【专项学习】 —— Typescript高级语法
一、类的装饰器
①package.json中添加dev命令
"dev": "ts-node ./src/index.ts"
②tsconfig.json中把实验类型的支持打开
"experimentalDecorators": true,
"emitDecoratorMetadata": true,
③使用多个装饰器,从上到下(从左到右)收集装饰器,从下到上(从右到左)执行装饰器
//类的装饰器
//装饰器本身是一个函数
//类装饰器接受的参数是构造函数
//装饰器通过 @ 符号来使用
function testDecorator(constructor: any) {
// constructor.prototype.getName = () => {
// console.log('dell');
// }
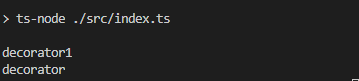
console.log('decorator');
}
function testDecorator1(constructor: any) {
console.log('decorator1');
}
//装饰器会在类创建好之后立即执行,对类做一些装饰
@testDecorator
@testDecorator1
class Test {}
const test = new Test();
// (test as any).getName();
④定义函数,使用工厂模式返回装饰器,使得在满足一定条件后才会执行装饰器
function testDecorator(flag: boolean){
if(flag) {
return function (constructor: any) {
constructor.prototype.getName = () => {
console.log('dell');
}
}
}else{
return function (constructor: any) {};
}
}
@testDecorator(true)
class Test {}
const test = new Test();
(test as any).getName();
⑤constructor类型由any类型改为定义为泛型T
// new后面是一个构造函数,接收很多参数,每一个参数的类型是any,返回的是一个any类型的内容
// T 类型可以被这个构造函数实例化出来
function testDecorator<T extends new (...args: any[]) => any>(constructor: T) {
return class extends constructor {
name = 'lee';
getName() {
return this.name;
}
};
}
@testDecorator
class Test {
name: string;
constructor(name: string) {
this.name = name;
}
}
const test = new Test('dell');
console.log((test as any).getName())
⑥解决test无法直接调用getName —— test.getName()会报错
function testDecorator() {
return function<T extends new (...args: any[]) => any>(constructor: T) {
return class extends constructor {
name = 'lee';
getName() {
return this.name;
}
};
};
}
//执行结果返回的装饰器,修饰class
const Test = testDecorator()(class {
name: string;
constructor(name: string) {
this.name = name;
}
})
const test = new Test('dell');
console.log(test.getName())
二、方法装饰器
//装饰器 永远都是一个函数
//普通方法, target对应的是类的prototype
//静态方法,target对应的是类的构造函数
//和Object.defineProperty类似
//Object.defineProperty(obj, prop, descriptor)
//参数:原型对象,属性,(descriptor保存着)控制函数的一些属性
function getNameDecorator(target: any, key: string, descriptor: PropertyDescriptor) {
//允许修改原始方法
// descriptor.writable = true;
//修改原始方法的值
descriptor.value = function () {
return 'decorator';
}
}
class Test {
name: string;
constructor(name: string) {
this.name = name;
}
@getNameDecorator
getName() {
return this.name;
}
}
const test = new Test('dell');
// test.getName = () => {
// return '123';
// }
console.log(test.getName());
三、访问器的装饰器
function visitDecorator(target: any, key: string, descriptor: PropertyDescriptor){
// 访问器不允许重写修改
// descriptor.writable = false;
}
class Test {
private _name: string;
constructor(name: string) {
this._name = name;
}
//Getter 访问器
get name() {
return this._name;
}
@visitDecorator
set name(name: string) {
this._name = name;
}
}
const test = new Test('dell');
test.name = '123123123123';
console.log(test.name);
四、属性的装饰器
// function nameDecorator(target: any, key: string): any{
// const descriptor: PropertyDescriptor = {
// writable: false
// };
// return descriptor; //会替换掉name属性的descriptor
// }
//修改的并不是实例上的name,而是原型上的name
function nameDecorator(target: any, key: string): any{
target[key] = 'lee';
}
//name 放在实例上
class Test {
@nameDecorator
name = 'Dell';
}
const test = new Test();
// test.name = 'dell lee';
// console.log(test.name); // Dell
console.log((test as any).__proto__.name); // lee
五、参数装饰器
// 原型, 方法名, 参数所在的位置
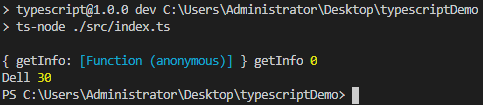
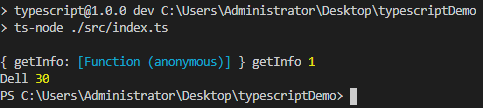
function paramDecorator(target: any, method: string, paramIndex: number){
console.log(target, method, paramIndex)
}
class Test {
getInfo( name: string, @paramDecorator age: number) {
console.log(name, age);
}
}
const test = new Test();
test.getInfo('Dell', 30);
六、装饰器实际使用的小例子
const userInfo: any = undefined;
//工厂模式写方法装饰器,解决代码复用中方法不同打印结果不同
function catchError(msg: string) {
return function (target: any, key: string, descriptor: PropertyDescriptor){
const fn = descriptor.value;
descriptor.value = function() {
try {
fn();
}catch(e) {
console.log(msg)
}
}
}
}
class Test {
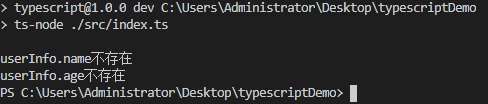
@catchError('userInfo.name不存在')
getName() {
// try{
// return userInfo.name
// }catch(e) {
// console.log('userInfo.name 不存在')
// }
return userInfo.name
}
@catchError('userInfo.age不存在')
getAge() {
// try{
// return userInfo.age
// }catch(e) {
// console.log('userInfo.age 不存在')
// }
return userInfo.age
}
}
const test = new Test();
test.getName();
test.getAge();
注:课程源自慕课网
越是迷茫、浮躁的时候,保持冷静和耐心,尤为重要


