Python3 字符串格式化
字符串的格式化方法分为两种,分别为占位符(%)和format方式。占位符方式在Python2.x中用的比较广泛,随着Python3.x的使用越来越广,format方式使用的更加广泛。
一 占位符(%)
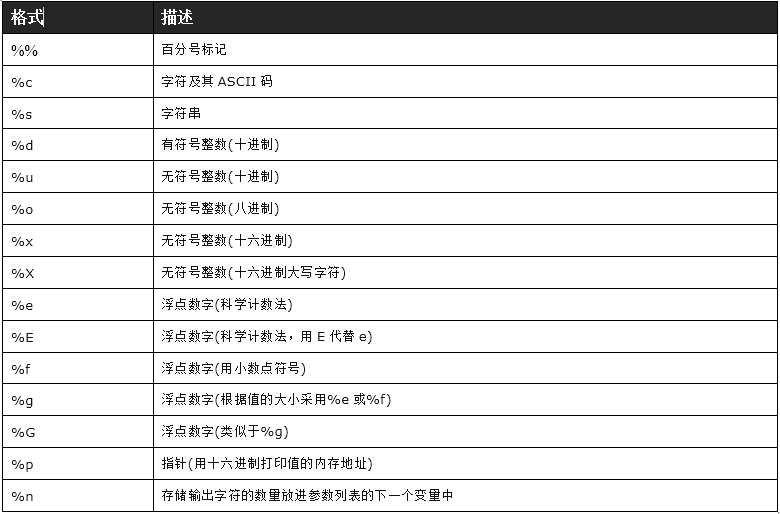
%d
实例(Python3.0+):
|
1
2
3
|
age = 29print("my age is %d" %age)#my age is 29 |
%s
实例(Python3.0+):
|
1
2
3
|
name = "makes"print("my name is %s" %name)#my name is makes |
%f
实例(Python3.0+):
|
1
2
3
4
|
print("%6.3f" % 2.3)#2.300print("%f" %2.3)#2.300000 |
二 format方法
位置映射

实例(Python3.0+):
|
1
2
|
print("{}:{}".format('192.168.0.100',8888))#192.168.0.100:8888 |
关键字映射

实例(Python3.0+):
|
1
2
|
print("{server}{1}:{0}".format(8888,'192.168.1.100',server='Web Server Info :'))#Web Server Info :192.168.1.100:8888 |
元素访问


实例(Python3.0+):
|
1
2
|
print("{0[0]}.{0[1]}".format(('baidu','com')))#baidu.com |
填充对齐
- ^、<、>分别是居中、左对齐、右对齐
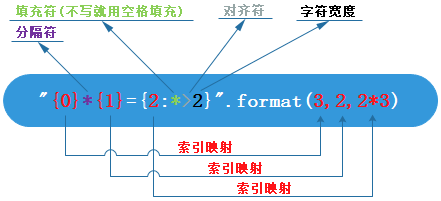
实例1(Python3.0+):
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
print("{0}*{1}={2:0>2}".format(3,2,2*3))#3*2=06print("{:*^30}".format('centered'))#***********centered*********** |
实例2(Python3.0+):九九乘法表
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
for i in range(1,10): a = 1 while a <= i: print("{0}*{1}={2:0>2}".format(a,i,a*i),end="\t") a +=1 print() """1*1=01 1*2=02 2*2=04 1*3=03 2*3=06 3*3=09 1*4=04 2*4=08 3*4=12 4*4=16 1*5=05 2*5=10 3*5=15 4*5=20 5*5=25 1*6=06 2*6=12 3*6=18 4*6=24 5*6=30 6*6=36 1*7=07 2*7=14 3*7=21 4*7=28 5*7=35 6*7=42 7*7=49 1*8=08 2*8=16 3*8=24 4*8=32 5*8=40 6*8=48 7*8=56 8*8=64 1*9=09 2*9=18 3*9=27 4*9=36 5*9=45 6*9=54 7*9=63 8*9=72 9*9=81 """ |
精度设置
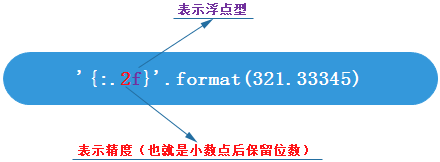
实例(Python3.0+):
|
1
2
3
4
|
print("{:.3f}".format(2.1415))#2.142print("{:.10f}".format(3.1415))#3.1415000000 |



