Java多线程-synchronized同步方法
1、synchronized 方法与锁对象
线程锁的是对象。
1)A线程先持有 object 对象的 Lock 锁, B线程可以以异步的方式调用 object 对象中的非 synchronized 类型的方法
2)A线程先持有 object 对象的 Lock 锁, B线程如果在这时调用 object 对象中的 synchronized 类型的方法,则需要等待,也就是同步。
2、脏读(DirtyRead)
示例:
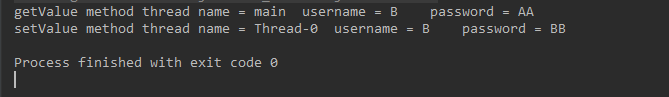
public class DirtyReadTest { public static void main(String[] args) { try { PublicVar publicVar = new PublicVar(); ThreadA thread = new ThreadA(publicVar); thread.start(); Thread.sleep(200); publicVar.getValue(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } static class ThreadA extends Thread { private PublicVar publicVar; public ThreadA(PublicVar publicVar) { this.publicVar = publicVar; } @Override public void run() { super.run(); publicVar.setValue("B", "BB"); } } static class PublicVar { public String username = "A"; public String password = "AA"; synchronized public void setValue(String username, String password) { try { this.username = username; Thread.sleep(1000); this.password = password; System.out.println("setValue method thread name = " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\tusername = " + username + "\tpassword = " + password); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } // 因为 getValue 方法是非 synchronized 方法,所以造成了脏读 public void getValue() { System.out.println("getValue method thread name = " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\tusername = " + username + "\tpassword = " + password); } } }
结果如图:
3、synchronized 锁重入
"可重入锁"的概念是:
自己可以再次活得自己的内部锁。比如有1条线程获得了某个对象的锁,此时这个对象锁还没有释放,当其再次想要获取这个对象的锁的时候还是可以获取的,如果不可以锁重入的话,就会造成死锁。
可重入锁也支持在父子类继承的环境中:在继承中,子类是完全可以通过“可重入锁”调用父类的同步方法的。
4、出现异常,锁自动释放
线程出现异常,会释放当前线程的锁
5、synchronizd 不具有继承性
示例:
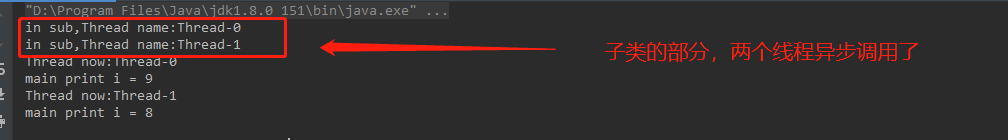
public class SyncExtend { public static void main(String[] args) { Sub sub = new Sub(); MyThread t1 = new MyThread(sub); MyThread t2 = new MyThread(sub); t1.start(); t2.start(); } static class MyThread extends Thread { Sub sub; public MyThread(Sub sub) { this.sub = sub; } @Override public void run() { try { sub.opera(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } static class Main { public int i = 10; synchronized public void opera() throws InterruptedException { try { System.out.println("Thread now:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); i--; Thread.sleep(3000); System.out.println("main print i = " + i); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } static class Sub extends Main { @Override public void opera() throws InterruptedException { System.out.println("in sub,Thread name:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); Thread.sleep(100); super.opera(); } } }
运行结果: