shiro-permission.ini
创建存放权限的配置文件shiro-permission.ini,如下:
[users] #用户zhang的密码是1111111,此用户具有role1和role2两个角色 zhang=111111,role1,role2 wang=111111,role2 [roles] #角色role1对资源user拥有create、update权限 role1=user:create,user:update #角色role2对资源user拥有create、delete权限 role2=user:create,user:delete #角色role3对资源user拥有create权限 role3=user:create
在ini文件中用户、角色、权限的配置规则是:“用户名=密码,角色1,角色2...” “角色=权限1,权限2...”,首先根据用户名找角色,再根据角色找权限,角色是权限集合。
权限字符串规则
权限字符串的规则是:“资源标识符:操作:资源实例标识符”,意思是对哪个资源的哪个实例具有什么操作,“:”是资源/操作/实例的分割符,权限字符串也可以使用*通配符。
例子:
用户创建权限:user:create,或user:create:*
用户修改实例001的权限:user:update:001
用户实例001的所有权限:user:*:001
测试代码
测试代码同认证代码,注意ini地址改为shiro-permission.ini,主要学习下边授权的方法,注意:在用户认证通过后执行下边的授权代码。

基于角色的授权
System.out.println("是否拥有role角色:"+subject.hasRole("role1"));
System.out.println("是否拥有role1,role2角色:"+subject.hasAllRoles(Arrays.asList("role1","role2")));
// check是否拥有role角色
subject.checkRole("role1");
subject.checkRoles("role1","role2");
上边check方法如果授权失败则抛出异常:
org.apache.shiro.authz.UnauthorizedException: Subject does not have role [.....]
基于资源权限
//基于资源的授权 System.out.println("是否拥有user:create的权限:"+subject.isPermitted("user:create")); System.out.println("是否拥有user的多个权限:"+subject.isPermittedAll("user:create","user:update"));//返回true //查询每个权限结果 boolean[] permitted = subject.isPermitted("user:create","user:update","user:add"); for (boolean b : permitted) { System.out.println(b);//返回 true,true,false } System.out.println("是否拥有user的多个权限:"+permitted.length);//返回3个结果 //check检查权限 subject.checkPermission("user:create"); //check检查全部权限是否都有 subject.checkPermissions("user:create","user:update");
上边check方法如果授权失败则抛出异常:
org.apache.shiro.authz.UnauthorizedException: Subject does not have permission [....]
自定义realm
与上边认证自定义realm一样,大部分情况是要从数据库获取权限数据,这里直接实现基于资源的授权。
realm代码
在认证章节写的自定义realm类中完善doGetAuthorizationInfo方法,此方法需要完成:根据用户身份信息从数据库查询权限字符串,由shiro进行授权。
查看jdbcRealm中的授权源码 尽心参照
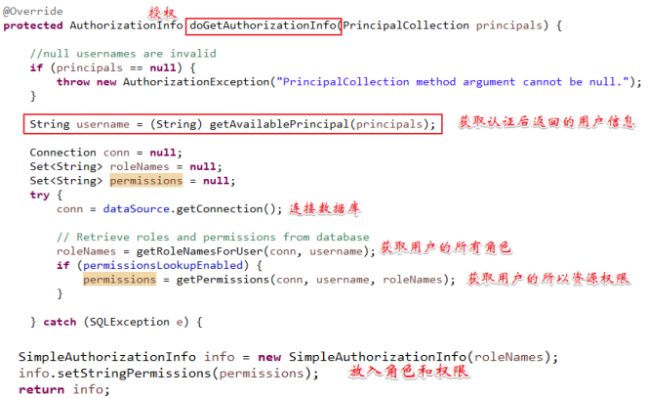
授权 @Override protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) { //null usernames are invalid if (principals == null) { throw new AuthorizationException("PrincipalCollection method argument cannot be null."); } //获取认证之后返回的身份信息 String username = (String) getAvailablePrincipal(principals); // 根据身份信息从数据库中查询权限数据 //....这里使用静态数据模拟 List<String> permissions = new ArrayList<>(); permissions.add("user:create"); permissions.add("user:add"); //将权限信息封闭为AuthorizationInfo SimpleAuthorizationInfo info = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo(); info.addStringPermissions(permissions); return info; }
测试源码不变
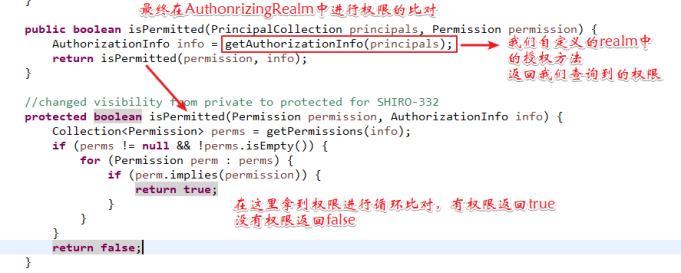
授权执行流程
1、 执行subject.isPermitted("user:create")
2、 securityManager最终通过AuthonrezingRealm进行授权
3、 AuthonrezingRealm调用realm获取权限信息
4、 AuthonrezingRealm再通过permissionResolver解析权限字符串,校验是否匹配