Android百分比支持布局库的使用和源码分析
Android-percent-support这个库
描述下这个support-lib。
这个库提供了:
-
两种布局供大家使用:
PercentRelativeLayout、PercentFrameLayout,通过名字就可以看出,这是继承自FrameLayout和RelativeLayout两个容器类; -
支持的属性有:
layout_widthPercent、layout_heightPercent、
layout_marginPercent、layout_marginLeftPercent、
layout_marginTopPercent、layout_marginRightPercent、
layout_marginBottomPercent、layout_marginStartPercent、layout_marginEndPercent。
可以看到支持宽高,以及margin。
也就是说,大家只要在开发过程中使用PercentRelativeLayout、PercentFrameLayout替换FrameLayout、RelativeLayout即可。
过没有LinearLayout,有人会说LinearLayout有weight属性呀。但是,weight属性只能支持一个方向,但可以去自定义一个PercentLinearLayout。
使用
关于使用,其实及其简单,并且github上也有例子,android-percent-support-lib-sample
build.gradle添加:
compile 'com.android.support:percent:22.2.0'
(一)PercentFrameLayout
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.percent.PercentFrameLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/activity_main"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.loaderman.percentsupportdemo.MainActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#ff0000"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="高10%"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
app:layout_heightPercent="10%"
app:layout_widthPercent="10%"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#00ff00"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="高20%"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
app:layout_heightPercent="20%"
app:layout_marginLeftPercent="10%"
app:layout_marginTopPercent="10%"
app:layout_widthPercent="20%"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#0000ff"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="高30%"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
app:layout_heightPercent="30%"
app:layout_marginLeftPercent="30%"
app:layout_marginTopPercent="30%"
app:layout_widthPercent="30%"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#3f5500"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="高40%"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
app:layout_heightPercent="40%"
app:layout_marginLeftPercent="60%"
app:layout_marginTopPercent="60%"
app:layout_widthPercent="40%"/>
</android.support.percent.PercentFrameLayout>
效果图:
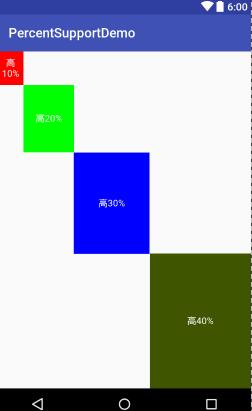
(二) PercentRelativeLayout
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.percent.PercentRelativeLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/activity_main"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.loaderman.percentsupportdemo.MainActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#ff0000"
android:gravity="center"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:text="高10%"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
app:layout_heightPercent="10%"
app:layout_widthPercent="10%"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#00ff00"
android:gravity="center"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:text="高20%"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
app:layout_heightPercent="20%"
app:layout_marginLeftPercent="10%"
app:layout_marginTopPercent="10%"
app:layout_widthPercent="20%"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#0000ff"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="高30%"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
app:layout_heightPercent="30%"
app:layout_marginLeftPercent="30%"
app:layout_marginTopPercent="30%"
app:layout_widthPercent="30%"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#3f5500"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="高40%"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
app:layout_heightPercent="40%"
app:layout_marginLeftPercent="60%"
app:layout_marginTopPercent="60%"
app:layout_widthPercent="40%"/>
</android.support.percent.PercentRelativeLayout>
效果图:

(三)、实现PercentLinearlayout
package com.loaderman.percentsupportdemo;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.res.TypedArray;
import android.support.percent.PercentLayoutHelper;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
/**
* Created by JCF on 2017/2/27.
*/
public class PercentLinearLayout extends LinearLayout {
private PercentLayoutHelper mPercentLayoutHelper;
public PercentLinearLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
mPercentLayoutHelper = new PercentLayoutHelper(this);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
mPercentLayoutHelper.adjustChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
if (mPercentLayoutHelper.handleMeasuredStateTooSmall()) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
super.onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
mPercentLayoutHelper.restoreOriginalParams();
}
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new LayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
public static class LayoutParams extends LinearLayout.LayoutParams
implements PercentLayoutHelper.PercentLayoutParams {
private PercentLayoutHelper.PercentLayoutInfo mPercentLayoutInfo;
public LayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(c, attrs);
mPercentLayoutInfo = PercentLayoutHelper.getPercentLayoutInfo(c, attrs);
}
@Override
public PercentLayoutHelper.PercentLayoutInfo getPercentLayoutInfo() {
return mPercentLayoutInfo;
}
@Override
protected void setBaseAttributes(TypedArray a, int widthAttr, int heightAttr) {
PercentLayoutHelper.fetchWidthAndHeight(this, a, widthAttr, heightAttr);
}
public LayoutParams(int width, int height) {
super(width, height);
}
public LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams source) {
super(source);
}
public LayoutParams(MarginLayoutParams source) {
super(source);
}
}
}
布局测试:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<com.loaderman.percentsupportdemo.PercentLinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:background="#ff44aacc"
android:text="width:60%,height:5%"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
app:layout_heightPercent="5%"
app:layout_marginBottomPercent="5%"
app:layout_widthPercent="60%"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:background="#ff4400cc"
android:gravity="center"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:text="width:70%,height:10%"
app:layout_heightPercent="10%"
app:layout_marginBottomPercent="5%"
app:layout_widthPercent="70%"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:background="#ff44aacc"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="width:80%,height:15%"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
app:layout_heightPercent="15%"
app:layout_marginBottomPercent="5%"
app:layout_widthPercent="80%"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:background="#ff4400cc"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="width:90%,height:5%"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
app:layout_heightPercent="20%"
app:layout_marginBottomPercent="10%"
app:layout_widthPercent="90%"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:background="#ff44aacc"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="width:100%,height:25%"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
app:layout_heightPercent="25%"
app:layout_marginBottomPercent="5%"
/>
</com.loaderman.percentsupportdemo.PercentLinearLayout>
效果图:

源码分析
其实细想一下,Google只是对我们原本熟悉的RelativeLayout和FrameLayout进行的功能的扩展,使其支持了percent相关的属性。
那么,我们考虑下,如果是我们添加这种扩展,我们会怎么做:
- 通过LayoutParams获取child设置的percent相关属性的值
- onMeasure的时候,将child的width,height的值,通过获取的自定义属性的值进行计算(eg:容器的宽 * fraction ),计算后传入给child.measure(w,h);
ok,有了上面的猜想,我们直接看PercentFrameLayout的源码。
public class PercentFrameLayout extends FrameLayout {
private final PercentLayoutHelper mHelper = new PercentLayoutHelper(this);
//省略了,两个构造方法
public PercentFrameLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new LayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
mHelper.adjustChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
if (mHelper.handleMeasuredStateTooSmall()) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
super.onLayout(changed, left, top, right, bottom);
mHelper.restoreOriginalParams();
}
public static class LayoutParams extends FrameLayout.LayoutParams
implements PercentLayoutHelper.PercentLayoutParams {
private PercentLayoutHelper.PercentLayoutInfo mPercentLayoutInfo;
public LayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(c, attrs);
mPercentLayoutInfo = PercentLayoutHelper.getPercentLayoutInfo(c, attrs);
}
//省略了一些代码...
@Override
public PercentLayoutHelper.PercentLayoutInfo getPercentLayoutInfo() {
return mPercentLayoutInfo;
}
@Override
protected void setBaseAttributes(TypedArray a, int widthAttr, int heightAttr) {
PercentLayoutHelper.fetchWidthAndHeight(this, a, widthAttr, heightAttr);
}
}
}
代码是相当的短,可以看到PercentFrameLayout里面首先重写了generateLayoutParams方法,当然了,由于支持了一些新的layout_属性,那么肯定需要定义对应的LayoutParams。
(一)percent相关属性的获取
可以看到PercentFrameLayout.LayoutParams在原有的FrameLayout.LayoutParams基础上,实现了PercentLayoutHelper.PercentLayoutParams接口。
这个接口很简单,只有一个方法:
public interface PercentLayoutParams {
PercentLayoutInfo getPercentLayoutInfo();
}
而,这个方法的实现呢,也只有一行:return mPercentLayoutInfo;,那么这个mPercentLayoutInfo在哪完成赋值呢?
看PercentFrameLayout.LayoutParams的构造方法:
public LayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(c, attrs);
mPercentLayoutInfo = PercentLayoutHelper.getPercentLayoutInfo(c, attrs);
}
可以看到,将attrs传入给getPercentLayoutInfo方法,那么不用说,这个方法的内部,肯定是获取自定义属性的值,然后将其封装到PercentLayoutInfo对象中,最后返回。代码如下:
public static PercentLayoutInfo getPercentLayoutInfo(Context context,
AttributeSet attrs) {
PercentLayoutInfo info = null;
TypedArray array = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.PercentLayout_Layout);
float value = array.getFraction(R.styleable.PercentLayout_Layout_layout_widthPercent, 1, 1,
-1f);
if (value != -1f) {
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
Log.v(TAG, "percent width: " + value);
}
info = info != null ? info : new PercentLayoutInfo();
info.widthPercent = value;
}
value = array.getFraction(R.styleable.PercentLayout_Layout_layout_heightPercent, 1, 1, -1f);
if (value != -1f) {
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
Log.v(TAG, "percent height: " + value);
}
info = info != null ? info : new PercentLayoutInfo();
info.heightPercent = value;
}
value = array.getFraction(R.styleable.PercentLayout_Layout_layout_marginPercent, 1, 1, -1f);
if (value != -1f) {
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
Log.v(TAG, "percent margin: " + value);
}
info = info != null ? info : new PercentLayoutInfo();
info.leftMarginPercent = value;
info.topMarginPercent = value;
info.rightMarginPercent = value;
info.bottomMarginPercent = value;
}
value = array.getFraction(R.styleable.PercentLayout_Layout_layout_marginLeftPercent, 1, 1,
-1f);
if (value != -1f) {
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
Log.v(TAG, "percent left margin: " + value);
}
info = info != null ? info : new PercentLayoutInfo();
info.leftMarginPercent = value;
}
value = array.getFraction(R.styleable.PercentLayout_Layout_layout_marginTopPercent, 1, 1,
-1f);
if (value != -1f) {
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
Log.v(TAG, "percent top margin: " + value);
}
info = info != null ? info : new PercentLayoutInfo();
info.topMarginPercent = value;
}
value = array.getFraction(R.styleable.PercentLayout_Layout_layout_marginRightPercent, 1, 1,
-1f);
if (value != -1f) {
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
Log.v(TAG, "percent right margin: " + value);
}
info = info != null ? info : new PercentLayoutInfo();
info.rightMarginPercent = value;
}
value = array.getFraction(R.styleable.PercentLayout_Layout_layout_marginBottomPercent, 1, 1,
-1f);
if (value != -1f) {
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
Log.v(TAG, "percent bottom margin: " + value);
}
info = info != null ? info : new PercentLayoutInfo();
info.bottomMarginPercent = value;
}
value = array.getFraction(R.styleable.PercentLayout_Layout_layout_marginStartPercent, 1, 1,
-1f);
if (value != -1f) {
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
Log.v(TAG, "percent start margin: " + value);
}
info = info != null ? info : new PercentLayoutInfo();
info.startMarginPercent = value;
}
value = array.getFraction(R.styleable.PercentLayout_Layout_layout_marginEndPercent, 1, 1,
-1f);
if (value != -1f) {
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
Log.v(TAG, "percent end margin: " + value);
}
info = info != null ? info : new PercentLayoutInfo();
info.endMarginPercent = value;
}
array.recycle();
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.DEBUG)) {
Log.d(TAG, "constructed: " + info);
}
return info;
}
是不是和我们平时的取值很类似,所有的值最终封装到PercentLayoutInfo对象中。
ok,到此我们的属性获取就介绍完成,有了这些属性,是不是onMeasure里面要进行使用呢?
(二) onMeasue中重新计算child的尺寸
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
mHelper.adjustChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
if (mHelper.handleMeasuredStateTooSmall()) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
可以看到onMeasure中的代码页很少,看来核心的代码都被封装在mHelper的方法中,我们直接看mHelper.adjustChildren方法。
/**
* Iterates over children and changes their width and height to one calculated from percentage
* values.
* @param widthMeasureSpec Width MeasureSpec of the parent ViewGroup.
* @param heightMeasureSpec Height MeasureSpec of the parent ViewGroup.
*/
public void adjustChildren(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//...
int widthHint = View.MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightHint = View.MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
for (int i = 0, N = mHost.getChildCount(); i < N; i++) {
View view = mHost.getChildAt(i);
ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = view.getLayoutParams();
if (params instanceof PercentLayoutParams) {
PercentLayoutInfo info =
((PercentLayoutParams) params).getPercentLayoutInfo();
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.DEBUG)) {
Log.d(TAG, "using " + info);
}
if (info != null) {
if (params instanceof ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams) {
info.fillMarginLayoutParams((ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams) params,
widthHint, heightHint);
} else {
info.fillLayoutParams(params, widthHint, heightHint);
}
}
}
}
}
通过注释也能看出,此方法中遍历所有的孩子,通过百分比的属性重新设置其宽度和高度。
首先在widthHint、heightHint保存容器的宽、高,然后遍历所有的孩子,判断其LayoutParams是否是PercentLayoutParams类型,如果是,通过params.getPercentLayoutInfo拿出info对象。
是否还记得,上面的分析中,PercentLayoutInfo保存了percent相关属性的值。
如果info不为null,则判断是否需要处理margin;我们直接看fillLayoutParams方法(处理margin也是类似的)。
/**
* Fills {@code ViewGroup.LayoutParams} dimensions based on percentage values.
*/
public void fillLayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams params, int widthHint,
int heightHint) {
// Preserve the original layout params, so we can restore them after the measure step.
mPreservedParams.width = params.width;
mPreservedParams.height = params.height;
if (widthPercent >= 0) {
params.width = (int) (widthHint * widthPercent);
}
if (heightPercent >= 0) {
params.height = (int) (heightHint * heightPercent);
}
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.DEBUG)) {
Log.d(TAG, "after fillLayoutParams: (" + params.width + ", " + params.height + ")");
}
}
首先保存原本的width和height,然后重置params的width和height为(int) (widthHint * widthPercent)和(int) (heightHint * heightPercent);。
到此,其实我们的百分比转换就结束了,理论上就已经实现了对于百分比的支持,不过Google还考虑了一些细节。
我们回到onMeasure方法:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
mHelper.adjustChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
if (mHelper.handleMeasuredStateTooSmall()) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
下面还有个mHelper.handleMeasuredStateTooSmall的判断,也就是说,如果你设置的百分比,最终计算出来的MeasuredSize过小的话,会进行一些操作。代码如下:
public boolean handleMeasuredStateTooSmall() {
boolean needsSecondMeasure = false;
for (int i = 0, N = mHost.getChildCount(); i < N; i++) {
View view = mHost.getChildAt(i);
ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = view.getLayoutParams();
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.DEBUG)) {
Log.d(TAG, "should handle measured state too small " + view + " " + params);
}
if (params instanceof PercentLayoutParams) {
PercentLayoutInfo info =
((PercentLayoutParams) params).getPercentLayoutInfo();
if (info != null) {
if (shouldHandleMeasuredWidthTooSmall(view, info)) {
needsSecondMeasure = true;
params.width = ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT;
}
if (shouldHandleMeasuredHeightTooSmall(view, info)) {
needsSecondMeasure = true;
params.height = ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT;
}
}
}
}
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.DEBUG)) {
Log.d(TAG, "should trigger second measure pass: " + needsSecondMeasure);
}
return needsSecondMeasure;
}
首先遍历所有的孩子,拿出孩子的layoutparams,如果是PercentLayoutParams实例,则取出info。如果info不为null,调用shouldHandleMeasuredWidthTooSmall判断:
private static boolean shouldHandleMeasuredWidthTooSmall(View view, PercentLayoutInfo info) {
int state = ViewCompat.getMeasuredWidthAndState(view) & ViewCompat.MEASURED_STATE_MASK;
return state == ViewCompat.MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL && info.widthPercent >= 0 &&
info.mPreservedParams.width == ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT;
}
这里就是判断,如果你设置的measuredWidth或者measureHeight过小的话,并且你在布局文件中layout_w/h 设置的是WRAP_CONTENT的话,将params.width / height= ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT,然后重新测量。
哈,onMeasure终于结束了~~~现在我觉得应该代码结束了吧,尺寸都设置好了,还需要干嘛么,but,你会发现onLayout也重写了,我们又不改变layout规则,在onLayout里面干什么毛线:
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
super.onLayout(changed, left, top, right, bottom);
mHelper.restoreOriginalParams();
}
继续看mHelper.restoreOriginalParams
/**
* Iterates over children and restores their original dimensions that were changed for
* percentage values. Calling this method only makes sense if you previously called
* {@link PercentLayoutHelper#adjustChildren(int, int)}.
*/
public void restoreOriginalParams() {
for (int i = 0, N = mHost.getChildCount(); i < N; i++) {
View view = mHost.getChildAt(i);
ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = view.getLayoutParams();
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.DEBUG)) {
Log.d(TAG, "should restore " + view + " " + params);
}
if (params instanceof PercentLayoutParams) {
PercentLayoutInfo info =
((PercentLayoutParams) params).getPercentLayoutInfo();
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.DEBUG)) {
Log.d(TAG, "using " + info);
}
if (info != null) {
if (params instanceof ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams) {
info.restoreMarginLayoutParams((ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams) params);
} else {
info.restoreLayoutParams(params);
}
}
}
}
}
噗,原来是重新恢复原本的尺寸值,也就是说onMeasure里面的对值进行了改变,测量完成后。在这个地方,将值又恢复成如果布局文件中的值,上面写的都是0。恢复很简单:
public void restoreLayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
params.width = mPreservedParams.width;
params.height = mPreservedParams.height;
}
你应该没有忘在哪存的把~忘了的话,麻烦Ctrl+F ‘mPreservedParams.width’ 。
也就是说,你去打印上面写法,布局文件中view的v.getLayoutParams().width,这个值应该是0。
这里感觉略微不爽~这个0没撒用处呀,还不如不重置~~
好了,到此就分析完了,其实主要就几个步骤:
- LayoutParams中属性的获取
- onMeasure中,改变params.width为百分比计算结果,测量
- 如果测量值过小且设置的w/h是wrap_content,重新测量
- onLayout中,重置params.w/h为布局文件中编写的值
可以看到,有了RelativeLayout、FrameLayout的扩展,竟然没有LinearLayout几个意思。好在,我们的核心代码都由PercentLayoutHelper封装了,自己扩展下LinearLayout也不复杂。
本文学习来源:http://blog.csdn.net/lmj623565791/article/details/46695347


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号