依赖注入框架之androidannotations
主页: http://androidannotations.org/
用途:
1. 使用依赖注入Views,extras,System
Service,resources
2. 简化线程模型
3. 事件绑定
4. REST Client
配置:
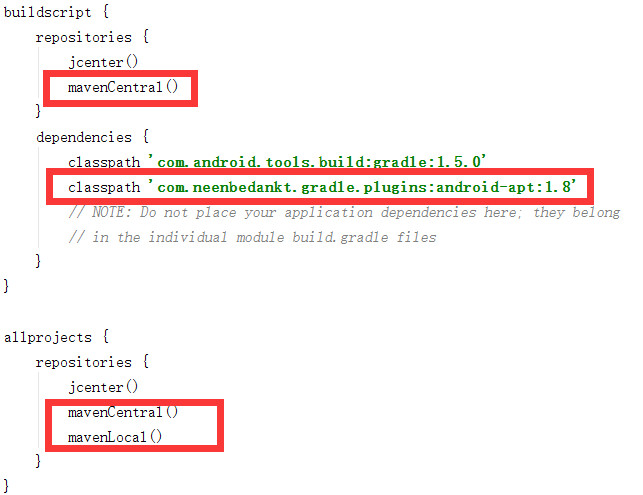
1. 在**project/build.gradle**文件中按下图所示添加代码:
mavenCentral()
classpath
'com.neenbedankt.gradle.plugins:android-apt:1.8'
mavenCentral()
mavenLocal()
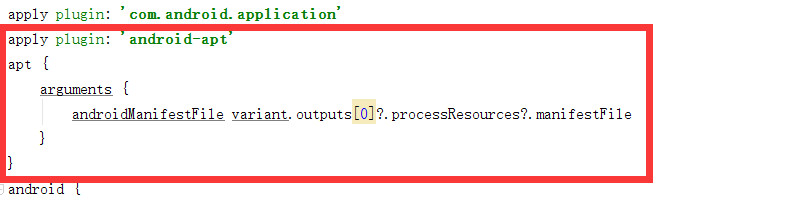
2. 在**app/build.gradle**文件中按下图所示添加代码:
apply plugin:
'android-apt'
apt
{
arguments
{
androidManifestFile
variant.outputs[0]?.processResources?.manifestFile
}
}
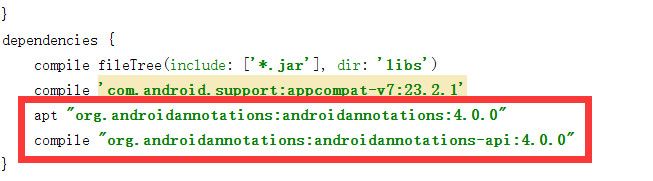
apt
"org.androidannotations:androidannotations:4.0.0"
compile
"org.androidannotations:androidannotations-api:4.0.0"
* 注意事项:
*
Manifest中注册的activity要在原类名后追加下划线”_”
* 使用注解的控件和方法不能使用private修饰符
*
大型项目并不适用
示例代码:
注意导包导入的是:
import org.androidannotations.annotations......
@Fullscreen //全屏
@WindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE) //Activity没有标题
@EActivity(R.layout.my_activity) //布局文件在这里声明,不用在setContentView
public class MyActivity extends Activity {
@ViewById //初始化控件,不需要自己实例化
EditText myEditText;
@ViewById(R.id.myTextView) //提供id来生成控件,如果不指定ID,默认以控件名进行查找,如上面的myEditText
TextView textView;
@StringRes(R.string.app_name) //字符串资源
String appName;
@ColorRes(R.color.colorAccent) //颜色资源
int androidColor;
@BooleanRes
boolean someBoolean;
@SystemService //系统服务
NotificationManager notificationManager;
@Click //事件控制,可以以按钮的id作为方法名,同时支持的事件还有onLongClick,onTextChange等
void myButtonClicked() {
String name = myEditText.getText().toString();
setProgressBarIndeterminateVisibility(true);
someBackgroundWork(name, 5);
}
@ViewById(R.id.textView)
TextView tv;
@Click(R.id.button)
void submit() {
tv.setText(appName);
someBackgroundWork();
}
@Background//开启新线程后台运行,注意不要引用UI控件,而且返回值类型一定是void
void someBackgroundWork() {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
updateUi(appName, androidColor);
}
@UiThread//UI线程
void updateUi(String message, int color) {
tv.setText(message);
tv.setTextColor(color);
}
@LongClick
void startExtraActivity() {
Intent intent = new Intent(this, ActivityWithExtra_.class);
intent.putExtra(ActivityWithExtra.MY_DATE_EXTRA, new Date());
intent.putExtra(ActivityWithExtra.MY_STRING_EXTRA, "hello !");
intent.putExtra(ActivityWithExtra.MY_INT_EXTRA, 42);
startActivity(intent);
}
@Touch
void myTextView(MotionEvent event) {
Log.d("MyActivity", "myTextView was touched!");
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号