C++ 之动态存储和类
特殊的成员函数
C++自动提供了下面这些成员函数
- 默认构造函数,如果没有定义构造函数
- 默认析构函数,如果没有定义
- 复制构造函数,如果没有定义
- 赋值运算符,如果没有定义
- 地址运算符,如果没有定义
C++ 11还提供了两个特殊的成员函数:移动构造函数和移动赋值运算符
copy构造函数
何时调用:新建一个对象并将其初始化为同类现有对象时, 复制构造函数都将被调用。
下面4种声明都会调用复制构造函数。
StringBad ditto(motto);
StringBad metoo = motto;
String also = StringBad(motto);
StringBad * pStringBad = new StringBad(motto);
中间的2种声明可能会使用复制构造函数直接创建metoo和also, 也可能使用复制构造函数生成一个临时对象, 然后将零时对象的内容赋给metoo和also, 这取决于具体的实现。 最后一种声明使用motto初始化一个匿名对象,并将新对象的地址赋给pstring指针。
按值传递意味着创建原始变量的一个副本。编译器生成临时对象时, 也将使用复制构造函数。
默认的复制函数的功能
默认的复制构造函数将逐个复制非静态成员(成员复制也称为浅复制),复制的是成员的值。
StringBad sailor = sports;
等效下面的代码:
StringBad sailor;
sailor.str = sports.str;
sailor.len = sports.len;
浅复制会带来 两次释放指针的错误。
解决这一问题使用深度复制(deep copy).
StringBad::StringBad(const StringBad & st)
{
num_strings ++ ;
len = st.len;
str = new char[len+1];
std::strcpy(str,st.str);
}
与复制构造函数类似,复制运算符的隐式实现也对成员进行逐个复制。 如果成员本身就是类对象,则程序将使用为这个;类定义的赋值运算符来复制该成员, 但静态数据成员不受影响。
Class_name &Class_name::operator=(const Class_name &);
编写赋值运算符:
StringBad & String::operator=(const StringBad & st)
{
if(this == &)
{
return *this;
}
delete [] str;
len = st.len;
str = new char[len+1];
std:: strcpy(str,st.str);
return *this;
}
C++11的空指针
str = nullstr;
头文件
string1.h
#ifndef STING1_H_
#define STING1_H_
#include <iostream>
using std::istream;
using std::ostream;
class String
{
private:
char *str;
int len;
static int num_strings;
static const int CINLIM = 80; // 字符长度限制
public:
// 构造函数
String(const char *s);
String();
String(const String &s);
~String();
// 成员方法
int length() const { return len; };
// 重载运算符成员方法
String &operator=(const String &);
String &operator=(const char *);
char &operator[](int i);
const char &operator[](int i) const;
// 重载运算符友元函数
friend bool operator>(const String &str1, const String &str2);
friend bool operator<(const String &str1, const String &str2);
friend bool operator==(const String &str1, const String &str2);
friend ostream & operator<<(ostream & os, const String &str);
friend istream & operator>>(istream & is, String &str);
};
#endif
string1.cpp源文件
#include "string1.h"
#include <cstring>
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::endl;
int String::num_strings = 0;
int String::HowMany()
{
return num_strings;
}
String::String(const char* s)
{
cout << "const char* s构造" << endl;
len = std::strlen(s);
str = new char[len + 1];
std::strcpy(str,s);
num_strings ++ ;
}
String::String()
{
cout << "无参构造" << endl;
len = 4;
str = new char[1];
str[0] = '\0';
num_strings ++;
}
String::String(const String & st)
{
cout << "拷贝(复制)构造函数" <<endl;
len = st.len;
str = new char[len+1];
std::strcpy(str,st.str);
num_strings ++;
}
String::~String()
{
--num_strings;
delete [] str;
}
// 成员运算符
String & String::operator=(const String & s)
{
if(this == &s)
{
return *this;
}
delete [] str;
len = s.len;
str = new char[len +1];
std::strcpy(str,s.str);
return * this;
}
String & String::operator=(const char * s)
{
delete [] str;
len = std::strlen(s);
str = new char[len + 1];
std::strcpy(str,s);
return *this;
}
// 元素可读可写
char & String::operator[](int i)
{
return str[i];
}
// 元素只读
const char & String::operator[](int i) const
{
return str[i];
}
// 重载运算符友元函数
bool operator<(const String &str1, const String &str2)
{
return std::strcmp(str1.str, str2.str) < 0;
}
bool operator>(const String &str1, const String &str2)
{
return str2 < str1;
}
bool operator==(const String &str1, const String &str2)
{
return std::strcmp(str1.str, str2.str) == 0;
}
ostream & operator<< (ostream & os, const String &str)
{
os << str.str;
return os;
}
istream & operator>>(istream & is, String &str)
{
char temp[String::CINLIM];
is.get(temp,String::CINLIM);
if (is)
str = temp;
// 如果到达文件尾或get(char *, int)读取的是一个空行,导致输入失败, istream的值将置为false
while(is && is.get() !='\n')
continue;
return is;
}
sayings1.cpp 主文件
#include <iostream>
#include "string1.h"
const int ArSize = 10;
const int Maxlen = 81;
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
using namespace std;
String name;
// name = "hello";
cout << "Enter your name: " ;
cin >> name;
cout << '\n';
cout << "your name is :"<< name;
String saying[ArSize];
char temp[Maxlen];
int i;
for(i = 0; i < ArSize; i++)
{
cout << i +1 << ":";
cin.get(temp, Maxlen);
while(cin && cin.get() != '\n')
{
continue;
}
if(!cin || temp[0] == '\0')
{
break;
}
else
{
saying[i] = temp;
}
}
int total = i;
if(total > 0)
{
cout << "Here are your sayings: \n" ;
for(i =0 ; i< total; i++)
{
cout << saying[i][0] << ": " << saying[i] << endl;
}
int shortest = 0;
int first = 0;
for(i = 1; i < total ; i ++)
{
if(saying[i].length() < saying[shortest].length())
{
shortest = i;
}
if(saying[i] < saying[first])
{
first = i ;
}
}
cout << "Shortest saying :\n" << saying[shortest] << endl;
cout << "First alphabetically :\n" << saying[first] << endl;
cout << "This program used " << String ::HowMany() << "String objects. Bye.\n";
}
else{
cout << "No Input! Bye. \n";
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
注意: 较早的get(chat *, int)版本在读取空行后,返回的值不为false。 然而,对于这些版本来说, 如果读取的是一个空行, 则字符串中第一个字符将是一个空字符。
if(!cin || temp[0] == '\0')
{
break;
}
// if语句中第一个条件检测空行, 第二个条件用于旧版本的实现中检测空行。
#ifndef A_H_
#define A_H_
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
A(){
cout << "A default constructor"<< endl;
}
A(const A & a)
{
cout << "A copy constructor"<< endl;
}
};
#endif
A test( A & a)
{
return a;
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
A a;
test(a);
return 0;
}
输出:
A default constructor
A copy constructor
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
private:
int a;
int b;
public:
A();
A(int a, int b);
A operator=(const A & a);
A(const A &a);
void test();
};
A::A()
{
cout << "default constructor \n";
this-> a= 0;
this->b = 0;
}
A::A(int a, int b)
{
cout << a << " \t "<< b<<endl;
this -> a = a;
this->b = b;
}
A A::operator=(const A & a)
{
cout << "copy" << endl;
return a;
}
A::A(const A & a)
{
cout << "copy constructor" << endl;
}
void A::test()
{
cout << this->a << " \t" << this->b << endl;
}
A test()
{
A a;
cout << typeid(a).name() << endl; // 1A
return a;
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
A a(2, 3);
A b = test(); // 底层做了优化 并没有调用复制构造函数
cout << typeid(b).name() << endl; // 1A
b.test();
return 0;
}
定位new运算符
定位new 运算符可以在分配内存时能够指定内存位置
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <new>
using namespace std;
const int BUF = 512;
class JustTesting
{
private:
string words;
int number;
public:
JustTesting(const string & s = "Justing Testing", int n = 0)
{words = s; number = n; cout << words << " constructed. \n";}
~JustTesting(){cout << words << " destroyed\n";}
void show() const { cout << words << ", " << number << endl; }
};
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
char * buffer = new char[BUF];
JustTesting *pc1, *pc2;
pc1 = new (buffer)JustTesting; // 在buffer中放置对象
pc2 = new JustTesting("Heap1",20); // 在堆中放置对象
cout << "Memory block address : \n" <<"buffer: "<< (void *)buffer << " heap: " << pc2 << endl;
cout << "Memory contents: \n" ;
cout << pc1 << ": ";
pc1 ->show();
cout << pc2 << ": ";
pc2 ->show();
JustTesting *pc3, *pc4;
pc3 = new (buffer)JustTesting("Bad Idea",6);
pc4 = new JustTesting("heap2", 10);
cout << "Memory contents: \n" ;
cout << pc3 << ": ";
pc3 ->show();
cout << pc4 << ": ";
pc4->show();
delete pc2; // 释放 heap1
delete pc4; // 释放 heap2
delete [] buffer;
cout << "Done \n";
return 0;
}
使用定位new运算符时存在两个问题:1. 首先在创建第二个对象时, 定位new 运算符使用一个新对象来覆盖用于第一个对象的内存单元。2.
其次, 将delete用于pc2和pc4时, 将自动调用pc2和pc4指向对象调用的析构函数, 然而使用, 将delete[] 用于buffer时, 不会为使用定位new运算符创建的对象调用析构函数。
解决方法: 1. 要使用不同的内存单元, 内存单元不能发生重叠。需要提供两个位于缓冲区的不同的地址, 并确保这两个内存单元不重叠。
例如,可以这样做:
pc1 = new (buffer)JustTesting;
pc2 = new (buffer + sizeof(JustTesting))JustTesting("Better Idea",6);
delete运算符可以与常规的new运算符配合使用,但不能与定位new运算符配合使用。
问题2的解决方案是,显式地为使用定位new 运算符创建的对象调用析构函数。需要显式地调用析构函数。
pc3->~JustTesting(); // 销毁pc3指向的对象
pc1->~JustTesting(); // 销毁pc3指向的对象
修复后的代码
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <new>
using namespace std;
const int BUF = 512;
class JustTesting
{
private:
string words;
int number;
public:
JustTesting(const string & s = "Justing Testing", int n = 0)
{words = s; number = n; cout << words << " constructed. \n";}
~JustTesting(){cout << words << " destroyed\n";}
void show() const { cout << words << ", " << number << endl; }
};
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
char * buffer = new char[BUF];
JustTesting *pc1, *pc2;
pc1 = new (buffer)JustTesting; // 在buffer中放置对象
pc2 = new JustTesting("Heap1",20); // 在堆中放置对象
cout << "Memory block address : \n" <<"buffer: "<< (void *)buffer << " heap: " << pc2 << endl;
cout << "Memory contents: \n" ;
cout << pc1 << ": ";
pc1 ->show();
cout << pc2 << ": ";
pc2 ->show();
JustTesting *pc3, *pc4;
pc3 = new (buffer)JustTesting("Bad Idea",6);
pc4 = new JustTesting("heap2", 10);
cout << "Memory contents: \n" ;
cout << pc3 << ": ";
pc3 ->show();
cout << pc4 << ": ";
pc4->show();
delete pc2; // 释放 heap1
delete pc4; // 释放 heap2
pc3->~JustTesting();
pc1->~JustTesting();
delete [] buffer;
cout << "Done! \n";
return 0;
}
队列模拟
要求:
限制等待人数
对顾客排队等待时间进行预测
1/3的顾客只需要1分钟就能获得服务,1/3的顾客需要3分钟,另外1/3的顾客需要3分钟。顾客到达的时间是随机的,但每个小时使用ATM的顾客数量相当稳定。 工程的另外两个任务是: 设计一个表示顾客的类; 编写一个程序来模拟顾客和队列之间的交互。
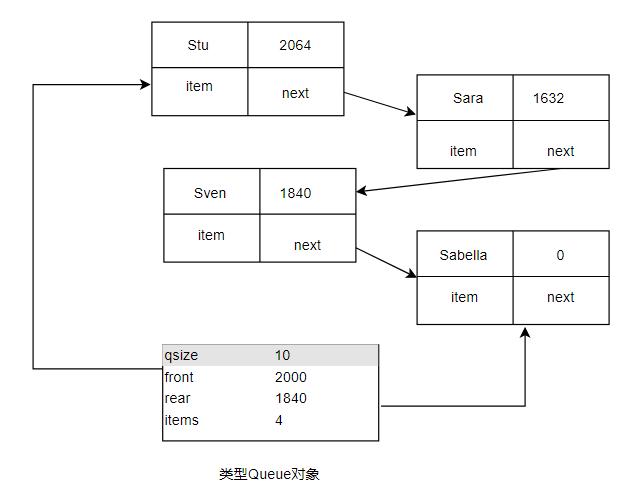
队列类
- 队列存储有序的项目队列
- 队列能容纳的项目数有一定的限制
- 应当能够创建空队列
- 应当能够检查队列是否为空
- 应该能够检查队列是否为满
- 能够在队尾添加项目
- 在队首删除项目
- 应当能够确定队列中项目数
在类声明中声明的结构、类或枚举被称为是被嵌套在类中, 其作用域为整个类。这种声明不会创建数据对象, 而只是指定了可以在类中使用的类型。
如果声明时在类的私有部分进行的, 则只能在这个类使用被声明的类型;如果声明是在公有部分进行的, 则可以从类的外部通过作用域解析运算符使用被声明的类型。例如: 如果Node是在Queue类的公有部分声明的,则可以在类的外面声明Queue::Node类型的变量。
对于const数据成员,必须在执行到构造函数之前,即创建对象时进行初始化。使用成员初始化列表,效率更高。
ATM模拟:
程序允许用户输入3个数: 队列的最大长度、程序模拟的持续性时间(单位为小时)以及平均每小时的客户数。
- 判断是否来了新客户,如果来了,且队列没有满,则将它添加到队列中,否则拒绝客户入队。
- 如果没有客户在进行交易,则选取队列中的第一个客户。 确定该客户的已等候的时间,并将wait_time计数器设置为新客户所需的处理时间。
- 如果客户正在处理中,则将wait_time计算器减1
- 记录各种数据,如获得服务的客户数目、被拒绝的客户数目、排队等候的累积时间以及累积的队列长度。、
RAND_MAX是rand()函数返回的最大值(cstdlib.h)
classy::Classy(int n , int m):mem1(n), mem2(0),mem3(n*m + 2)
{
}
// 这种格式只能用于构造函数
// 必须用这种格式来初始化非静态const数据成员
// 必须用这种格式初始化引用数据成员
数据成员初始化顺序与它们出现在类声明中的顺序相同, 与初始化器中的排列顺序无关。
C++ 11 允许 在类声明成员属性的时候,直接赋值。 这与使用初始化列表等价。
queue.h头文件
#ifndef QUEUE_H_
#define QUEUE_H_
class Customer
{
private:
long arrive; // 客户到达的时间
int processtime; // 交易处理的时间
public:
Customer():arrive(0),processtime(0)
{}
void set(long when);
long when() const {return arrive;} // 获取到达时间
int ptime() const {return processtime;} // 获取处理时间
};
typedef Customer Item;
class Queue
{
private:
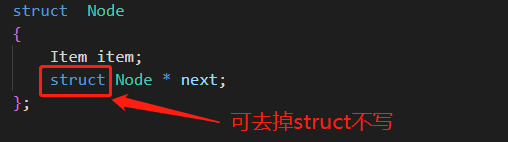
struct Node
{
Item item;
struct Node * next;
};
enum{Q_SIZE = 10};
Node *front;
Node *rear;
int items ; // 当前队列中items数
const int qsize; // 当前队列中items的最大数目
Queue(const Queue & q):qsize(0){}
Queue & operator=(const Queue & q){return *this;}
public:
Queue(int qs = Q_SIZE); // 创建一个队列, 队列的长度最大为Q_SIZE
~Queue();
bool isempty() const;
bool isfull() const;
int queuecount() const ;
bool enqueue(const Item &item); // 将item添加到对尾
bool dequeue(Item & item); // 从队头移除item
};
#endif
queue.cpp文件
#include "queue.h"
#include <cstdlib> // rand() 函数 头文件
#include <iostream>
Queue::Queue(int qs):qsize(qs)
{
front = rear = NULL;
items = 0;
}
Queue::~Queue()
{
Node * temp;
while(front != NULL)
{
temp = front;
front = front->next;
delete temp;
}
}
bool Queue::isempty() const
{
return items == 0;
}
bool Queue::isfull() const
{
return items == Q_SIZE;
}
int Queue::queuecount() const
{
return items;
}
bool Queue::enqueue(const Item & item)
{
if(isfull())
{
return false;
}
Node *add = new Node; // 创建一个节点
add ->item = item;
add->next = nullptr;
items ++;
if(front == NULL)
{
front = add;
}else
{
rear->next = add;
}
rear = add;
return true;
}
bool Queue::dequeue(Item &item) // 出队
{
if(front == NULL)
{
return false;
}
item = front -> item; // 队头
items --;
Node *temp = front;
front = front -> next;
delete temp;
if(items == 0 )
{
rear = NULL;
}
return true;
}
void Customer::set(long when)
{
processtime = std::rand() % 3 + 1; // 模拟处理时间
std::cout << "processtime="<<processtime << std::endl;
arrive = when;
}
bank.cpp文件
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
#include "queue.h"
using namespace std;
const int MIN_PER_HR = 60; // 60分钟 1小时
bool newcustomer(double x); // 是否来了新客户
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
srand(time(0));
int qs;
// 输入队列的最大元素个数
cout << "Enter max size of queue: ";
cin >> qs;
Queue line(qs);
// 输入模拟的小时数
cout << "Enter the number of simulation hours: " ;
int hours ;
cin >> hours;
// 每分钟执行一次模拟
long cyclelimit = MIN_PER_HR * hours; // 一个小时60分钟 一共多少分钟
// 输入每小时客户的平均数量
cout <<"Enter the average number of customers per hour" <<endl;
double perhour;
cin >> perhour;
double min_per_cust ; // 两次到达的平均时间
min_per_cust = MIN_PER_HR / perhour;
Item temp; // 新的用户数据
long turnways = 0; // 拒绝客户数
long customers = 0 ; // 加入到队列数
long served = 0; // 服务客户数
long sum_line = 0; // 累计队伍长度
int wait_time = 0; // 单个用户的等待服务的时间
long line_wait = 0; // 排队等候的累计时间
// 运行模拟
for(int cycle = 0; cycle < cyclelimit ; cycle ++) // 1分钟循环一次 平均每6分钟来1次顾客
{
if(newcustomer(min_per_cust))
{
if(line.isfull())
{
turnways ++ ;
}else
{
customers ++ ;
temp.set(cycle); // 设置到达的时间
line.enqueue(temp); // 入队
}
if(wait_time <= 0 && !line.isempty()) // 对列不空
{
line.dequeue(temp);
wait_time = temp.ptime(); // 等待时间
line_wait += cycle - temp.when();
served ++ ;
}
if(wait_time > 0)
{
wait_time -- ;
}
sum_line += line.queuecount();
}
}
// 报告结果
if(customers > 0)
{
cout << "customers accepted:" << customers << endl;
cout << "customers served:" << served << endl;
cout << "turnaways: " << turnways <<endl;
cout << "average queue size: " ;
cout.precision(2);
cout.setf(ios_base::fixed, ios_base::floatfield);
cout << (double)sum_line/cyclelimit << endl;
cout << "average wait time: " << (double) line_wait /served << " minutes\n" ;
}
else
{
cout << "No customers! \n" << endl;
}
cout << "Done! \n" ;
return 0;
}
bool newcustomer(double x)
{
return (rand() * x / RAND_MAX) < 1;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号