1、定义一个结构体
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int ElemType; // 自定义链表的数据元素为整数。
typedef struct DNode
{
ElemType data; // 存放结点的数据元素。
struct DNode *prior,*next; // 前驱和后继结点的指针。
}DNode,*LinkList;
int main()
{
return 0;
}
2、初始化链表
// 初始化链表LL,返回值:失败返回NULL,成功返回头结点的地址。
DNode *InitList1();
int main()
{
LinkList LL=NULL; // 声明链表指针变量。
LL=InitList1(); // 初始化链表。
printf("LL=%p\n",LL);
return 0;
}
// 初始化链表LL,返回值:失败返回NULL,成功返回头结点的地址。
DNode *InitList1()
{
DNode *head = (DNode *)malloc(sizeof(DNode)); // 分配头结点。
if (head == NULL) return NULL; // 内存不足,返回失败。
head->prior=head->next=NULL; // 前驱后继结点都置为空。
return head;
}
3、创建一个数据元素。
int main()
{
LinkList LL=NULL; // 声明链表指针变量。
LL=InitList1(); // 初始化链表。
printf("LL=%p\n",LL);
ElemType ee; // 创建一个数据元素。
return 0;
}
4、插入元素
int InsertList(LinkList LL, unsigned int ii, ElemType *ee);
int main()
{
LinkList LL=NULL; // 声明链表指针变量。
LL=InitList1(); // 初始化链表。
printf("LL=%p\n",LL);
ElemType ee; // 创建一个数据元素。
printf("在表中插入元素(1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9、10)。\n");
ee=1; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=2; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=3; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=4; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=5; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=6; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=7; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=8; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=9; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=10; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
return 0;
}
// 在链表LL的第ii个位置插入元素ee,返回值:0-失败;1-成功。
int InsertList(LinkList LL, unsigned int ii, ElemType *ee)
{
if ( (LL == NULL) || (ee == NULL) ) { printf("链表LL或元素ee不存在。\n"); return 0; } // 判断表和元素是否存在。
// 判断插入位置是否合法
if (ii < 1) { printf("插入位置(%d)不合法,应该在大于0。\n",ii); return 0; }
// 要在位序ii插入结点,必须找到ii-1结点。
DNode *pp=LL; // 指针pp指向头结点,逐步往后移动,如果为空,表示后面没结点了。
int kk=0; // kk指向的是第几个结点,从头结点0开始,pp每向后移动一次,kk就加1。
while ( (pp != NULL) && (kk < ii-1) )
{
pp=pp->next; kk++;
// printf("pp=%p,kk=%d\n",pp,kk);
}
if ( pp==NULL ) { printf("位置(%d)不合法,超过了表长。\n",ii); return 0; }
DNode *tmp = (DNode *)malloc(sizeof(DNode)); // 分配一个结点。
if (tmp == NULL) return 0; // 内存不足,返回失败。
// 考虑数据元素为结构体的情况,这里采用了memcpy的方法而不是直接赋值。
memcpy(&tmp->data,ee,sizeof(ElemType));
// 处理前驱后续结点的指针。
tmp->next=pp->next;
tmp->prior=pp;
if (tmp->next != NULL) tmp->next->prior=tmp; // 特殊处理,如果是在尾部插入,tmp->next根本不存在。
pp->next=tmp;
return 1;
///////////////////////////////////////
// 以上代码可以用以下代码代替。
// DNode *pp=LocateNode(LL,ii-1);
// return InsertNextNode(pp,ee);
///////////////////////////////////////
}

5、打印表中全部的元素
void PrintList(LinkList LL);
int main()
{
LinkList LL=NULL; // 声明链表指针变量。
LL=InitList1(); // 初始化链表。
printf("LL=%p\n",LL);
ElemType ee; // 创建一个数据元素。
printf("在表中插入元素(1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9、10)。\n");
ee=1; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=2; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=3; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=4; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=5; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=6; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=7; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=8; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=9; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=10; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
PrintList(LL);
return 0;
}
// 打印链表中全部的元素。
void PrintList(LinkList LL)
{
if (LL == NULL) { printf("链表LL不存在。\n"); return; } // 判断链表是否存在。
DNode *pp=LL->next; // 从第1个结点开始。
while (pp != NULL)
{
printf("%-3d", pp->data); // 如果元素ee为结构体,这行代码要修改。
pp=pp->next;
}
printf("\n");
/*
// 以下代码用于显示全部结点的地址和元素的值。
DNode *pp=LL; // 从第0个结点开始。
while (pp != NULL)
{
printf("pp=%p,prior=%p,next=%p,data=%-3d\n",pp,pp->prior,pp->next,pp->data);
pp=pp->next;
}
*/
}
6、尾部插入元素
int PushBack(LinkList LL, ElemType *ee);
int main()
{
LinkList LL=NULL; // 声明链表指针变量。
LL=InitList1(); // 初始化链表。
printf("LL=%p\n",LL);
ElemType ee; // 创建一个数据元素。
printf("在表中插入元素(1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9、10)。\n");
ee=1; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=2; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=3; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=4; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=5; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=6; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=7; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=8; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=9; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=10; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
PrintList(LL);
printf("表尾插入元素(12)。\n");
ee=12; PushBack(LL, &ee);
PrintList(LL);
return 0;
}
// 在链表LL的尾部插入元素ee,返回值:0-失败;1-成功。
int PushBack(LinkList LL, ElemType *ee)
{
if ( (LL == NULL) || (ee == NULL) ) { printf("链表LL或元素ee不存在。\n"); return 0; } // 判断表和元素是否存在。
DNode *pp=LL; // 从头结点开始。
// 找到最后一个结点。
while (pp->next != NULL) pp=pp->next;
DNode *tmp = (DNode *)malloc(sizeof(DNode)); // 分配一个结点。
if (tmp == NULL) return 0; // 内存不足,返回失败。
// 考虑数据元素为结构体的情况,这里采用了memcpy的方法而不是直接赋值。
memcpy(&tmp->data,ee,sizeof(ElemType));
// 处理前驱后续结点的指针。
tmp->next=pp->next;
tmp->prior=pp;
if (tmp->next != NULL) tmp->next->prior=tmp; // 特殊处理,如果是在尾部插入,tmp->next根本不存在。
pp->next=tmp;
return 1;
}
7、删除某个节点
int DeleteNode(LinkList LL, unsigned int ii);
int main()
{
LinkList LL=NULL; // 声明链表指针变量。
LL=InitList1(); // 初始化链表。
printf("LL=%p\n",LL);
ElemType ee; // 创建一个数据元素。
printf("在表中插入元素(1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9、10)。\n");
ee=1; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=2; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=3; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=4; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=5; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=6; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=7; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=8; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=9; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=10; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
PrintList(LL);
printf("删除表中第7个结点。\n");
DeleteNode(LL,7); PrintList(LL);
return 0;
}
// 删除链表LL中的第ii个结点,返回值:0-位置ii不合法;1-成功。
int DeleteNode(LinkList LL, unsigned int ii)
{
if (LL == NULL) { printf("链表L不存在。\n"); return 0; } // 判断链表是否存在。
// 判断删除位置是否合法
if (ii < 1) { printf("删除位置(%d)不合法,应该在大于0。\n",ii); return 0; }
// 要删除位序ii结点,必须找到ii-1结点。
DNode *pp=LL; // 指针pp指向头结点,逐步往后移动,如果为空,表示后面没结点了。
int kk=0; // kk指向的是第几个结点,从头结点0开始,pp每向后移动一次,kk就加1。
while ( (pp != NULL) && (kk < ii-1) )
{
pp=pp->next; kk++;
}
// 注意,以下行的代码与视频中的不一样,视频中的是 if ( pp==NULL ),有bug。
if ( pp->next==NULL ) { printf("位置(%d)不合法,超过了表长。\n",ii); return 0; }
DNode *tmp=pp->next; // tmp为将要删除的结点。
// 处理前驱后续结点的指针。
pp->next=tmp->next;
if (tmp->next != NULL) tmp->next->prior=pp; // 特殊处理,如果tmp是尾结点,tmp->next根本不存在。
free(tmp);
return 1;
}
8、查询节点地址
DNode *LocateNode(LinkList LL, unsigned int ii);
int main()
{
LinkList LL=NULL; // 声明链表指针变量。
LL=InitList1(); // 初始化链表。
printf("LL=%p\n",LL);
ElemType ee; // 创建一个数据元素。
printf("在表中插入元素(1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9、10)。\n");
ee=1; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=2; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=3; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=4; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=5; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=6; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=7; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=8; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=9; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=10; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
PrintList(LL);
DNode *tmp;
if ( (tmp=LocateNode(LL,3)) != NULL)
printf("第3个结点的地址是=%p,ee=%d\n",tmp,tmp->data);
return 0;
}
/ 获取链表中第ii个结点,成功返回结点的地址,失败返回空。
// 注意,ii可以取值为0,表示头结点。
DNode *LocateNode(LinkList LL, unsigned int ii)
{
if ( LL == NULL ) { printf("链表LL不存在。\n"); return NULL; } // 判断表和元素是否存在。
DNode *pp=LL; // 指针pp指向头结点,逐步往后移动,如果为空,表示后面没结点了。
int kk=0; // kk指向的是第几个结点,从头结点0开始,pp每向后移动一次,kk就加1。
while ( (pp != NULL) && (kk < ii) )
{
pp=pp->next; kk++;
}
if ( pp==NULL ) { printf("位置(%d)不合法,超过了表长。\n",ii); return NULL; }
return pp;
}
9、查询元素地址
DNode *LocateElem(LinkList LL, ElemType *ee);
int main()
{
LinkList LL=NULL; // 声明链表指针变量。
LL=InitList1(); // 初始化链表。
printf("LL=%p\n",LL);
ElemType ee; // 创建一个数据元素。
printf("在表中插入元素(1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9、10)。\n");
ee=1; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=2; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=3; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=4; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=5; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=6; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=7; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=8; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=9; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=10; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
PrintList(LL);
DNode *tmp;
ee=8;
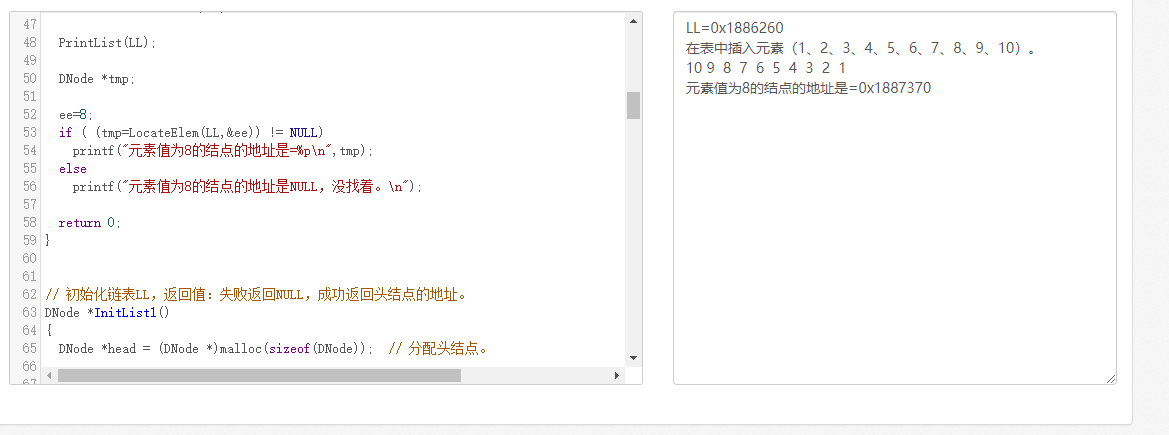
if ( (tmp=LocateElem(LL,&ee)) != NULL)
printf("元素值为8的结点的地址是=%p\n",tmp);
else
printf("元素值为8的结点的地址是NULL,没找着。\n");
return 0;
}
// 查找元素ee在链表LL中的结点地址,如果没找到返回NULL,否则返回结点的地址。
DNode *LocateElem(LinkList LL, ElemType *ee)
{
DNode *pp=LL->next; // 从第1个数据结点开始。
while (pp != NULL)
{
// 如果数据元素是结构体,以下代码要修改。
if (pp->data == *ee) return pp;
pp = pp->next;
}
return NULL;
}
10、在某个节点之后插入元素
int InsertNextNode(DNode *pp, ElemType *ee);
int main()
{
LinkList LL=NULL; // 声明链表指针变量。
LL=InitList1(); // 初始化链表。
printf("LL=%p\n",LL);
ElemType ee; // 创建一个数据元素。
printf("在表中插入元素(1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9、10)。\n");
ee=1; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=2; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=3; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=4; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=5; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=6; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=7; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=8; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=9; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=10; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
PrintList(LL);
DNode *tmp;
ee=8;
if ( (tmp=LocateElem(LL,&ee)) != NULL)
printf("元素值为8的结点的地址是=%p\n",tmp);
else
printf("元素值为8的结点的地址是NULL,没找着。\n");
printf("在结点%p之后插入66\n",tmp);
ee=66;
InsertNextNode(tmp,&ee); PrintList(LL);
return 0;
}
// 在指定结点pp之后插入元素ee,返回值:0-失败;1-成功。
int InsertNextNode(DNode *pp, ElemType *ee)
{
if (pp == NULL) { printf("结点pp不存在。\n"); return 0; }
DNode *tmp = (DNode *)malloc(sizeof(DNode));
if (tmp == NULL) return 0;
memcpy(&tmp->data,ee,sizeof(ElemType));
// 处理前驱后续结点的指针。
tmp->next=pp->next;
tmp->prior=pp;
if (tmp->next != NULL) tmp->next->prior=tmp; // 特殊处理,如果是在尾部插入,tmp->next根本不存在。
pp->next=tmp;
return 1;
}
11、在某个节点之前插入元素
int InsertPriorNode(DNode *pp, ElemType *ee);
int main()
{
LinkList LL=NULL; // 声明链表指针变量。
LL=InitList1(); // 初始化链表。
printf("LL=%p\n",LL);
ElemType ee; // 创建一个数据元素。
printf("在表中插入元素(1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9、10)。\n");
ee=1; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=2; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=3; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=4; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=5; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=6; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=7; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=8; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=9; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=10; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
PrintList(LL);
DNode *tmp;
ee=8;
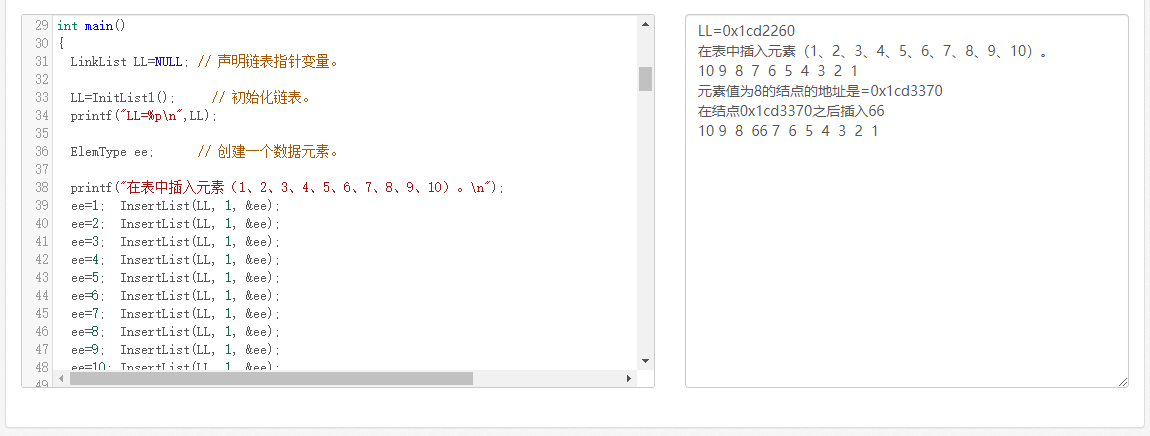
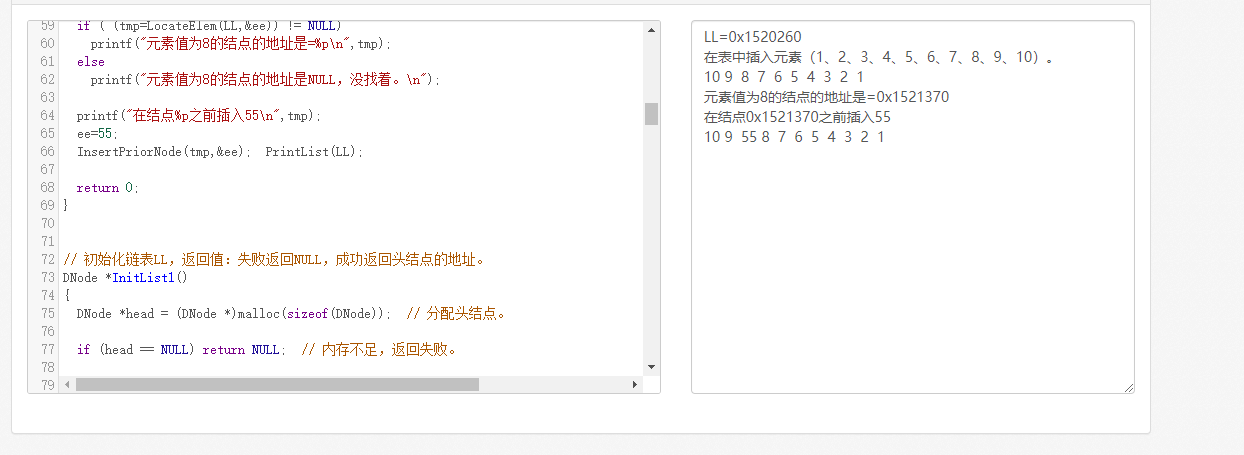
if ( (tmp=LocateElem(LL,&ee)) != NULL)
printf("元素值为8的结点的地址是=%p\n",tmp);
else
printf("元素值为8的结点的地址是NULL,没找着。\n");
printf("在结点%p之前插入55\n",tmp);
ee=55;
InsertPriorNode(tmp,&ee); PrintList(LL);
return 0;
}
// 在指定结点pp之前插入元素ee,返回值:0-失败;1-成功。
int InsertPriorNode(DNode *pp, ElemType *ee)
{
if (pp == NULL) { printf("结点pp不存在。\n"); return 0; }
// 在单链表中,如果要在指定结点pp之前插入元素,采用的是偷梁换柱的方法。
// 在双链表中,偷不偷都行,因为pp->prior有前驱结点的地址。
DNode *tmp = (DNode *)malloc(sizeof(DNode));
if (tmp == NULL) return 0;
// 把待插入的元素存入tmp中。
memcpy(&tmp->data,ee,sizeof(ElemType));
// 处理前驱后继指针。
tmp->prior=pp->prior;
pp->prior->next=tmp;
tmp->next=pp;
pp->prior=tmp;
return 1;
}
12、销毁链表
void DestroyList1(LinkList LL);
int main()
{
LinkList LL=NULL; // 声明链表指针变量。
LL=InitList1(); // 初始化链表。
printf("LL=%p\n",LL);
ElemType ee; // 创建一个数据元素。
printf("在表中插入元素(1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9、10)。\n");
ee=1; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=2; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=3; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=4; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=5; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=6; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=7; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=8; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=9; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=10; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
PrintList(LL);
DestroyList1(LL); LL=NULL; // 销毁链表,LL置为空。
return 0;
}
// 销毁链表LL。
void DestroyList1(LinkList LL)
{
// 销毁链表LL是指释放链表全部的结点,包括头结点。
DNode *tmp;
while(LL!=NULL)
{
tmp=LL->next; // tmp保存下一结点的地址。
free(LL); // 释放当前结点。
LL=tmp; // LL指针移动到下一结点。
}
// LL=NULL; // LL在本函数中相当于局部变量,就算置空了也不会影响调用者传递的LL,所以LL=NULL没有意义。
return;
}
13、完整的代码
/*
* 程序名:linklist4.c,此程序演示带头结点的双链表的实现,数据元素是整数。
* 作者:C语言技术网(www.freecplus.net) 日期:20201230
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int ElemType; // 自定义链表的数据元素为整数。
typedef struct DNode
{
ElemType data; // 存放结点的数据元素。
struct DNode *prior,*next; // 前驱和后继结点的指针。
}DNode,*LinkList;
// 初始化链表LL,返回值:失败返回NULL,成功返回头结点的地址。
DNode *InitList1();
// 传入指针变量的地址的方法。
// 初始化链表,返回值:0-失败;1-成功。
int InitList2(LinkList *LL);
// C++引用的方法,在Linux下,需要用g++编译。
// 初始化链表,返回值:0-失败;1-成功。
// int InitList3(LinkList &LL);
// 如果参数采用转指针LL的值,LL的值只能传进去,无法返回,这种方法是不行的。
int InitList4(LinkList LL);
// 销毁链表LL。
void DestroyList1(LinkList LL);
// 销毁链表LL。
// 传入指针的地址的方法。
void DestroyList2(LinkList *LL);
// C++引用的方法,在Linux下,需要用g++编译。
// 传入指针的地址的方法。
// void DestroyList3(LinkList &LL);
// 清空链表。
void ClearList(LinkList LL);
// 在链表LL的第ii个位置插入元素ee,返回值:0-失败;1-成功。
int InsertList(LinkList LL, unsigned int ii, ElemType *ee);
// 打印链表中全部的元素。
void PrintList(LinkList LL);
// 在链表LL的头部插入元素ee,返回值:0-失败;1-成功。
int PushFront(LinkList LL, ElemType *ee);
// 在链表LL的尾部插入元素ee,返回值:0-失败;1-成功。
int PushBack(LinkList LL, ElemType *ee);
// 删除链表LL中的第ii个结点,返回值:0-位置ii不合法;1-成功。
int DeleteNode(LinkList LL, unsigned int ii);
// 删除链表LL中第一个结点,返回值:0-位置不合法;1-成功。
int PopFront(LinkList LL);
// 删除链表LL中最后一个结点,返回值:0-位置不合法;1-成功。
int PopBack(LinkList LL);
// 求链表的长度,返回值:>=0-表LL结点的个数。
int LengthList(LinkList LL);
// 判断链表是否为空,返回值:0-非空或失败,1-空。
int IsEmpty(LinkList LL);
// 获取链表中第ii个结点,成功返回结点的地址,失败返回空。
// 注意,ii可以取值为0,表示头结点。
DNode *LocateNode(LinkList LL, unsigned int ii);
// 查找元素ee在链表LL中的结点地址,如果没找到返回NULL,否则返回结点的地址。
DNode *LocateElem(LinkList LL, ElemType *ee);
// 在指定结点pp之后插入元素ee,返回值:0-失败;1-成功。
int InsertNextNode(DNode *pp, ElemType *ee);
// 在指定结点pp之前插入元素ee,返回值:0-失败;1-成功。
int InsertPriorNode(DNode *pp, ElemType *ee);
// 删除指定结点。
int DeleteNode1(DNode *pp);
int main()
{
LinkList LL=NULL; // 声明链表指针变量。
LL=InitList1(); // 初始化链表。
// 如果要在函数中对变量进行赋值,必须把变量的地址传入函数。
// 指针变量简称指针,如果要在函数中对指针变量赋值,也必须把指针的地址传入函数。
// LL是指针,在InitList2函数中,需要把头结点的地址赋值给LL,所以要传入LL的地址。
// 指针是变量,用于存放变量的地址,指针不是地址,指针里存放的内容才是地址。
// 所以,这里要把指针变量LL的地址传给InitList2()函数。
// 各位菜鸡,明白鸟吗?
// InitList2(&LL); // 初始化链表,传入指针变量LL的地址。
// InitList3(LL); // 初始化链表,C++的引用。
// 如果参数采用转指针LL的值,LL的值只能传进去,无法返回,这种方法是不行的。
// InitList4(LL);
printf("LL=%p\n",LL);
ElemType ee; // 创建一个数据元素。
printf("在表中插入元素(1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9、10)。\n");
ee=1; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=2; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=3; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=4; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=5; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=6; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=7; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=8; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=9; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
ee=10; InsertList(LL, 1, &ee);
printf("length=%d\n",LengthList(LL));
PrintList(LL);
printf("在第5个位置插入元素(13)。\n");
ee=13; InsertList(LL, 5, &ee);
PrintList(LL);
printf("在表头插入元素(11),表尾插入元素(12)。\n");
ee=11; PushFront(LL, &ee);
ee=12; PushBack(LL, &ee);
PrintList(LL);
printf("删除表中第7个结点。\n");
DeleteNode(LL,7); PrintList(LL);
printf("删除表中第一个结点。\n");
PopFront(LL); PrintList(LL);
DNode *tmp;
if ( (tmp=LocateNode(LL,3)) != NULL)
printf("第3个结点的地址是=%p,ee=%d\n",tmp,tmp->data);
ee=8;
if ( (tmp=LocateElem(LL,&ee)) != NULL)
printf("元素值为8的结点的地址是=%p\n",tmp);
else
printf("元素值为8的结点的地址是NULL,没找着。\n");
printf("在结点%p之后插入66\n",tmp);
ee=66;
InsertNextNode(tmp,&ee); PrintList(LL);
printf("在结点%p之前插入55\n",tmp);
ee=55;
InsertPriorNode(tmp,&ee); PrintList(LL);
// 找到第10个节点并删除它。
if ( (tmp=LocateNode(LL,10)) != NULL)
printf("第10个结点的地址是=%p,ee=%d\n",tmp,tmp->data);
printf("删除结点%p\n",tmp);
DeleteNode1(tmp); PrintList(LL);
DestroyList1(LL); LL=NULL; // 销毁链表,LL置为空。
// DestroyList2(&LL); // 销毁链表,传入指针的地址,LL在函数中会置为空。
// DestroyList3(LL); // 销毁链表,C++的引用,LL在函数中会置为空。
printf("LL=%p\n",LL);
return 0;
}
// 如果参数采用转指针LL的值,LL的值只能传进去,无法返回,这种方法是不行的。
int InitList4(LinkList LL)
{
DNode *head = (DNode *)malloc(sizeof(DNode)); // 分配头结点。
if (head == NULL) return 0; // 内存不足,返回失败。
head->next=NULL; // 头结点的下一结点暂时不存在,置空。
LL=head;
printf("LL1=%p\n",LL);
return 1;
}
// 初始化链表LL,返回值:失败返回NULL,成功返回头结点的地址。
DNode *InitList1()
{
DNode *head = (DNode *)malloc(sizeof(DNode)); // 分配头结点。
if (head == NULL) return NULL; // 内存不足,返回失败。
head->prior=head->next=NULL; // 前驱后继结点都置为空。
return head;
}
// 传入指针变量的地址的方法。
// 初始化链表,返回值:0-失败;1-成功。
int InitList2(LinkList *LL)
{
// 在本函数中,LL是指针的指针,用于存放指针的地址。
if ( *LL != NULL ) { printf("链表LL已存在,在初始化之前请先释放它。\n"); return 0; }
DNode *head = (DNode *)malloc(sizeof(DNode)); // 分配头结点。
if (head == NULL) return 0; // 内存不足,返回失败。
head->prior=head->next=NULL; // 前驱后继结点都置为空。
*LL=head;
return 1;
}
/*
// C++引用的方法。
// 初始化链表,返回值:0-失败;1-成功。
int InitList3(LinkList &LL)
{
if ( LL != NULL ) { printf("链表L已存在,在初始化之前请先释放它。\n"); return 0; }
DNode *head = (DNode *)malloc(sizeof(DNode)); // 分配头结点。
if (head == NULL) return 0; // 内存不足,返回失败。
head->prior=head->next=NULL; // 前驱后继结点都置为空。
LL=head;
return 1;
}
*/
// 销毁链表LL。
void DestroyList1(LinkList LL)
{
// 销毁链表LL是指释放链表全部的结点,包括头结点。
DNode *tmp;
while(LL!=NULL)
{
tmp=LL->next; // tmp保存下一结点的地址。
free(LL); // 释放当前结点。
LL=tmp; // LL指针移动到下一结点。
}
// LL=NULL; // LL在本函数中相当于局部变量,就算置空了也不会影响调用者传递的LL,所以LL=NULL没有意义。
return;
}
// 销毁链表LL。
void DestroyList2(LinkList *LL)
{
// 如果函数的参数是指针的指针,可以启用以下代码。
DNode *tmp1,*tmp2;
tmp1=*LL;
while(tmp1!=NULL)
{
tmp2=tmp1->next; // tmp保存下一结点的地址。
free(tmp1); // 释放当前结点。
tmp1=tmp2; // LL指针移动到下一结点。
}
*LL=NULL; // 把链表的指针置为空,表示链表不存在了。
return;
}
/*
// C++引用的方法。
// 传入指针的地址的方法。
void DestroyList3(LinkList &LL)
{
// 销毁链表LL是指释放链表全部的结点,包括头结点。
DNode *tmp;
while(LL!=NULL)
{
tmp=LL->next; // tmp保存下一结点的地址。
free(LL); // 释放当前结点。
LL=tmp; // LL指针移动到下一结点。
}
LL=NULL; // 把链表的指针置为空,表示链表不存在了。
return;
}
*/
// 清空链表。
void ClearList(LinkList LL)
{
// 清空链表LL是指释放链表全部的结点,但不包括头结点。
if (LL == NULL) { printf("链表LL不存在。\n"); return; } // 判断链表是否存在。
DNode *tmp1;
DNode *tmp2=LL->next; // 保留头结点,从头结点的下一个结点开始释放。
while(tmp2!=NULL)
{
tmp1=tmp2->next;
free(tmp2);
tmp2=tmp1;
}
LL->next=NULL; // 这行代码一定不能少,否则会留下野指针。
return;
}
// 在链表LL的第ii个位置插入元素ee,返回值:0-失败;1-成功。
int InsertList(LinkList LL, unsigned int ii, ElemType *ee)
{
if ( (LL == NULL) || (ee == NULL) ) { printf("链表LL或元素ee不存在。\n"); return 0; } // 判断表和元素是否存在。
// 判断插入位置是否合法
if (ii < 1) { printf("插入位置(%d)不合法,应该在大于0。\n",ii); return 0; }
// 要在位序ii插入结点,必须找到ii-1结点。
DNode *pp=LL; // 指针pp指向头结点,逐步往后移动,如果为空,表示后面没结点了。
int kk=0; // kk指向的是第几个结点,从头结点0开始,pp每向后移动一次,kk就加1。
while ( (pp != NULL) && (kk < ii-1) )
{
pp=pp->next; kk++;
// printf("pp=%p,kk=%d\n",pp,kk);
}
if ( pp==NULL ) { printf("位置(%d)不合法,超过了表长。\n",ii); return 0; }
DNode *tmp = (DNode *)malloc(sizeof(DNode)); // 分配一个结点。
if (tmp == NULL) return 0; // 内存不足,返回失败。
// 考虑数据元素为结构体的情况,这里采用了memcpy的方法而不是直接赋值。
memcpy(&tmp->data,ee,sizeof(ElemType));
// 处理前驱后续结点的指针。
tmp->next=pp->next;
tmp->prior=pp;
if (tmp->next != NULL) tmp->next->prior=tmp; // 特殊处理,如果是在尾部插入,tmp->next根本不存在。
pp->next=tmp;
return 1;
///////////////////////////////////////
// 以上代码可以用以下代码代替。
// DNode *pp=LocateNode(LL,ii-1);
// return InsertNextNode(pp,ee);
///////////////////////////////////////
}
// 删除链表LL中的第ii个结点,返回值:0-位置ii不合法;1-成功。
int DeleteNode(LinkList LL, unsigned int ii)
{
if (LL == NULL) { printf("链表L不存在。\n"); return 0; } // 判断链表是否存在。
// 判断删除位置是否合法
if (ii < 1) { printf("删除位置(%d)不合法,应该在大于0。\n",ii); return 0; }
// 要删除位序ii结点,必须找到ii-1结点。
DNode *pp=LL; // 指针pp指向头结点,逐步往后移动,如果为空,表示后面没结点了。
int kk=0; // kk指向的是第几个结点,从头结点0开始,pp每向后移动一次,kk就加1。
while ( (pp != NULL) && (kk < ii-1) )
{
pp=pp->next; kk++;
}
// 注意,以下行的代码与视频中的不一样,视频中的是 if ( pp==NULL ),有bug。
if ( pp->next==NULL ) { printf("位置(%d)不合法,超过了表长。\n",ii); return 0; }
DNode *tmp=pp->next; // tmp为将要删除的结点。
// 处理前驱后续结点的指针。
pp->next=tmp->next;
if (tmp->next != NULL) tmp->next->prior=pp; // 特殊处理,如果tmp是尾结点,tmp->next根本不存在。
free(tmp);
return 1;
}
// 在链表LL的头部插入元素ee,返回值:0-失败;1-成功。
int PushFront(LinkList LL, ElemType *ee)
{
return InsertList(LL,1,ee);
}
// 在链表LL的尾部插入元素ee,返回值:0-失败;1-成功。
int PushBack(LinkList LL, ElemType *ee)
{
if ( (LL == NULL) || (ee == NULL) ) { printf("链表LL或元素ee不存在。\n"); return 0; } // 判断表和元素是否存在。
DNode *pp=LL; // 从头结点开始。
// 找到最后一个结点。
while (pp->next != NULL) pp=pp->next;
DNode *tmp = (DNode *)malloc(sizeof(DNode)); // 分配一个结点。
if (tmp == NULL) return 0; // 内存不足,返回失败。
// 考虑数据元素为结构体的情况,这里采用了memcpy的方法而不是直接赋值。
memcpy(&tmp->data,ee,sizeof(ElemType));
// 处理前驱后续结点的指针。
tmp->next=pp->next;
tmp->prior=pp;
if (tmp->next != NULL) tmp->next->prior=tmp; // 特殊处理,如果是在尾部插入,tmp->next根本不存在。
pp->next=tmp;
return 1;
}
// 删除链表LL中第一个结点,返回值:0-位置不合法;1-成功。
int PopFront(LinkList LL)
{
return DeleteNode(LL, 1);
}
// 删除链表LL中最后一个结点,返回值:0-位置不合法;1-成功。
int PopBack(LinkList LL)
{
if ( LL == NULL ) { printf("链表LL不存在。\n"); return 0; } // 判断表和元素是否存在。
// 必须加上这个判断,不要误删了头结点。
if ( LL->next == NULL) { printf("链表LL为空,没有尾结点。\n"); return 0; } // 判断表是否为空。
// 如果是单链表,要删除最后一个结点,必须找到最后一个结点的前一个结点。
// 如果是双链表,要删除最后一个结点,找到最后一个结点或最后一个结点的前一个结点都可以,但代码实现略有不同。
DNode *pp=LL; // 从第0个结点开始。
// 找到最后一个结点。
while (pp->next != NULL) pp=pp->next;
pp->prior->next=NULL; // 把最后一个节点的前一结点的next指针置为空。
// 释放最后一个结点。
free(pp);
return 1;
}
// 打印链表中全部的元素。
void PrintList(LinkList LL)
{
if (LL == NULL) { printf("链表LL不存在。\n"); return; } // 判断链表是否存在。
DNode *pp=LL->next; // 从第1个结点开始。
while (pp != NULL)
{
printf("%-3d", pp->data); // 如果元素ee为结构体,这行代码要修改。
pp=pp->next;
}
printf("\n");
/*
// 以下代码用于显示全部结点的地址和元素的值。
DNode *pp=LL; // 从第0个结点开始。
while (pp != NULL)
{
printf("pp=%p,prior=%p,next=%p,data=%-3d\n",pp,pp->prior,pp->next,pp->data);
pp=pp->next;
}
*/
}
// 求链表的长度,返回值:>=0-表LL结点的个数。
int LengthList(LinkList LL)
{
if (LL == NULL) { printf("链表LL不存在。\n"); return 0; } // 判断链表是否存在。
DNode *pp=LL->next; // 头结点不算,从第1个结点开始。
int length=0;
while (pp != NULL) { pp=pp->next; length++; }
return length;
// 不使用临时变量,如何计算链表(包括头结点)的长度?
// if (LL==NULL) return 0;
// return LengthList(LL->next)+1;
}
// 判断链表是否为空,返回值:0-非空或失败,1-空。
int IsEmpty(LinkList LL)
{
if (LL == NULL) return 0;
if (LL->next == NULL) return 1;
return 0;
}
// 获取链表中第ii个结点,成功返回结点的地址,失败返回空。
// 注意,ii可以取值为0,表示头结点。
DNode *LocateNode(LinkList LL, unsigned int ii)
{
if ( LL == NULL ) { printf("链表LL不存在。\n"); return NULL; } // 判断表和元素是否存在。
DNode *pp=LL; // 指针pp指向头结点,逐步往后移动,如果为空,表示后面没结点了。
int kk=0; // kk指向的是第几个结点,从头结点0开始,pp每向后移动一次,kk就加1。
while ( (pp != NULL) && (kk < ii) )
{
pp=pp->next; kk++;
}
if ( pp==NULL ) { printf("位置(%d)不合法,超过了表长。\n",ii); return NULL; }
return pp;
}
// 查找元素ee在链表LL中的结点地址,如果没找到返回NULL,否则返回结点的地址。
DNode *LocateElem(LinkList LL, ElemType *ee)
{
DNode *pp=LL->next; // 从第1个数据结点开始。
while (pp != NULL)
{
// 如果数据元素是结构体,以下代码要修改。
if (pp->data == *ee) return pp;
pp = pp->next;
}
return NULL;
}
// 在指定结点pp之后插入元素ee,返回值:0-失败;1-成功。
int InsertNextNode(DNode *pp, ElemType *ee)
{
if (pp == NULL) { printf("结点pp不存在。\n"); return 0; }
DNode *tmp = (DNode *)malloc(sizeof(DNode));
if (tmp == NULL) return 0;
memcpy(&tmp->data,ee,sizeof(ElemType));
// 处理前驱后续结点的指针。
tmp->next=pp->next;
tmp->prior=pp;
if (tmp->next != NULL) tmp->next->prior=tmp; // 特殊处理,如果是在尾部插入,tmp->next根本不存在。
pp->next=tmp;
return 1;
}
// 在指定结点pp之前插入元素ee,返回值:0-失败;1-成功。
int InsertPriorNode(DNode *pp, ElemType *ee)
{
if (pp == NULL) { printf("结点pp不存在。\n"); return 0; }
// 在单链表中,如果要在指定结点pp之前插入元素,采用的是偷梁换柱的方法。
// 在双链表中,偷不偷都行,因为pp->prior有前驱结点的地址。
DNode *tmp = (DNode *)malloc(sizeof(DNode));
if (tmp == NULL) return 0;
// 把待插入的元素存入tmp中。
memcpy(&tmp->data,ee,sizeof(ElemType));
// 处理前驱后继指针。
tmp->prior=pp->prior;
pp->prior->next=tmp;
tmp->next=pp;
pp->prior=tmp;
return 1;
}
// 删除指定结点。
int DeleteNode1(DNode *pp)
{
if (pp == NULL) { printf("结点pp不存在。\n"); return 0; }
// 在单链表中,删除指定结点根本不可行,也不能采用偷梁换柱的方法。
// 但是,在双链表中,删除指定结点是可行的。
pp->prior->next=pp->next;
if (pp->next != NULL) pp->next->prior=pp->prior; // 特殊处理,如果pp是尾结点,pp->next->prior根本不存在。
free(pp);
return 1;
}










