使用Python处理CSV文件的一些代码示例
笔记:使用Python处理CSV文件的一些代码示例,来自于《Python数据分析基础》一书,有删改
# 读写CSV文件,不使用CSV模块,仅使用基础Python # 20181110 wangml #!/usr/bin/env python3 input_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data.csv' output_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data_out.csv' # 分别以读、写方式打开input_file、output_file,当以 w 方式打开的文件不存在,则创建它 with open(input_file, 'r', newline='') as filereader: with open(output_file, 'w', newline='') as filewriter: # 读取一行文件内容 header = filereader.readline() header = header.strip() header_list = header.split(',') print(header_list) filewriter.write(','.join(map(str, header_list))+'\n') for row in filereader: row = row.strip() row_list = row.split(',') print(row_list) filewriter.write(','.join(map(str, row_list))+'\n')
# 使用CSV模块读写CSV文件 # 20181112 wangml # csv_pandas_1 #!/usr/bin/env python3 # 导入CSV库 import csv input_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data.csv' output_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data_out.csv' with open(input_file, 'r', newline='') as csv_in_file: with open(output_file, 'w', newline='') as csv_out_file: # 使用CVS模块中csv.reader()、csv.writer()函数,创建一个读取对象、一个写入对象 # delimiter指定CSV文件的分隔符,默认为 , 逗号 filereader = csv.reader(csv_in_file, delimiter=',') filewriter = csv.writer(csv_out_file, delimiter=',') header = next(filereader) filewriter.writerow(header) # 循环,每次从CSV读取文件中读取一行数据,并将其打印出来,然后写入CSV写入对象 for row_list in filereader: print(row_list) filewriter.writerow(row_list) # 筛选符合条件的行 for row_list in filereader: #print(row_list[1]) name = str(row_list[0]).strip() #print(row_list[3]) cost = str(row_list[3]).strip('$').replace(',', '') #print(cost) #print(type(cost)) # 选择name为z或者cost大于600的row,此处使用float()函数将cost由str类型转换为flost if name == 'z' or float(cost) > 600.0: filewriter.writerow(row_list)
# # csv_pandas_1 #!/usr/bin/env python3 import pandas as pd input_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data.csv' output_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data_out.csv' # 使用pandas库函数pandas.read_csv()读取一个CSV文件,并由此创建一个数据框对象 data_frame = pd.read_csv(input_file) # 通过列名作为index选取该数据框中的指定列 data_frame['Cost'] = data_frame['Cost'].str.strip('$').astype(float) #print(type(data_frame['Cost'])) data_frame_value_meets_condition = data_frame.loc[(data_frame['Name'].str.contains('Z')) | (data_frame['Cost'] > 600.0), :] # 此处导致CSV文件的Cost列的$消失了 # 下面的语句并没有将$加上去,暂时不知道怎么弄 data_frame['Cost'] = '$' + str(data_frame['Cost']) # 将data_frame_value_meets_condition写入输出文件 data_frame_value_meets_condition.to_csv(output_file, index=False)
# 20181113 # csv_pandas_2 #!/usr/bin/env python3 # 导入CSV库 import csv input_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data.csv' output_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data_out.csv' important_dates = ['1/1/2018', '2/1/2018'] with open(input_file, 'r', newline='') as csv_in_file: with open(output_file, 'w', newline='') as csv_out_file: filereader = csv.reader(csv_in_file) filewriter = csv.writer(csv_out_file) header = next(filereader) filewriter.writerow(header) for row_list in filereader: a_date = row_list[4] # 选取date值在important_dates中的行 if a_date in important_dates: filewriter.writerow(row_list)
# # csv_pandas_2 #!/usr/bin/env python3 import pandas as pd input_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data.csv' output_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data_out.csv' # 使用pandas库函数pandas.read_csv()读取一个CSV文件,并由此创建一个数据框对象 data_frame = pd.read_csv(input_file) important_dates = ['1/1/2018', '2/1/2018'] # 选取date值在important_dates中的行 data_frame_value_set = data_frame.loc[data_frame['Date'].isin(important_dates), :] data_frame_value_set.to_csv(output_file, index=False)
# 20181113 # csv_pandas_3 #!/usr/bin/env python3 # 导入CSV库、正则表达式库 import csv import re input_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data.csv' output_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data_out.csv' # 使用re.compile(正则表达式),创建一个正则表达式变量 # 元字符?P<my_pattern_group>捕获了名为<my_pattern_group>的组中匹配了的字符串 # pattern表示满足以:'001-'开头,后面可跟除任意字串的字符串 # re.I表示大小写敏感 pattern = re.compile(r'(?P<my_pattern_group>^001-.*)', re.I) with open(input_file, 'r', newline='') as csv_in_file: with open(output_file, 'w', newline='') as csv_out_file: filereader = csv.reader(csv_in_file) filewriter = csv.writer(csv_out_file) header = next(filereader) filewriter.writerow(header) for row_list in filereader: id_number = row_list[1] if pattern.search(id_number): filewriter.writerow(row_list)
# 20181113 # csv_pandas_3 #!/usr/bin/env python3 import pandas as pd input_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data.csv' output_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data_out.csv' # 使用pandas库函数pandas.read_csv()读取一个CSV文件,并由此创建一个数据框对象 data_frame = pd.read_csv(input_file) # 筛选出ID值以001-开头的行 data_frame_value_matches_pattern = data_frame.loc[data_frame['ID'].str.startswith("001-"), :] data_frame_value_matches_pattern.to_csv(output_file, index=False)
# 选取CSV文件中符合条件的列 # 20181113 # csv_pandas_4 # 通过列索引值选取特定列 # 在只知道需要选取的列名称时,我们可以通过列名称取得相应的索引值,在进行选取 # 具体方法是判断相应标题行每个元素是否在已知列名称中,若是,记下该item的index #!/usr/bin/env python3 import csv input_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data.csv' output_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data_out.csv' my_columns = [0, 3] with open(input_file, 'r', newline='') as csv_in_file: with open(output_file, 'w', newline='') as csv_out_file: filereader = csv.reader(csv_in_file) filewriter = csv.writer(csv_out_file) for row_list in filereader: # 每次向输出文件中写入的一行值 row_list_output = [] for index_value in my_columns: row_list_output.append(row_list[index_value]) filewriter.writerow(row_list_output)
# 选取CSV文件中符合条件的列 # 20181113 # csv_pandas_4 # 通过列索引值选取特定列 # 在只知道需要选取的列名称时,不需要像基本Python一样处理标题行,pandas可以将列名称当做index一样处理 #!/usr/bin/env python3 import pandas as pd input_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data.csv' output_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data_out.csv' # 使用pandas库函数pandas.read_csv()读取一个CSV文件,并由此创建一个数据框对象 data_frame = pd.read_csv(input_file) # 选取data_frame数据框对象中的所有行的列索引值为0,3的列 # iloc(行,列)函数可以选取数据框中选定的行、列 data_frame_value_column_by_value = data_frame.iloc[:, [0, 3]] # data_frame_value_column_by_value = data_frame.iloc[:, [‘Name’, 'Cost']] data_frame_value_column_by_value.to_csv(output_file, index=False) # 给一个CSV文件添加标题行,在基础Python中,可能是将标题行通过csv库的writerow()函数写入 # 而pandas库提供了更加简单的方法 # title = [‘One’, 'Two'...] # data_frame = pd.read_csv(input_file, header=None, names=title)
# 读取多个CSV文件,输出读取了多少个CSV文件 #!/usr/bin/env python3 import csv import glob import os input_path = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python' file_counter = 0 for input_file in glob.glob(os.path.join(input_path, '*.csv')): file_counter = file_counter + 1 #row_counter = 1 #with open(input_file, 'r', newline='') as csv_input_file: #filereader = csv.reader(csv_input_file) #... print(file_counter)
# 20181114 # 合并多个CSV文件 #!/usv/bin/env python3 import pandas as pd import os import glob input_path = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python' output_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data_out.csv' #all_files = glob.glob(os.path.join(input_path, 'supplier_data_副本*')) # OSError: Initializing from file failed上面这句出现错误,因为文件名含有中文,改成下面这句就行了 all_files = glob.glob(os.path.join(input_path, 'supplier_data_copy*')) all_data_frame = [] for file in all_files: data_frame = pd.read_csv(file, index_col=None) all_data_frame.append(data_frame) # pandas.concat()函数将数据框数据垂直堆叠(axis=0), 当水平连接数据时(asis=1) data_frame_concat = pd.concat(all_data_frame, axis=0, ignore_index=True) data_frame_concat.to_csv(output_file, index=False)
# 分别计算多个CSV文件中的某项数据的和、平均值等 # 在基本python中,可以读取多个CSV文件,然后要被计算的项的值一个一个取出来,然后计算 # 这里展示了使用pandas提供的方法 #!/usv/bin/env python3 import pandas as pd import os import glob input_path = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python' output_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data_out.csv' all_files = glob.glob(os.path.join(input_path, 'supplier_data_copy*')) all_data_frame = [] for file in all_files: data_frame = pd.read_csv(file, index_col=None) # 和 total_cost = pd.DataFrame([float(str(value).strip('$').replace(',', '')) \ for value in data_frame.loc[:, 'Cost']]).sum() # 平均值 average_cost = pd.DataFrame([float(str(value).strip('$').replace(',', '')) \ for value in data_frame.loc[:, 'Cost']]).mean() data = {'file_name': os.path.basename(file), 'total_cost': total_cost, 'average_cost': average_cost} all_data_frame.append(pd.DataFrame(data, columns=['file_name', 'total_cost', 'average_cost'])) data_frames_concat = pd.concat(all_data_frame, axis=0, ignore_index=True) data_frames_concat.to_csv(output_file, index=False)
代码示例中使用的CSV文件:
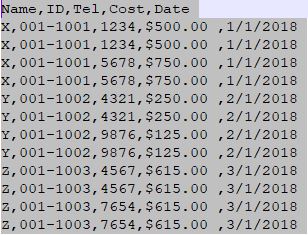
上述代码分别使用CSV库、pandas库来对CSV文件进行相同的操作
上述代码运行在Python 3.6版本下,在Win10、Spyder中
有关Python的csv库的详细介绍:https://docs.python.org/2/library/csv.html
转载请注明出处



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号