背包、队列和栈
前言: 我们为包,队列和堆栈定义API。除了基础知识,这些API反映了两个Java特性:泛型和可迭代集合。

背包:
一种不支持删除操作的数据结构,目的是为了帮助用例搜集元素并迭代遍历所有元素。比如一个人喜欢搜集各种石头,他将搜集到的石头都放到一个包里,一次一个,这些搜集到的石头他都很喜欢,不会扔掉,并且有时还会从背包里找出具有某些特征的石头。在这种数据结构中,顺序显得一点也不重要。
队列:
一种基于先进先出策略的集合类型,按照他们到达的顺序执行任务的政策是我们在日常生活中经常遇到的任务:从在剧院排队等候的人,到在收费站排队等候的车,到等待应用程序提供服务的任务。
栈:
一种基于先进后出策略的集合类型,例如:单击超链接时,浏览器将显示新页面(并将其推送到堆栈)。您可以继续单击超链接以访问新页面,但您可以通过单击后退按钮(从堆栈中弹出)来重新访问上一页
实现:
定容栈:
我们用一个数组来存储压入栈中的元素。

1 public class FixedCapacityStack<T> { 2 private T[] ary; 3 private int N; 4 public FixedCapacityStack(int cap) 5 { 6 ary=(T[])new Object[cap]; 7 N=0; 8 9 } 10 public boolean isEmpty() 11 { 12 return N==0; 13 } 14 15 public int size() 16 { 17 return N; 18 } 19 20 public void push(T t) 21 { 22 23 ary[N++]=t; 24 } 25 public T pop() 26 { 27 return ary[--N]; 28 } 29 30 }
调整数组大小:

1 public class ResizingArrayStack<T> implements Iterable<T> { 2 private T[] a; // array of Ts 3 private int n; // number of elements on stack 4 5 6 public ResizingArrayStack() { 7 a = (T[]) new Object[2]; 8 n = 0; 9 } 10 11 12 public boolean isEmpty() { 13 return n == 0; 14 } 15 16 17 public int size() { 18 return n; 19 } 20 21 22 23 private void resize(int capacity) { 24 assert capacity >= n; 25 26 27 T[] temp = (T[]) new Object[capacity]; 28 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 29 temp[i] = a[i]; 30 } 31 a = temp; 32 33 } 34 35 36 37 38 public void push(T T) { 39 if (n == a.length) resize(2*a.length); 40 a[n++] = T; 41 } 42 43 44 public T pop() { 45 if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Stack underflow"); 46 T T = a[n-1]; 47 a[n-1] = null; 48 n--; 49 50 if (n > 0 && n == a.length/4) resize(a.length/2); 51 return T; 52 } 53 54 55 56 public T peek() { 57 if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Stack underflow"); 58 return a[n-1]; 59 } 60 61 public Iterator<T> iterator() { 62 return new ReverseArrayIterator(); 63 } 64 65 66 private class ReverseArrayIterator implements Iterator<T> { 67 private int i; 68 69 public ReverseArrayIterator() { 70 i = n-1; 71 } 72 73 public boolean hasNext() { 74 return i >= 0; 75 } 76 77 public void remove() { 78 throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); 79 } 80 81 public T next() { 82 if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException(); 83 return a[i--]; 84 } 85 } 86 }
ResizingArrayStack的缺点在于进行某些pop和push操作时会调整数组大小,耗时和数组大小成正比。
队列实现:

1 public class ResizingArrayQueue<T> implements Iterable<T> { 2 private T[] q; 3 private int n; 4 private int first; 5 private int last; 6 7 8 9 public ResizingArrayQueue() { 10 q = (T[]) new Object[2]; 11 n = 0; 12 first=0; 13 last=0; 14 15 } 16 17 18 public boolean isEmpty() { 19 return n == 0; 20 } 21 22 23 public int size() { 24 return n; 25 } 26 27 28 29 private void resize(int capacity) { 30 assert capacity >= n; 31 32 33 T[] temp = (T[]) new Object[capacity]; 34 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 35 temp[i] = q[(i+first)%q.length]; 36 } 37 q=temp; 38 first=0; 39 last=n; 40 41 } 42 43 44 45 public void enqueue(T t) { 46 if (n == q.length) resize(2*q.length); 47 q[last++]=t; 48 if(last==q.length) last=0; 49 n++; 50 51 } 52 53 54 public T dequeue() { 55 if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Queue underflow"); 56 T t = q[first]; 57 q[first] = null; 58 first++; 59 if(first==q.length) 60 first=0; 61 62 63 if (n > 0 && n == q.length/4) resize(q.length/2); 64 return t; 65 } 66 67 68 69 public T peek() { 70 if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Stack underflow"); 71 return q[n-1]; 72 } 73 74 75 public Iterator<T> iterator() { 76 return new ReverseArrayIterator(); 77 } 78 79 80 private class ReverseArrayIterator implements Iterator<T> { 81 private int i=0; 82 83 84 public boolean hasNext() { 85 return i<n; 86 } 87 88 public void remove() { 89 throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); 90 } 91 92 public T next() { 93 if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException(); 94 T t=q[(i+first)%q.length]; 95 i++; 96 return t; 97 } 98 } 99 }
下面我们使用链表来表示:
链表:
链表是一个递归的数据结构,它或者为空、或者指向一个节点的引用,该节点含有一个泛型元素和一个指向另一条链表的引用。
例如: private class node
{ T t;
Node next;
}
构造链表:
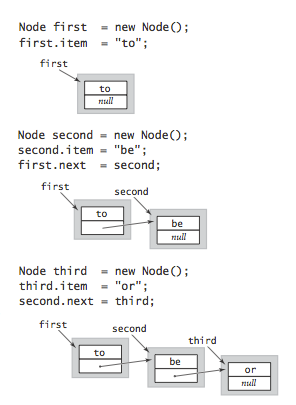
Node first=new Node();
Node second=new Node();
Node third=new Node();
现在为t赋值,假定t为String类型。
first.t=”to”;
second=”be”;
third=”or”;
设置next域来连接节点。
first.next=second;
second.next=third;
如图:
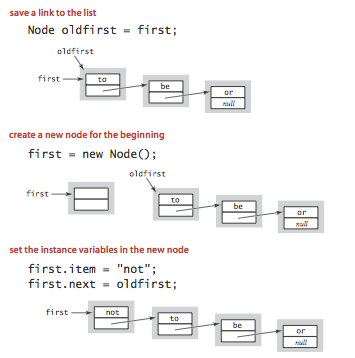
在表头插入和删除元素:
对一个节点操作,要注意先取值保存再赋值。
插入:
删除:
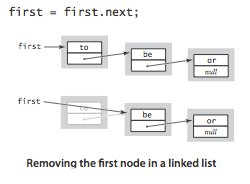
Java中的垃圾回收会确保老的first节点被回收。
在表尾插入节点:
要在链表的末尾插入节点,我们会保留指向列表中最后一个节点的链接:
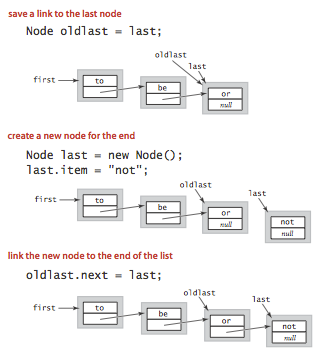
如果想在任意位置插入删除,需要用到双向链表(Java就是这么做的),在阅读源码系列里再讨论。
遍历:
for(Node x=first;x!=null;x=x.next)
{
x.t;
}
具体实现:
栈的链表实现:

1 public class Stack<T> implements Iterable<T> { 2 private Node<T> first; 3 private int n; 4 5 public Stack() 6 { 7 first=null; 8 n=0; 9 } 10 public boolean isEmpty() 11 { 12 return n==0;//first==null; 13 } 14 public int size() 15 { 16 return n; 17 } 18 19 public void push(T t) 20 { 21 Node<T> oldfirst=first; 22 first=new Node<T>(); 23 first.t=t; 24 first.next=oldfirst; 25 n++; 26 27 } 28 29 public T pop() 30 { 31 if(isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Stack underflow"); 32 T t=(T) first.t; 33 first=first.next; 34 n--; 35 return t; 36 37 } 38 39 public T peek() { 40 if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Stack underflow"); 41 return (T) first.t; 42 } 43 44 45 46 @Override 47 public String toString() { 48 StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(); 49 for ( T item : this) { 50 s.append(item); 51 s.append(' '); 52 } 53 return s.toString(); 54 } 55 private class Node<T> 56 { T t; 57 Node<T> next; 58 } 59 60 @Override 61 public Iterator<T> iterator() { 62 return new ListIterator(first); 63 } 64 65 private class ListIterator implements Iterator<T> 66 { 67 private Node<T> current; 68 69 public ListIterator(Node<T> first) 70 { 71 current=first; 72 } 73 74 @Override 75 public boolean hasNext() { 76 return (current!=null); 77 } 78 79 @Override 80 public T next() { 81 if(!hasNext())throw new NoSuchElementException("Stack underflow"); 82 T t=current.t; 83 current=current.next; 84 return t; 85 } 86 87 } 88 89 90 }
队列实现:

1 public class Queue<T> implements Iterable<T>{ 2 3 private Node<T> first; 4 private Node<T> last; 5 private int n; 6 7 public Queue() 8 { 9 first=null; 10 last=null; 11 n=0; 12 } 13 14 public boolean isEmpty() { 15 return first == null; 16 } 17 18 public int size() { 19 return n; 20 } 21 22 public T peek() { 23 if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Queue underflow"); 24 return first.t; 25 } 26 27 public void enqueue(T t) 28 { 29 Node<T> oldlast=last; 30 last=new Node<T>(); 31 last.t=t; 32 last.next=null; 33 if(isEmpty()) first=last; 34 else 35 oldlast.next=last; 36 n++; 37 } 38 39 @Override 40 public String toString() { 41 StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(); 42 for ( T item : this) { 43 s.append(item); 44 s.append(' '); 45 } 46 return s.toString(); 47 } 48 @Override 49 public Iterator<T> iterator() { 50 return new ListIterator(first); 51 } 52 private class ListIterator implements Iterator<T> 53 { 54 private Node<T> current; 55 56 public ListIterator(Node<T> first) 57 { 58 current=first; 59 } 60 @Override 61 public boolean hasNext() { 62 return current!=null; 63 } 64 65 @Override 66 public T next() { 67 if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException(); 68 T t=current.t; 69 current=current.next; 70 return t; 71 } 72 73 } 74 public T dequeue() 75 { 76 if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Queue underflow"); 77 T t=first.t; 78 first=first.next; 79 n--; 80 if(isEmpty()) last=null; 81 return null; 82 } 83 private static class Node<T> 84 { 85 private T t; 86 private Node<T> next; 87 } 88 89 90 91 92 }
背包实现:
//除了将push()的名称更改为add()和删除 pop()之外,其实现与Stack.java相同

1 public class Bag<T> implements Iterable<T> { 2 private Node<T> first; 3 private int n; 4 5 public Bag() 6 { 7 first=null; 8 n=0; 9 } 10 public boolean isEmpty() 11 { 12 return n==0;//first==null; 13 } 14 public int size() 15 { 16 return n; 17 } 18 19 public void add(T t) 20 { 21 Node<T> oldfirst=first; 22 first=new Node<T>(); 23 first.t=t; 24 first.next=oldfirst; 25 n++; 26 27 } 28 29 30 public T peek() { 31 if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Stack underflow"); 32 return (T) first.t; 33 } 34 35 36 37 @Override 38 public String toString() { 39 StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(); 40 for ( T item : this) { 41 s.append(item); 42 s.append(' '); 43 } 44 return s.toString(); 45 } 46 private class Node<T> 47 { T t; 48 Node<T> next; 49 } 50 51 @Override 52 public Iterator<T> iterator() { 53 return new ListIterator(first); 54 } 55 56 private class ListIterator implements Iterator<T> 57 { 58 private Node<T> current; 59 60 public ListIterator(Node<T> first) 61 { 62 current=first; 63 } 64 65 @Override 66 public boolean hasNext() { 67 return (current!=null); 68 } 69 70 @Override 71 public T next() { 72 if(!hasNext())throw new NoSuchElementException("Stack underflow"); 73 T t=current.t; 74 current=current.next; 75 return t; 76 } 77 78 } 79 80 81 }




