static int f;f=0;static char ch;ch=gc();
for(;ch<'0'||ch>'9';ch=gc())ch=='-'&&(f=1);
for(;ch>='0'&&ch<='9';ch=gc())x=(x<<1)+(x<<3)+(ch^48);
f&&(x=-x);
}
TP void write(T x)
{
if(x<0)
pc('-'),x=-x;
static T sta[35],top;top=0;
do
sta[++top]=x%10,x/=10;
while(x);
while(top)
pc(sta[top--]^48);
}
TP_ void read(T &x,T_&...y){read(x);read(y...);}
TP void writeln(const T x){write(x);pc('\n');}
TP void writesp(const T x){write(x);pc(' ');}
TP_ void writeln(const T x,const T_ ...y){writesp(x);writeln(y...);}
TP void debugsp(const T x){fprintf(stderr,"%d ",x);}
TP void debug(const T x){fprintf(stderr,"%d\n",x);}
TP_ void debug(const T x,const T_...y){debugsp(x);debug(y...);}
TP inline T max(const T &a,const T &b){return a>b?a:b;}
TP_ inline T max(const T &a,const T_&...b){return max(a,max(b...));}
TP inline T min(const T &a,const T &b){return a<b?a:b;}
TP_ inline T min(const T &a,const T_&...b){return min(a,min(b...));}
TP inline void swap(T &a,T &b){static T t;t=a;a=b;b=t;}
TP inline T abs(const T &a){return a>0?a:-a;}
#undef TP
#undef TP_
}
using namespace IO;
using std::cerr;
using LL=long long;
constexpr int inf=1e9,N=2e2+5,M=1e4+2*N;
struct edge
{
int y,f,pre;
}a[M<<1];int alen=1,last[N];
void ins(int x,int y,int f)
{
a[++alen]=edge{y,f,last[x]};
last[x]=alen;
a[++alen]=edge{x,0,last[y]};
last[y]=alen;
}
int n,m,st,ed;
int w[M],in[N];
int h[N],cur[N];
bool pd()
{
static std::deque<int>q;q.clear();
q.push_back(st);
memset(h,0,sizeof(h));h[st]=1;
while(q.size())
{
int x=q.front();q.pop_front();
for(int k=last[x];k;k=a[k].pre)
{
int y=a[k].y;
if(a[k].f&&!h[y])
{
h[y]=h[x]+1;
q.push_back(y);
}
}
}
return h[ed];
}
int findflow(int x,int f)
{
if(x==ed)
return f;
int sx=0,sy;
for(int &k=cur[x];k;k=a[k].pre)
{
int y=a[k].y;
if(a[k].f&&h[y]==h[x]+1)
{
sy=findflow(y,min(a[k].f,f-sx));
a[k].f-=sy;sx+=sy;
a[k^1].f+=sy;
if(sx==f)
return sx;
}
}
if(!sx)
h[x]=-1;
return sx;
}
int dinic()
{
int s=0;
while(pd())
{
memcpy(cur,last,sizeof(cur));
s+=findflow(st,inf);
}
return s;
}
bool _End;
int main()
{
// fprintf(stderr,"%.2 MBlf\n",(&_End-&_Start)/1048576.0);
read(n,m);st=n+1;ed=st+1;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
int x,y,up,dn;
read(x,y,dn,up);
w[i]=dn;ins(x,y,up-dn);
in[x]-=dn,in[y]+=dn;
}
int sum=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(in[i]<0)
ins(i,ed,-in[i]);
else if(in[i]>0)
ins(st,i,in[i]),sum+=in[i];
if(dinic()==sum)
{
puts("YES");
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
writeln(w[i]+a[i<<1|1].f);
}
else
puts("NO");
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号