java的fail-fast 和 fail-safe机制
fail-fast机制是在遍历一个集合时,当集合结构被修改,可能会抛出ConcurrentModificationException。
ArrayList源码中,Fail-fast iterators throw {@code ConcurrentModificationException} on a best-effort basis.
快速失败迭代器会做出最大的努力来抛出ConcurrentModificationException。
这里的集合包括:HashMap,Vector,ArrayList,HashSet。
看下面的例子:
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); for(int i = 0; i < 20; i++){ list.add(i); } Iterator<Integer> it = list.iterator(); int temp = 0; while(it.hasNext()){ if(temp == 3){ temp++; list.remove(3); }else{ temp++; System.out.println(it.next()); } } } }
这里的list.remove(3);会导致程序抛出ConcurrentModificationException。
Exception in thread "main" java.util.ConcurrentModificationException at java.util.ArrayList$Itr.checkForComodification(ArrayList.java:901) at java.util.ArrayList$Itr.next(ArrayList.java:851) at com.raisecom.ems.pon.system.service.nemanager.impl.iscom6810.v4_0.Test.main(Test.java:22)
ArrayList$Itr的checkForComodification打断点分析一下:
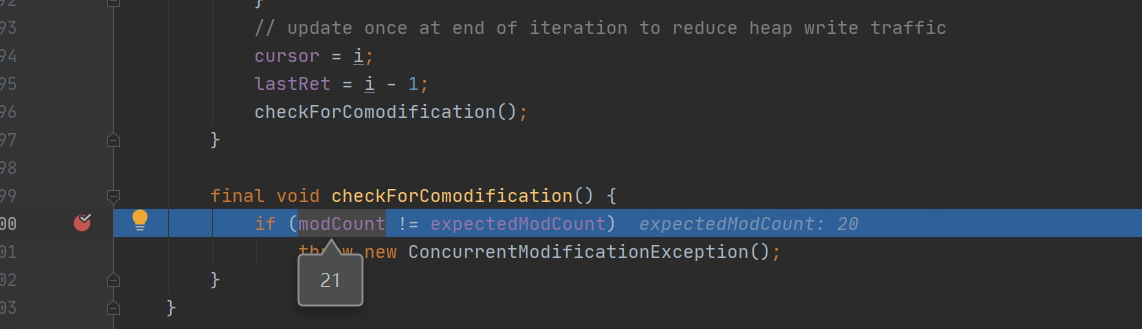
Iterator的remove方法不会抛出ConcurrentModificationException。 下面的例子不会抛出异常。
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); for(int i = 0; i < 20; i++){ list.add(i); } Iterator<Integer> it = list.iterator(); int temp = 0; while(it.hasNext()){ if(temp == 3){ temp++; //list.remove(3); it.remove(); }else{ temp++; System.out.println(it.next()); } } } }
fail-safe会在一个复制的集合上进行修改,因此不会抛出ConcurrentModificationException。无法保证读取的数据是目前原始数据结构中的数据。
这里的集合包括:CopyOnWriteArrayList,ConcurrentHashMap,使用Collections.synchronizedList生成的集合。
public class Test2 { public static void main(String[] args) { ConcurrentHashMap<String, String> premiumPhone = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, String>(); premiumPhone.put("Apple", "iPhone"); premiumPhone.put("HTC", "HTC one"); premiumPhone.put("Samsung", "S5"); Iterator iterator = premiumPhone.keySet().iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { System.out.println(premiumPhone.get(iterator.next())); premiumPhone.put("Sony", "Xperia Z"); } } }
运行的结果是:
iPhone
HTC one
S5



