asm:dosbox安装及汇编环境配置(win)
一、dosbox安装及汇编环境配置
dosbox的安装以及汇编测试
1、建立文件夹:
1.1 G:\assemblyWorkspaces\masm_dos
功能1:“汇编依赖文件夹”存放位置:
功能2:dosbox挂载位置(mount c G:\assemblyWorkspaces\masm_dos)
功能3:masm源文件存放位置;G:\assemblyWorkspaces\masm_dos\src。
1.2 D:\tools\asm\masm_dos\dosbox_install
功能:安装dosbox
2、 dosbox
2.1 安装dosbox,安装位置:D:\tools\asm\masm_dos\dosbox_install,一直ok到结束
2.2 汇编的工作区的目录:
2.2.1 汇编工作区根目录: G:\assemblyWorkspaces\masm_dos
2.2.2 汇编工作区子目录: G:\assemblyWorkspaces\masm_dos\src
2.3 dosbox配置:
2.3.1 dosbox配置位置1:
-- C:/Users/Administrator/AppData/Local/DOSBox/dosbox-0.74-3.conf
2.3.1.1 屏幕分辨率配置、字体大小配置:
2.3.1.2 汇编环境配置:
2.3.2 dosbox配置文件位置2:
-- D:\tools\asm\masm_dos\dosbox_install\DOSBox-0.74-3\DOSBox 0.74-3 Options.bat
2.3.3 双击文件"DOSBox 0.74-3 Options.bat",在文件末尾添加如下文字:
“
# 井号部分的是注释语句,不用写
mount c G:\assemblyWorkspaces\masm_dos #把“g:\xx”盘挂载在dosbox的c盘位置。
c: #启动时,进入dosbox的c盘
path=c:\;src; # 配置环境变量: 进入工作区的子目录后,可以使用汇编工具(masm/debug/link/...)
”
2.3.4 说明:
2.3.4.1 命令: mount “挂载点(c)” 汇编工作区的根目录
2.3.4.2 说明: 将“汇编工作区的根目录”挂载在“C盘”;即将“汇编工作区的根目录”当作“C盘”。
2.3.4.3 实例: mount c G:\assemblyWorkspaces\masm_dos
2.4 将“asm_tools(masm/debug/link/...)”的内容复制到 G:\assemblyWorkspaces\masm_dos 位置;
3.使用dosbox汇编
3.1 编写汇编文件,命名为test.asm,保存在 G:\assemblyWorkspaces\masm_dos\src 位置;
3.2 启动dosbox;在dosbox内进行“汇编、链接、执行”等动作。
3.3 汇编(dosbox): masm test.asm
3.4 链接(dosbox): link test.obj
3.5 执行(dosbox): c:\> test.exe
二、dosbox配置的实例
1 # This is the configuration file for DOSBox 0.74-3. (Please use the latest version of DOSBox)
2 # Lines starting with a # are comment lines and are ignored by DOSBox.
3 # They are used to (briefly) document the effect of each option.
4
5 [sdl]
6 # fullscreen: Start dosbox directly in fullscreen. (Press ALT-Enter to go back)
7 # fulldouble: Use double buffering in fullscreen. It can reduce screen flickering, but it can also result in a slow DOSBox.
8 # fullresolution: What resolution to use for fullscreen: original, desktop or fixed size (e.g. 1024x768).
9 # Using your monitor's native resolution (desktop) with aspect=true might give the best results.
10 # If you end up with small window on a large screen, try an output different from surface.
11 # On Windows 10 with display scaling (Scale and layout) set to a value above 100%, it is recommended
12 # to use a lower full/windowresolution, in order to avoid window size problems.
13 # windowresolution: Scale the window to this size IF the output device supports hardware scaling.
14 # (output=surface does not!)
15 # output: What video system to use for output.
16 # Possible values: surface, overlay, opengl, openglnb, ddraw.
17 # autolock: Mouse will automatically lock, if you click on the screen. (Press CTRL-F10 to unlock)
18 # sensitivity: Mouse sensitivity.
19 # waitonerror: Wait before closing the console if dosbox has an error.
20 # priority: Priority levels for dosbox. Second entry behind the comma is for when dosbox is not focused/minimized.
21 # pause is only valid for the second entry.
22 # Possible values: lowest, lower, normal, higher, highest, pause.
23 # mapperfile: File used to load/save the key/event mappings from. Resetmapper only works with the defaul value.
24 # usescancodes: Avoid usage of symkeys, might not work on all operating systems.
25
26 fullscreen=false
27 fulldouble=false
28 # fullresolution=original
29 # windowresolution=original
30 # output=surface
31
32 autolock=true
33 sensitivity=100
34 waitonerror=true
35 priority=higher,normal
36 mapperfile=mapper-0.74-3.map
37 usescancodes=true
38
39
40
41
42 # part1 -- config by david; date:2023-01-07
43 fullresolution=1024x768
44 windowresolution=1024x768
45 output=opengl
46 hwscale=2.00
47
48
49
50
51
52
53 [dosbox]
54 # language: Select another language file.
55 # machine: The type of machine DOSBox tries to emulate.
56 # Possible values: hercules, cga, tandy, pcjr, ega, vgaonly, svga_s3, svga_et3000, svga_et4000, svga_paradise, vesa_nolfb, vesa_oldvbe.
57 # captures: Directory where things like wave, midi, screenshot get captured.
58 # memsize: Amount of memory DOSBox has in megabytes.
59 # This value is best left at its default to avoid problems with some games,
60 # though few games might require a higher value.
61 # There is generally no speed advantage when raising this value.
62
63 language=
64 machine=svga_s3
65 captures=capture
66 memsize=16
67
68 [render]
69 # frameskip: How many frames DOSBox skips before drawing one.
70 # aspect: Do aspect correction, if your output method doesn't support scaling this can slow things down!
71 # scaler: Scaler used to enlarge/enhance low resolution modes. If 'forced' is appended,
72 # then the scaler will be used even if the result might not be desired.
73 # To fit a scaler in the resolution used at full screen may require a border or side bars,
74 # to fill the screen entirely, depending on your hardware, a different scaler/fullresolution might work.
75 # Possible values: none, normal2x, normal3x, advmame2x, advmame3x, advinterp2x, advinterp3x, hq2x, hq3x, 2xsai, super2xsai, supereagle, tv2x, tv3x, rgb2x, rgb3x, scan2x, scan3x.
76
77 frameskip=0
78 aspect=false
79 scaler=normal2x
80
81 [cpu]
82 # core: CPU Core used in emulation. auto will switch to dynamic if available and
83 # appropriate.
84 # Possible values: auto, dynamic, normal, simple.
85 # cputype: CPU Type used in emulation. auto is the fastest choice.
86 # Possible values: auto, 386, 386_slow, 486_slow, pentium_slow, 386_prefetch.
87 # cycles: Amount of instructions DOSBox tries to emulate each millisecond.
88 # Setting this value too high results in sound dropouts and lags.
89 # Cycles can be set in 3 ways:
90 # 'auto' tries to guess what a game needs.
91 # It usually works, but can fail for certain games.
92 # 'fixed #number' will set a fixed amount of cycles. This is what you usually
93 # need if 'auto' fails. (Example: fixed 4000).
94 # 'max' will allocate as much cycles as your computer is able to
95 # handle.
96 # Possible values: auto, fixed, max.
97 # cycleup: Amount of cycles to decrease/increase with keycombos.(CTRL-F11/CTRL-F12)
98 # cycledown: Setting it lower than 100 will be a percentage.
99
100 core=auto
101 cputype=auto
102 cycles=auto
103 cycleup=10
104 cycledown=20
105
106 [mixer]
107 # nosound: Enable silent mode, sound is still emulated though.
108 # rate: Mixer sample rate, setting any device's rate higher than this will probably lower their sound quality.
109 # Possible values: 44100, 48000, 32000, 22050, 16000, 11025, 8000, 49716.
110 # blocksize: Mixer block size, larger blocks might help sound stuttering but sound will also be more lagged.
111 # Possible values: 1024, 2048, 4096, 8192, 512, 256.
112 # prebuffer: How many milliseconds of data to keep on top of the blocksize.
113
114 nosound=false
115 rate=44100
116 blocksize=1024
117 prebuffer=25
118
119 [midi]
120 # mpu401: Type of MPU-401 to emulate.
121 # Possible values: intelligent, uart, none.
122 # mididevice: Device that will receive the MIDI data from MPU-401.
123 # Possible values: default, win32, alsa, oss, coreaudio, coremidi, none.
124 # midiconfig: Special configuration options for the device driver. This is usually the id of the device you want to use
125 # (find the id with mixer/listmidi).
126 # Or in the case of coreaudio, you can specify a soundfont here.
127 # See the README/Manual for more details.
128
129 mpu401=intelligent
130 mididevice=default
131 midiconfig=
132
133 [sblaster]
134 # sbtype: Type of Soundblaster to emulate. gb is Gameblaster.
135 # Possible values: sb1, sb2, sbpro1, sbpro2, sb16, gb, none.
136 # sbbase: The IO address of the soundblaster.
137 # Possible values: 220, 240, 260, 280, 2a0, 2c0, 2e0, 300.
138 # irq: The IRQ number of the soundblaster.
139 # Possible values: 7, 5, 3, 9, 10, 11, 12.
140 # dma: The DMA number of the soundblaster.
141 # Possible values: 1, 5, 0, 3, 6, 7.
142 # hdma: The High DMA number of the soundblaster.
143 # Possible values: 1, 5, 0, 3, 6, 7.
144 # sbmixer: Allow the soundblaster mixer to modify the DOSBox mixer.
145 # oplmode: Type of OPL emulation. On 'auto' the mode is determined by sblaster type. All OPL modes are Adlib-compatible, except for 'cms'.
146 # Possible values: auto, cms, opl2, dualopl2, opl3, none.
147 # oplemu: Provider for the OPL emulation. compat might provide better quality (see oplrate as well).
148 # Possible values: default, compat, fast.
149 # oplrate: Sample rate of OPL music emulation. Use 49716 for highest quality (set the mixer rate accordingly).
150 # Possible values: 44100, 49716, 48000, 32000, 22050, 16000, 11025, 8000.
151
152 sbtype=sb16
153 sbbase=220
154 irq=7
155 dma=1
156 hdma=5
157 sbmixer=true
158 oplmode=auto
159 oplemu=default
160 oplrate=44100
161
162 [gus]
163 # gus: Enable the Gravis Ultrasound emulation.
164 # gusrate: Sample rate of Ultrasound emulation.
165 # Possible values: 44100, 48000, 32000, 22050, 16000, 11025, 8000, 49716.
166 # gusbase: The IO base address of the Gravis Ultrasound.
167 # Possible values: 240, 220, 260, 280, 2a0, 2c0, 2e0, 300.
168 # gusirq: The IRQ number of the Gravis Ultrasound.
169 # Possible values: 5, 3, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12.
170 # gusdma: The DMA channel of the Gravis Ultrasound.
171 # Possible values: 3, 0, 1, 5, 6, 7.
172 # ultradir: Path to Ultrasound directory. In this directory
173 # there should be a MIDI directory that contains
174 # the patch files for GUS playback. Patch sets used
175 # with Timidity should work fine.
176
177 gus=false
178 gusrate=44100
179 gusbase=240
180 gusirq=5
181 gusdma=3
182 ultradir=C:\ULTRASND
183
184 [speaker]
185 # pcspeaker: Enable PC-Speaker emulation.
186 # pcrate: Sample rate of the PC-Speaker sound generation.
187 # Possible values: 44100, 48000, 32000, 22050, 16000, 11025, 8000, 49716.
188 # tandy: Enable Tandy Sound System emulation. For 'auto', emulation is present only if machine is set to 'tandy'.
189 # Possible values: auto, on, off.
190 # tandyrate: Sample rate of the Tandy 3-Voice generation.
191 # Possible values: 44100, 48000, 32000, 22050, 16000, 11025, 8000, 49716.
192 # disney: Enable Disney Sound Source emulation. (Covox Voice Master and Speech Thing compatible).
193
194 pcspeaker=true
195 pcrate=44100
196 tandy=auto
197 tandyrate=44100
198 disney=true
199
200 [joystick]
201 # joysticktype: Type of joystick to emulate: auto (default), none,
202 # 2axis (supports two joysticks),
203 # 4axis (supports one joystick, first joystick used),
204 # 4axis_2 (supports one joystick, second joystick used),
205 # fcs (Thrustmaster), ch (CH Flightstick).
206 # none disables joystick emulation.
207 # auto chooses emulation depending on real joystick(s).
208 # (Remember to reset dosbox's mapperfile if you saved it earlier)
209 # Possible values: auto, 2axis, 4axis, 4axis_2, fcs, ch, none.
210 # timed: enable timed intervals for axis. Experiment with this option, if your joystick drifts (away).
211 # autofire: continuously fires as long as you keep the button pressed.
212 # swap34: swap the 3rd and the 4th axis. Can be useful for certain joysticks.
213 # buttonwrap: enable button wrapping at the number of emulated buttons.
214
215 joysticktype=auto
216 timed=true
217 autofire=false
218 swap34=false
219 buttonwrap=false
220
221 [serial]
222 # serial1: set type of device connected to com port.
223 # Can be disabled, dummy, modem, nullmodem, directserial.
224 # Additional parameters must be in the same line in the form of
225 # parameter:value. Parameter for all types is irq (optional).
226 # for directserial: realport (required), rxdelay (optional).
227 # (realport:COM1 realport:ttyS0).
228 # for modem: listenport (optional).
229 # for nullmodem: server, rxdelay, txdelay, telnet, usedtr,
230 # transparent, port, inhsocket (all optional).
231 # Example: serial1=modem listenport:5000
232 # Possible values: dummy, disabled, modem, nullmodem, directserial.
233 # serial2: see serial1
234 # Possible values: dummy, disabled, modem, nullmodem, directserial.
235 # serial3: see serial1
236 # Possible values: dummy, disabled, modem, nullmodem, directserial.
237 # serial4: see serial1
238 # Possible values: dummy, disabled, modem, nullmodem, directserial.
239
240 serial1=dummy
241 serial2=dummy
242 serial3=disabled
243 serial4=disabled
244
245 [dos]
246 # xms: Enable XMS support.
247 # ems: Enable EMS support.
248 # umb: Enable UMB support.
249 # keyboardlayout: Language code of the keyboard layout (or none).
250
251 xms=true
252 ems=true
253 umb=true
254 keyboardlayout=auto
255
256 [ipx]
257 # ipx: Enable ipx over UDP/IP emulation.
258
259 ipx=false
260
261 [autoexec]
262 # Lines in this section will be run at startup.
263 # You can put your MOUNT lines here.
264
265
266
267 # part2 -- config by david; date:2023-01-07
268 mount c G:\assemblyWorkspaces\masm_dos
269 c:
270 path=c:\;src;
271 cd src
三、asm_tools配置的实例
1、asm_tools(win11):
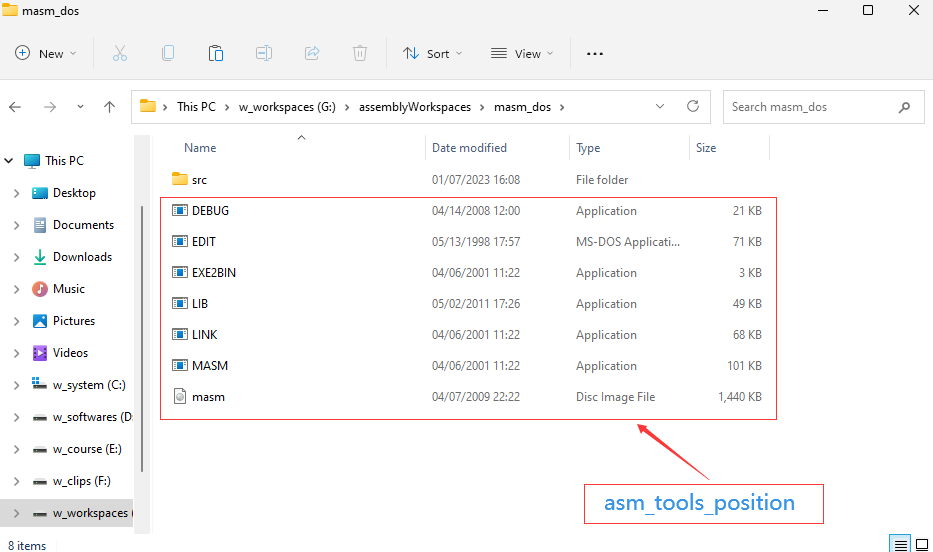
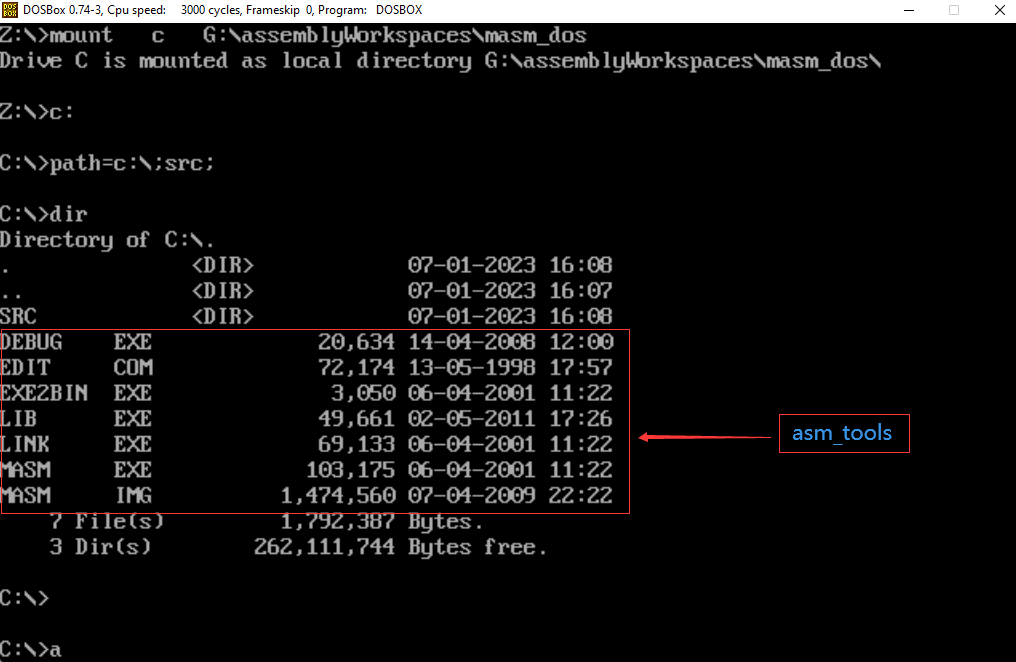
2、asm_tools(dosbox):
四、测试源码
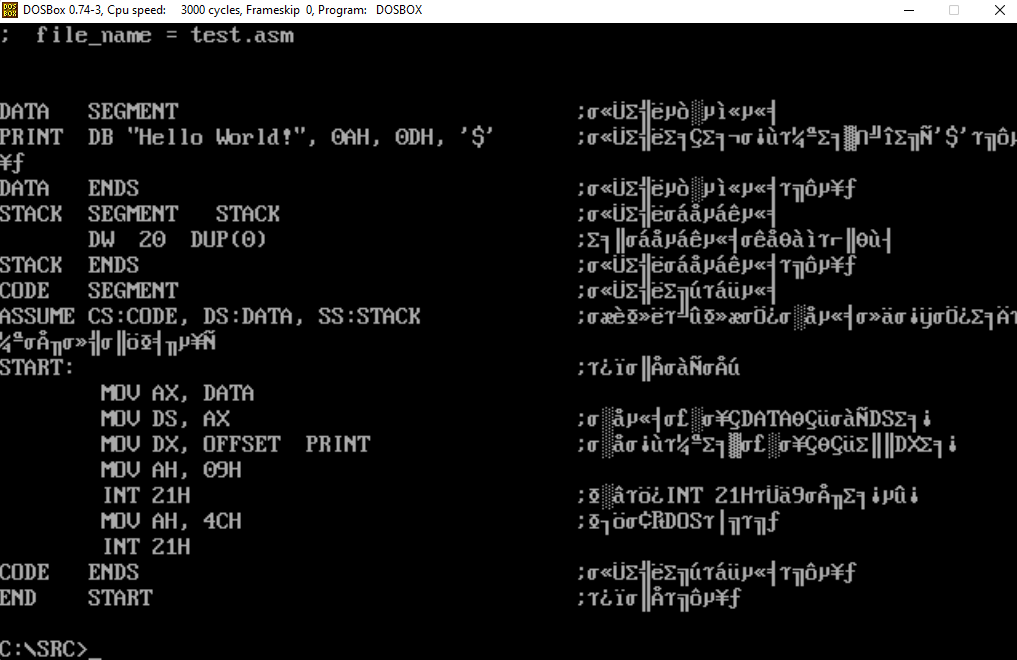
1 ; file_name = test.asm
2
3
4 DATA SEGMENT ;定义数据段
5 PRINT DB "Hello World!", 0AH, 0DH, '$' ;定义一个字符串,以'$'结束
6 DATA ENDS ;定义数据段结束
7 STACK SEGMENT STACK ;定义堆栈段
8 DW 20 DUP(0) ;为堆栈段分配空间
9 STACK ENDS ;定义堆栈段结束
10 CODE SEGMENT ;定义代码段
11 ASSUME CS:CODE, DS:DATA, SS:STACK ;告诉编译器将段寄存器与符号对应起来
12 START: ;程序入口
13 MOV AX, DATA
14 MOV DS, AX ;将段地址DATA送入DS中
15 MOV DX, OFFSET PRINT ;将字符串地址送人DX中
16 MOV AH, 09H
17 INT 21H ;调用INT 21H的9号中断
18 MOV AH, 4CH ;返回DOS系统
19 INT 21H
20 CODE ENDS ;定义代码段结束
21 END START
五、测试过程
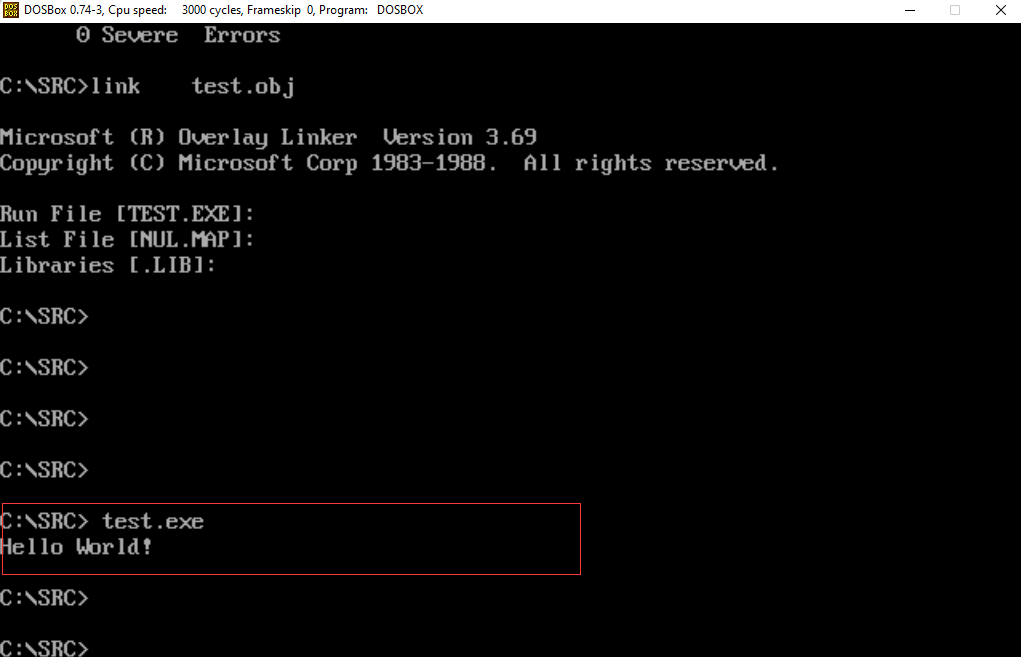
1、测试环境
2、测试文件源码:
3、测试过程
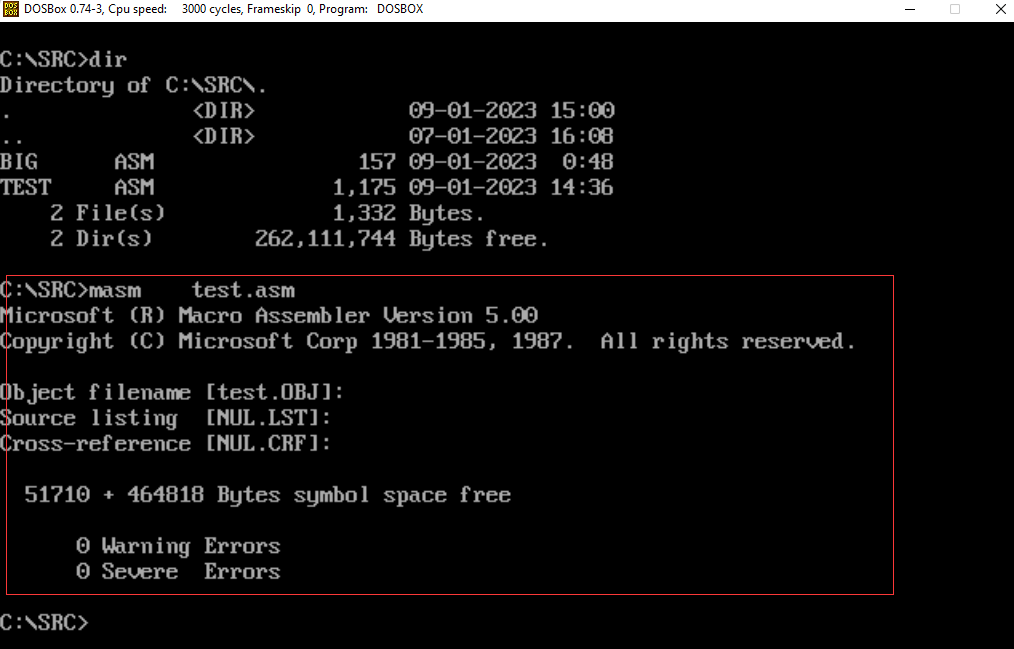
3.1、汇编: masm test.asm
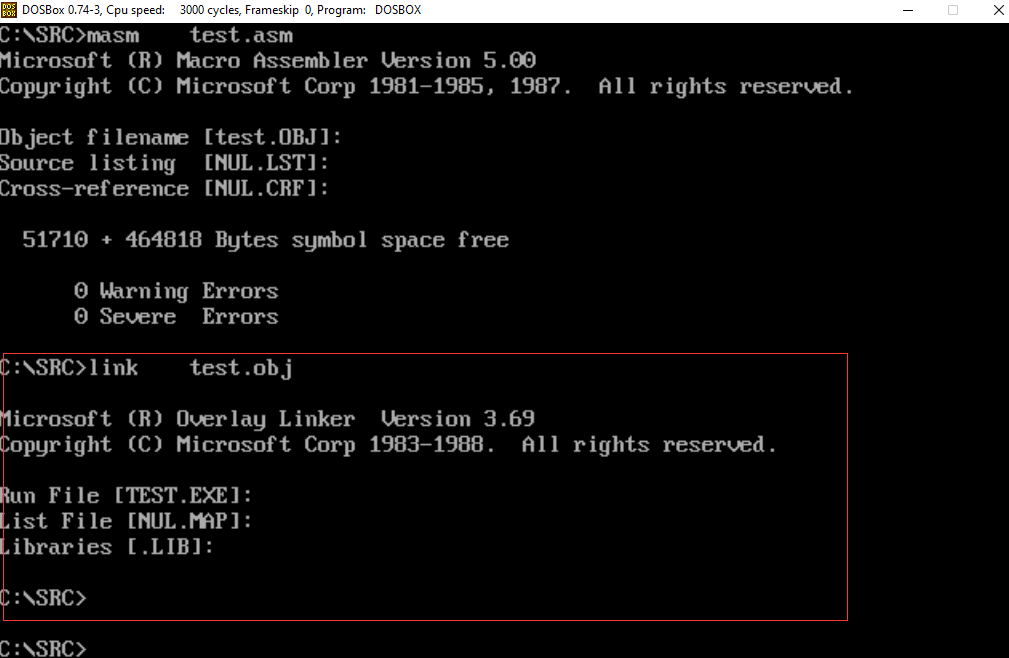
3.2、连接: link test.obj
3.3、运行:c:\src> test.exe
六、参考文档
1、Ubuntu18.04/Linux下安装DosBox进行8086汇编: https://www.codenong.com/cs105499537/
2、在Ubuntu下使用Dosbox编译第一个汇编程序: https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000043235868
本文由 lnlidawei 原创、整理、转载,本文来自于【博客园】; 整理和转载的文章的版权归属于【原创作者】; 转载或引用时请【保留文章的来源信息】:https://www.cnblogs.com/lnlidawei/p/17032950.html




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号