POJ 3585 Accumulation Degree 题解
POJ 3585 Accumulation Degree 题解
题目的字面意思
给出了一个带权无向图,然后可以任意选一个点做源点,往里面倒水,问最终,可以从叶子节点中流出多少水

在了解题意之后, 基本就可以想到是赤裸裸的树形dp
先来考虑需要注意的问题
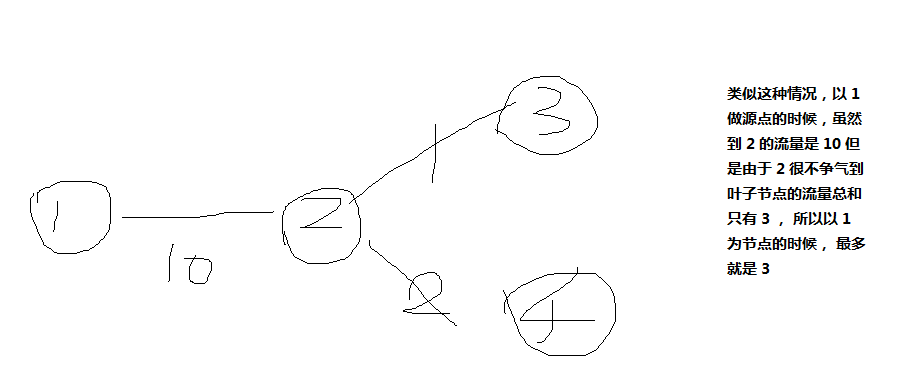
在弄清以上的概念之后,就可开始设计算法了
众所周知, 树形dp 是没法往上走的, 所以我们需要维护两个数组,一个down一个up (down 表示 该节点以dfs序往下走的最大叶子节点流量的和, up则表示往父节点的),最后只需要遍历每个节点的down和up 的和就可以了
转移方程(u 表示父节点 v 表示子节点 w 为当前边的权值)
Down[u] += min(w[i], down[v])
需要考虑,子节点够不够争气, 能不能承受那么w[i]多的流量
第一遍dfs 处理完down
Up[v] = min(w[i], up[u] + down[u] – min(w[i], down[v]));
需要考虑能不能往父节点流w[i]多的流量
up[u] + down[u] – min(w[i], down[v]) 这个是计算如果父节点不往当前子节点流, 最多可以流向叶子节点多少。
然后需要特殊处理子节点是叶子节点的情况, 就不要取最小值了, 一定可以流w[i] 那么多
第二遍dfs 处理up
Talk is cheap, I will show you my code
#include <stdio.h> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> using namespace std; const int N = 2e5+10; int head[N] = {0}, tot = 0, to[N*2], nt[N*2]; long long w[N*2]; void add(int a, int b, int c) { ++tot;to[tot]=b;nt[tot]=head[a];head[a]=tot;w[tot]=c; ++tot;to[tot]=a;nt[tot]=head[b];head[b]=tot;w[tot]=c; } long long res = 0; long long up[N], down[N]; void dfs1(int now, int pre) { for(int i = head[now]; i; i = nt[i]) { if(to[i]==pre) continue; dfs1(to[i], now); if(down[to[i]]==0) down[now] += w[i]; // 叶子节点情况 else down[now] += min(down[to[i]], w[i]); } } void dfs2(int now, int pre) { for(int i = head[now]; i; i = nt[i]) { if(to[i]==pre) continue; // 叶子节点情况 if(down[to[i]]==0) up[to[i]] = min(w[i], up[now] + down[now] - w[i]); else up[to[i]] = min(w[i], up[now] + down[now] - min(w[i], down[to[i]])); dfs2(to[i], now); } } int main() { int T, n, a, b, c; scanf("%d", &T); while(T--) { scanf("%d", &n); tot = 0; // 初始化 没有就是RE memset(head, 0, sizeof(head)); memset(up, 0, sizeof(up)); memset(down, 0, sizeof(down)); for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) { scanf("%d %d %d", &a, &b, &c); add(a, b, c); //自写邻接表建图 } dfs1(1, 0); dfs2(1, 0); res = 0; //遍历取个最大值 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) res = max(res, up[i] + down[i]); printf("%lld\n", res); } }





