Python中的Matplotlib绘图
Matplotlib 是一个 Python 的 2D绘图库,通过 Matplotlib,开发者可以仅需要几行代码,便可以生成绘图,直方图,功率谱,条形图,错误图,散点图等。
-
用于创建出版质量图表的绘图工具库
-
目的是为Python构建一个Matlab式的绘图接口
-
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt -
pyploy模块包含了常用的matplotlib API函数
figure
-
Matplotlib的图像均位于figure对象中
-
创建figure:
fig = plt.figure()
# 引入matplotlib包
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 创建figure对象
fig = plt.figure()
print(fig)
运行结果:
Figure(640x480)
设置图片大小
#设置图片大小
plt.figure(figsize=(20,8),dpi=80)
subplot
fig.add_subplot(a, b, c)
-
a,b 表示将fig分割成 a*b 的区域
-
c 表示当前选中要操作的区域,
-
注意:从1开始编号(不是从0开始)
-
plot 绘图的区域是最后一次指定subplot的位置 (jupyter notebook里不能正确显示)
# 引入matplotlib包
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# 创建figure对象
fig = plt.figure()
# 指定切分区域的位置
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 1)
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 2)
ax3 = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 3)
ax4 = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 4)
# 在subplot上作图
random_arr = np.random.randn(100)
# print random_arr
# 默认是在最后一次使用subplot的位置上作图,但是在jupyter notebook 里可能显示有误
plt.plot(random_arr)
# 可以指定在某个或多个subplot位置上作图
# ax1 = fig.plot(random_arr)
# ax2 = fig.plot(random_arr)
# ax3 = fig.plot(random_arr)
# 显示绘图结果
plt.show()
效果:

直方图:hist
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
plt.hist(np.random.randn(100), bins=10, color='b', alpha=0.3)
plt.show()
效果:
散点图:scatter
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# 绘制散点图
x = np.arange(50)
y = x + 5 * np.random.rand(50)
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.show()
效果:
柱状图:bar
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# 柱状图
x = np.arange(5)
y1, y2 = np.random.randint(1, 25, size=(2, 5))
width = 0.25
ax = plt.subplot(1,1,1)
ax.bar(x, y1, width, color='r')
ax.bar(x+width, y2, width, color='g')
ax.set_xticks(x+width)
ax.set_xticklabels(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'])
plt.show()
效果:
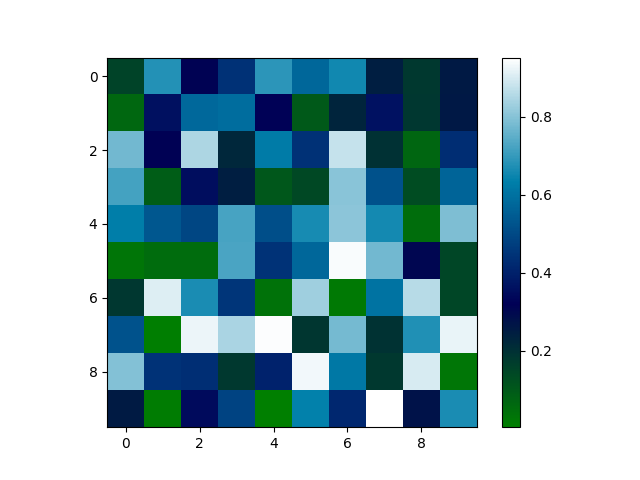
矩阵绘图:plt.imshow()
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# 矩阵绘图
m = np.random.rand(10,10)
print(m)
plt.imshow(m, interpolation='nearest', cmap=plt.cm.ocean)
plt.colorbar()
plt.show()
效果:
[[0.15380616 0.67762688 0.31357941 0.44390774 0.68979664 0.57513838
0.65629381 0.24503583 0.17923525 0.2571893 ]
[0.06369402 0.36195036 0.58082668 0.58933892 0.32347774 0.09951149
0.23330702 0.36485022 0.1841848 0.25991682]
[0.7744867 0.31752527 0.84919452 0.22417739 0.62335052 0.44209677
0.88063286 0.19690092 0.06757865 0.43073916]
[0.72169407 0.09201384 0.35502444 0.24738157 0.10429607 0.14403884
0.80343884 0.52208509 0.13111979 0.56812907]
[0.63104273 0.53591166 0.49502278 0.72547993 0.51190937 0.66443688
0.81036998 0.66157919 0.05206029 0.789589 ]
[0.0310165 0.05378353 0.05515481 0.72832536 0.44728534 0.5773849
0.94230944 0.7759232 0.30541425 0.14620932]
[0.18399998 0.90858104 0.6671387 0.45428731 0.03820414 0.82961184
0.02153911 0.60371894 0.86004263 0.14734495]
[0.52464806 0.01133297 0.92722803 0.84628634 0.94730856 0.18697352
0.78097648 0.19477215 0.67503973 0.92493486]
[0.79691249 0.44451484 0.43481649 0.18034901 0.40381674 0.93531157
0.61592443 0.18013501 0.90300771 0.02653334]
[0.25387343 0.01286532 0.34527955 0.48654444 0.00421852 0.63679139
0.41644148 0.95119758 0.27467997 0.66819625]]
plt.subplots()
-
同时返回新创建的
figure和subplot对象数组 -
生成2行2列subplot:
fig, subplot_arr = plt.subplots(2,2) -
在jupyter里可以正常显示,推荐使用这种方式创建多个图表
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
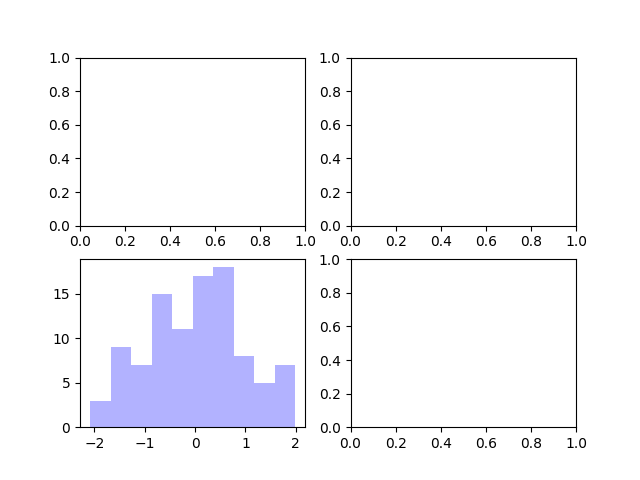
fig, subplot_arr = plt.subplots(2, 2)
# bins 为显示个数,一般小于等于数值个数
subplot_arr[1, 0].hist(np.random.randn(100), bins=10, color='b', alpha=0.3)
plt.savefig("./test.png")
plt.show()
效果:
颜色、标记、线型
- ax.plot(x, y, ‘r--’)
等价于ax.plot(x, y, linestyle=‘--’, color=‘r’)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
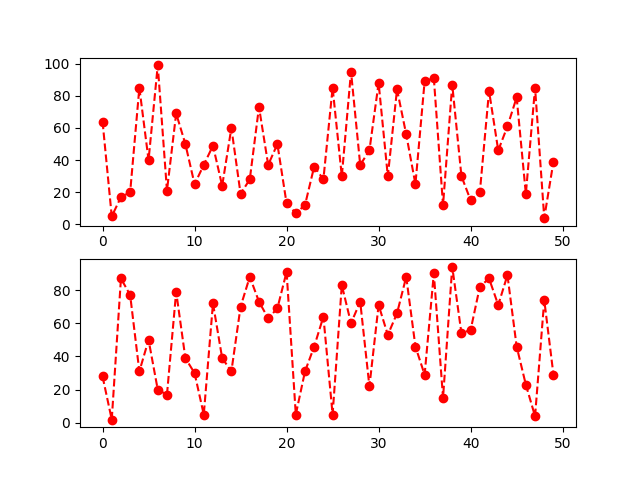
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2)
axes[0].plot(np.random.randint(0, 100, 50), 'ro--')
# 等价
axes[1].plot(np.random.randint(0, 100, 50), color='r', linestyle='dashed', marker='o')
效果:
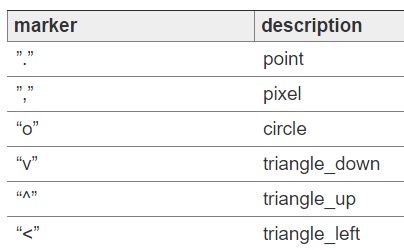
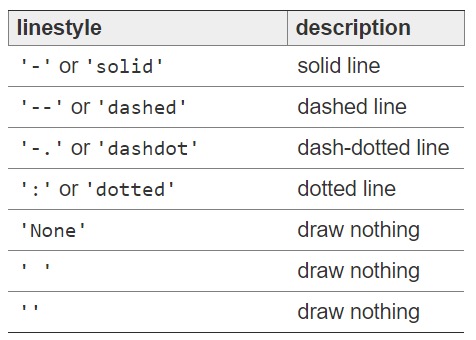
常用的颜色、标记、线型

刻度、标签、图例
-
设置刻度范围
plt.xlim(), plt.ylim()
ax.set_xlim(), ax.set_ylim()
-
设置显示的刻度
plt.xticks(), plt.yticks()
ax.set_xticks(), ax.set_yticks()
-
设置刻度标签
ax.set_xticklabels(), ax.set_yticklabels()
-
设置坐标轴标签
ax.set_xlabel(), ax.set_ylabel()
-
设置标题
ax.set_title()
-
图例
ax.plot(label=‘legend’)
ax.legend(), plt.legend()
loc=‘best’:自动选择放置图例最佳位置
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1)
ax.plot(np.random.randn(1000).cumsum(), label='line0')
# 设置刻度
#plt.xlim([0,500])
ax.set_xlim([0, 800])
# 设置显示的刻度
#plt.xticks([0,500])
ax.set_xticks(range(0,500,100))
# 设置刻度标签
ax.set_yticklabels(['Jan', 'Feb', 'Mar'])
# 设置坐标轴标签
ax.set_xlabel('Number')
ax.set_ylabel('Month')
# 设置标题
ax.set_title('Example')
# 图例
ax.plot(np.random.randn(1000).cumsum(), label='line1')
ax.plot(np.random.randn(1000).cumsum(), label='line2')
ax.legend()
ax.legend(loc='best')
#plt.legend()
plt。show()
效果:

设置中文显示
为什么无法显示中文: matplotlib默认不支持中文字符,因为默认的英文字体无法显示汉字
查看linux/mac下面支持的字体:
fc-list 查看支持的字体
fc-list :lang=zh 查看支持的中文(冒号前面有空格)
如何修改matplotlib的默认字体?
通过matplotlib.rc可以修改,具体方法参见源码(windows/linux)
通过matplotlib 下的font_manager可以解决(windows/linux/mac)
# coding=utf-8
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import random
from matplotlib import font_manager
# windws和linux设置字体的放
# font = {'family' : 'MicroSoft YaHei',
# 'weight': 'bold',
# 'size': 'larger'}
# matplotlib.rc("font",**font)
# matplotlib.rc("font",family='MicroSoft YaHei',weight="bold")
# 另外一种设置字体的方式
my_font = font_manager.FontProperties(fname="/System/Library/Fonts/PingFang.ttc")
x = range(0, 120)
y = [random.randint(20, 35) for i in range(120)]
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 8), dpi=80)
plt.plot(x, y)
# 调整x轴的刻度
_xtick_labels = ["10点{}分".format(i) for i in range(60)]
_xtick_labels += ["11点{}分".format(i) for i in range(60)]
# 取步长,数字和字符串一一对应,数据的长度一样
plt.xticks(list(x)[::3], _xtick_labels[::3], rotation=45, fontproperties=my_font) # rotaion旋转的度数
# 添加描述信息
plt.xlabel("时间", fontproperties=my_font)
plt.ylabel("温度 单位(℃)", fontproperties=my_font)
plt.title("10点到12点每分钟的气温变化情况", fontproperties=my_font)
plt.show()
图片保存
#在plt.show()前面放置即可 plt.savefig("./picture.png")
对比常用统计图总结:
折线图:以折线的上升或下降来表示统计数量的增减变化的统计图
特点:能够显示数据的变化趋势,反映事物的变化情况。(变化)
直方图:由一系列高度不等的纵向条纹或线段表示数据分布的情况。一般用横轴表示数据范围,纵轴表示分布情况。
特点:绘制连续性的数据,展示一组或者多组数据的分布状况(统计)
条形图:排列在工作表的列或行中的数据可以绘制到条形图中。
特点:绘制连离散的数据,能够一眼看出各个数据的大小,比较数据之间的差别。(统计)
散点图:用两组数据构成多个坐标点,考察坐标点的分布,判断两变量间是否存在某种关联或总结坐标点的分布模式。
特点:判断变量之间是否存在数量关联趋势,展示离群点(分布规律)
示例demo
# coding=utf-8 from matplotlib import pyplot as plt from matplotlib import font_manager my_font = font_manager.FontProperties(fname="/System/Library/Fonts/PingFang.ttc") y_1 = [1, 0, 1, 1, 2, 4, 3, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 5, 4, 3, 3, 1, 1, 1] y_2 = [1, 0, 3, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1] x = range(11, 31) # 设置图形大小 plt.figure(figsize=(20, 8), dpi=80) plt.plot(x, y_1, label="自己", color="#F08080") plt.plot(x, y_2, label="同桌", color="#DB7093", linestyle="--") # 设置x轴刻度 _xtick_labels = ["{}岁".format(i) for i in x] plt.xticks(x, _xtick_labels, fontproperties=my_font) # plt.yticks(range(0,9)) # 绘制网格 plt.grid(alpha=0.4, linestyle=':') # 添加图例 plt.legend(prop=my_font, loc="upper left") # 保存 plt.savefig("./save.png") #显示 plt.show()
效果:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号