平衡树学习笔记
平衡树学习笔记
一.BST:
Binary Search Tree,二叉搜索树。
用来维护满足某一大小关系的序列。
可实现操作如下:
1.插入x数
2.删除x数
3.查询x数的排名
4.查询排名为x的数
5.求x的前驱
6.求x的后继
对于每一种操作,最多只会从树根到叶子(后面会详细讲解),时间复杂度最大是树高。
满足以下性质:
对于树上任意一点x,左子树中所有点的权值小于x的权值,右子树中所有点的权值大于x的权值。
不难发现,对于同一种大小关系,此树有多种结构。
如图:
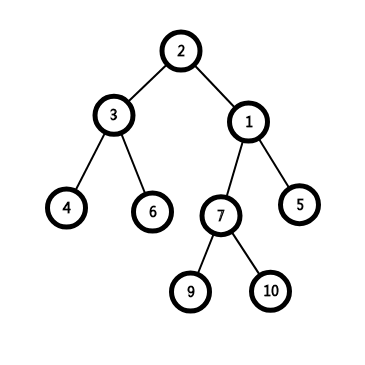

所以,我们为什么不调整结构,使树高最小(即最好变成完全二叉树,使时间复杂度达到稳定的O(㏒2n)呢?)
1.平衡树核心操作:旋转:(当然,BST不能,因为没有东西判断什么时候旋转)

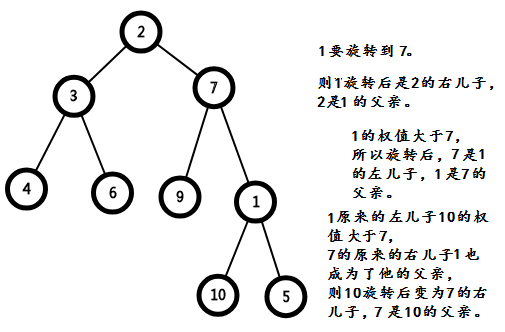
即为代码:
1 inline void pushup(int x){siz[x]=siz[son[x][0]]+siz[son[x][1]]+num[x];}
1 inline void rotate(int x) 2 { 3 int y=f[x]; int z=f[y],k=(son[y][1]==x); 4 if(z) son[z][son[z][1]==y]=x; f[x]=z; 5 son[y][k]=son[x][k^1],f[son[y][k]]=y; 6 son[x][k^1]=y,f[y]=x; 7 pushup(y),pushup(x); 8 }
2.插入:
对于任一节点x,插入的值为u,
则若x的权值小于u,u应该在x的右子树,x变为x的右儿子;
若x的权值大于u,u应该在x的左子树,x变为x的左儿子;
最后当x==0时,新建一个点。
//下面代码中:w[x]是权值,siz[x]是子树大小,num[x]是权值都为w[x]的值有几个,son[x][0]:左儿子,son[x][1]:右儿子,f[x]:父亲。
1 void ins(int x,int u) 2 { 3 if(!x){++o,w[1]=u,siz[1]=num[1]=1,f[1]=0,root=1; return;} 4 int t=son[x][w[x]<u]; 5 while(w[x]!=u&&t) ++siz[x],x=t,t=son[x][w[x]<u]; 6 if(w[x]!=u) ++siz[x],++o,w[o]=u,siz[o]=num[o]=1,son[x][w[x]<u]=o,f[o]=x; 7 else ++num[x]; 8 }
3.删除:
首先找到应被删除的点x,
当x的左儿子或右儿子为空时,直接让他们顶替x的位置。
如果x的左、右儿子都在时,怎么办呢?
将x旋到左儿子或右儿子为空时就行了。
1 void del(int x,int y){ 2 x=root;//root:根 3 while(w[x]!=y&&x) --siz[x],x=son[x][w[x]<y]; 4 if(!x) return -1; 5 if(num[x]>1) --num[x],--siz[x]; 6 else{ 7 while(son[x][1]&&son[x][0]) rotate(son[x][0]),--siz[f[x]]; 8 son[f[x]][son[f[x]][1]==x]=(son[x][0]|son[x][1]); f[son[x][0]|son[x][1]]=f[x]; 9 } 10 } 11 //临时手打,有错勿怪 12 //丑陋码风,不喜勿喷
4.排名:
找到权值为y的x,在找的过程中求出小于y的数sum,输出siz[son[x][0]]+sum+1。
1 void rnk(int x,int y){ 2 x=root; int sum=0; 3 while(w[x]!=y&&x){ 4 if(w[x]<y) sum+=siz[son[x][0]]+num[x],x=son[x][1]; 5 else x=son[x][0]; 6 } 7 if(!x) return -1; 8 return siz[son[x][0]]+1+sum; 9 }
5.k大数:
像3一样,当siz[son[x][0]]<y-sum<=siz[son[x][0]]+num[x]时输出w[x]。
1 int kth(int x,int y) 2 { 3 int t; 4 while(1) 5 { 6 t=siz[son[x][0]]+num[x]; 7 if(y>t) y-=t,x=son[x][1]; 8 else if(y>siz[son[x][0]]&&y<=t) return w[x]; 9 else x=son[x][0]; 10 } 11 }
6.前缀:
找到权值为y的x,在找的过程中求出小于y的数最大值,返回x左子树中最大值与路上最大值的最大值。(都快把自己绕晕了)
1 void pre(int x,int y){ 2 int maxn=-1; 3 while(w[x]!=y&&x){ 4 if(w[x]<y) maxn=max(w[x],maxn),x=son[x][1]; 5 else x=son[x][0]; 6 } 7 while(x) x=son[x][0],maxn=max(maxn,w[x]); 8 return maxn; 9 } 10 //临时手打,有错勿怪 11 //丑陋码风,不喜勿喷
7.后缀:
找到权值为y的x,在找的过程中求出大于y的数最小值,返回x左子树中最小值与路上最小值的最小值。
1 void nxt(int x,int y){ 2 int minw=inf; 3 while(w[x]!=y&&x){ 4 if(w[x]>y) minw=min(w[x],minw),x=son[x][0]; 5 else x=son[x][1]; 6 } 7 while(x) x=son[x][1],minw=min(minw,w[x]); 8 return minw; 9 } 10 //临时手打,有错勿怪 11 //丑陋码风,不喜勿喷
BST中代码只是临时手打,帮助大家理解,最好不要仿照,如有错误请指出,非常感谢。
不过接下来代码是测过的。
二.Treap:
1.介绍:
Treap=tree+heap,是一种满足BST和堆性质的数据结构。
其用递归和‘&’减少了很多码量,代码简洁,常数小,是写普通平衡树是最好打的数据结构。
缺点:也只能维护普通平衡树的操作,对于可持久化和翻转、合并、分离等操作无能为力。
2.特点:
用rnd数组储存随机值,用随机来满足树的平衡。
父亲rnd值始终比儿子的(大或小自己定义,我这里是按大)。
3.变化:(较BST)
多用'&'和递归,不需要父亲。
<1>.rotate:
1 void size(int u){siz[u]=siz[son[u][0]]+siz[son[u][1]]+1;} 2 void rotate(int &u,int d){//son[u][d^1] d==0?左旋:右旋。 3 int p=son[u][d^1]; 4 son[u][d^1]=son[p][d]; 5 son[p][d]=u; 6 size(u),size(p);//重新统计,先儿子后父亲 7 u=p;//实际上是将p顶替u的位置 8 }
<2>.ins:
1 int cmp(int u,int x){if(w[u]==x) return -1; return w[u]<x;} 2 //判断是左儿子还是右儿子 3 void ins(int &u,int x) 4 { 5 if(!u){u=++cnt; w[u]=x; rnd[u]=rand()%inf; siz[u]=1;}//新建点 6 else{ 7 ++siz[u]; 8 int d=cmp(u,x); if(d==-1) d=0; 9 ins(son[u][d],x); 10 if(rnd[u]<rnd[son[u][d]]) rotate(u,d^1); 11 //插入后如果不满足堆的性质,将插入的数旋上来 12 } 13 }
<3>.del:
1 void del(int &u,int x){ 2 int d=cmp(u,x); 3 if(d==-1){ 4 if(!(son[u][0]*son[u][1])){u=son[u][0]+son[u][1]; return;}//左或右儿子为空 5 else{ 6 int d2=(rnd[son[u][0]]>rnd[son[u][1]]?1:0); 7 rotate(u,d2); del(son[u][d2],x); 8 //将rnd大的儿子放在父亲处 9 } 10 } 11 else del(son[u][d],x); 12 size(u); 13 }
<4>.rnk ,<5>.kth ,<6>.pre和<7>.nxt可以沿用BST的,只不过,这里给出不用num且递归的做法:
1 int rnk(int u,int x){ 2 if(!u) return 1; 3 int d=cmp(u,x); 4 int e=rnk(son[u][d<=0?0:1],x); 5 if(d==-1&&!flag){flag=1; return siz[son[u][0]]+1;} 6 if(d<=0) return e; 7 return e+siz[son[u][0]]+1; 8 } 9 int kth(int u,int x){ 10 if(siz[son[u][0]]+1==x) return w[u]; 11 if(x<=siz[son[u][0]]) return kth(son[u][0],x); 12 else return kth(son[u][1],x-siz[son[u][0]]-1); 13 } 14 int pre(int u,int x){ 15 int d=cmp(u,x); 16 if(!u) return -inf; 17 if(d==-1) return pre(son[u][0],x); 18 if(d) return max(pre(son[u][1],x),w[u]); 19 return pre(son[u][0],x); 20 } 21 int nxt(int u,int x){ 22 int d=cmp(u,x); 23 if(!u) return inf; 24 if(d==-1) return nxt(son[u][1],x); 25 if(!d) return min(nxt(son[u][0],x),w[u]); 26 return nxt(son[u][1],x); 27 }
最后例题:
总代码:
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 const int N=100006,inf=1e8; 4 int son[N][2],w[N],rnd[N],siz[N],cnt=1,t,o,n,q=1,num=0; 5 bool flag; 6 inline int read() 7 { 8 int T=0,F=1; char ch=getchar(); 9 while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-') F=-1; ch=getchar();} 10 while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') T=(T<<3)+(T<<1)+(ch-48),ch=getchar(); 11 return F*T; 12 } 13 void size(int u){siz[u]=siz[son[u][0]]+siz[son[u][1]]+1;} 14 void rotate(int &u,int d){//son[u][d^1] d==0?左旋:右旋。 15 int p=son[u][d^1]; 16 son[u][d^1]=son[p][d]; 17 son[p][d]=u; 18 size(u),size(p);//重新统计,先儿子后父亲 19 u=p;//实际上是将p顶替u的位置 20 } 21 int cmp(int u,int x){if(w[u]==x) return -1; return w[u]<x;} 22 //判断是左儿子还是右儿子 23 void ins(int &u,int x) 24 { 25 if(!u){u=++cnt; w[u]=x; rnd[u]=rand()%inf; siz[u]=1;}//新建点 26 else{ 27 ++siz[u]; 28 int d=cmp(u,x); if(d==-1) d=0; 29 ins(son[u][d],x); 30 if(rnd[u]<rnd[son[u][d]]) rotate(u,d^1); 31 //插入后如果不满足堆的性质,将插入的数旋上来 32 } 33 } 34 void del(int &u,int x){ 35 int d=cmp(u,x); 36 if(d==-1){ 37 if(!(son[u][0]*son[u][1])){u=son[u][0]+son[u][1]; return;}//左或右儿子为空 38 else{ 39 int d2=(rnd[son[u][0]]>rnd[son[u][1]]?1:0); 40 rotate(u,d2); del(son[u][d2],x); 41 //将rnd大的儿子放在父亲处 42 } 43 } 44 else del(son[u][d],x); 45 size(u); 46 } 47 int rnk(int u,int x){ 48 if(!u) return 1; 49 int d=cmp(u,x); 50 int e=rnk(son[u][d<=0?0:1],x); 51 if(d==-1&&!flag){flag=1; return siz[son[u][0]]+1;} 52 if(d<=0) return e; 53 return e+siz[son[u][0]]+1; 54 } 55 int kth(int u,int x){ 56 if(siz[son[u][0]]+1==x) return w[u]; 57 if(x<=siz[son[u][0]]) return kth(son[u][0],x); 58 else return kth(son[u][1],x-siz[son[u][0]]-1); 59 } 60 int pre(int u,int x){ 61 int d=cmp(u,x); 62 if(!u) return -inf; 63 if(d==-1) return pre(son[u][0],x); 64 if(d) return max(pre(son[u][1],x),w[u]); 65 return pre(son[u][0],x); 66 } 67 int nxt(int u,int x){ 68 int d=cmp(u,x); 69 if(!u) return inf; 70 if(d==-1) return nxt(son[u][1],x); 71 if(!d) return min(nxt(son[u][0],x),w[u]); 72 return nxt(son[u][1],x); 73 } 74 int main() 75 { 76 srand(time(NULL)); siz[1]=1; w[1]=inf; rnd[1]=inf; memset(son,0,sizeof(son)); n=read(); 77 for(register int i=1;i<=n;++i){ 78 o=read(); t=read(); 79 switch(o){ 80 case 1:ins(q,t);break; 81 case 2:del(q,t);break; 82 case 3:flag=0,printf("%d\n",rnk(1,t));break; 83 case 4:printf("%d\n",kth(1,t));break; 84 case 5:printf("%d\n",pre(1,t));break; 85 case 6:printf("%d\n",nxt(1,t));break; 86 } 87 } 88 return 0; 89 }
三.fhq treap:
1.介绍:
fan hao qiang巨佬首创,你值得拥有。
它,操作简单,核心操作只有两项;它,码量极小,给你从未体验过的舒爽感觉;
它,常数巨大,不过跟Splay差不多(略大一点);它,功能多样,插、删、排、k大数、前、后、翻、离、并,样样精通。
你还在等什么,赶紧看完这篇博客,投入到代码的海洋里去吧!
2.特点:
<1>.拥有treap的性质
<2>.两个核心操作:split(分离)和merge(合并):
(1).split(x,k,y,z):将根为x的fhq treap分为权值小于等于k的、以y为根的fhq treap和权值大于k的、以z为根的fhq treap;
(2).merge(x,y,z):将以x为根的fhq treap和以y为根的fhq treap合为以z为根的fhq treap。(条件:x树中所有数的权值小于y树中任意一数的权值[即:max(x)<min(y)])
<3>.可持久化
<4>.支持区间操作(插入,删除,翻转,修改,求和,最大子序列和)
3.代码:
(1).普通平衡树:
<1>.分离:
真的不知道讲些什么,非常短小精悍,只能靠自己理解。
1 void split(int x,int k,int &l,int &r) 2 { 3 if(!x){l=0,r=0; return;} 4 if(k<w[x]) r=x,split(son[x][0],k,l,son[x][0]),pushup(x); 5 else l=x,split(son[x][1],k,son[x][1],r),pushup(x); 6 }
<2>.合并:
作者表示还是蒻得没话说。
1 void merge(int l,int r,int &o) 2 { 3 if(!l||!r){o=l+r; return;} 4 if(rnd[l]<rnd[r]) o=l,merge(son[l][1],r,son[l][1]),pushup(l); 5 else o=r,merge(l,son[r][0],son[r][0]),pushup(r); 6 }
<3>.插入:
插入一个数k。
直接将fhq treap分为<=k和>k的两部分t1和t2,再将t1与k合并为t1,t1与t2合并为root。
1 inline void new_point(int x){siz[++n]=1,rnd[n]=((rand()<<15)|rand()),w[n]=x;} 2 //我是个丧心病狂的压行狂魔 3 void ins(int k) 4 { 5 new_point(k); split(root,k,t1,t2);//new_point是新建一个点 6 merge(t1,n,root),merge(root,t2,root); 7 //n是权值为k的节点的编号 8 }
<4>.删除:
插入一个数k。
直接将fhq treap分为<=k和>k的两部分t2和t3,再将t2分为t1<k和t2==k的两部分,t1与t3合并为root即可。
1 void del(int x) 2 { 3 split(root,x,t1,t2),split(t1,x-1,t1,t3); 4 merge(son[t3][0],son[t3][1],t3); 5 }
<5>.排名:
求权值k的排名(不包括权值与其相等的)
直接将fhq treap分为权值<k和权值>=k的两部分t1和t2,k的排名为siz[t1]+1
1 split(root,t-1,t1,t2),printf("%d\n",siz[t1]+1),merge(t1,t2,root);
<6>.k大数:
求树中权值第k大数的权值。
实现操作和普通Treap一样,只不过这里用非递归形式,常数更小。
1 int kth(int x,int k) 2 //以x为根的树中的第k大数 3 { 4 while(1) 5 { 6 t=siz[son[x][0]]; 7 if(k<=t) x=son[x][0]; 8 else if(k==t+1) return w[x]; 9 else k=k-t-1,x=son[x][1]; 10 } 11 }
<7>.前驱:
求k的前驱。(权值小于k的最大值)
我们可以将树分为小于k的t1和大于等于k的t2两部分,k的前驱即是树t1中的最大权值(即kth(t1,size[t1])。
别忘了重新将树t1和t2合并为root。
1 split(root,t-1,t1,t2),printf("%d\n",kth(t1,siz[t1])),merge(t1,t2,root);
<8>.后继:(权值大于k的最小值)
同理,将树分为小于等于k的t1和大于k的t2两部分,k的后继即是树t2中的最小权值(kth(t2,1)),最后合并。
1 split(root,t,t1,t2),printf("%d\n",kth(t2,1)),merge(t1,t2,root);
总代码:
请叫我压行怪
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 #include<time.h> 3 #include<stdlib.h> 4 #define re register 5 using namespace std; 6 const int N=100006,inf=1e9; 7 int n=0,m,son[N][2],w[N],siz[N],rnd[N],root,t,opt,t1,t2,t3; 8 inline int read() 9 { 10 int T=0,F=1; char ch=getchar(); 11 while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-') F=-1; ch=getchar();} 12 while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') T=(T<<3)+(T<<1)+(ch-48),ch=getchar(); 13 return F*T; 14 } 15 inline void new_point(int x){siz[++n]=1,rnd[n]=((rand()<<15)|rand()),w[n]=x;} 16 inline void pushup(int x){siz[x]=siz[son[x][0]]+siz[son[x][1]]+1;} 17 void split(int x,int k,int &l,int &r) 18 { 19 if(!x){l=0,r=0; return;} 20 if(k<w[x]) r=x,split(son[x][0],k,l,son[x][0]),pushup(x); 21 else l=x,split(son[x][1],k,son[x][1],r),pushup(x); 22 } 23 void merge(int l,int r,int &o) 24 { 25 if(!l||!r){o=l+r; return;} 26 if(rnd[l]<rnd[r]) o=l,merge(son[l][1],r,son[l][1]),pushup(l); 27 else o=r,merge(l,son[r][0],son[r][0]),pushup(r); 28 } 29 int kth(int x,int k) 30 { 31 while(1) 32 { 33 t=siz[son[x][0]]; 34 if(k<=t) x=son[x][0]; 35 else if(k==t+1) return w[x]; 36 else k=k-t-1,x=son[x][1]; 37 } 38 } 39 void ins(int x){new_point(x),split(root,x,t1,t2),merge(t1,n,root),merge(root,t2,root);} 40 void del(int x){split(root,x,t1,t2),split(t1,x-1,t1,t3),merge(son[t3][0],son[t3][1],t3),merge(t1,t3,t1),merge(t1,t2,root);} 41 int main() 42 { 43 m=read(); 44 for(re int i=1;i<=m;++i) 45 { 46 opt=read(),t=read(); 47 switch(opt) 48 { 49 case 1:ins(t);break; 50 case 2:del(t);break; 51 case 3:split(root,t-1,t1,t2),printf("%d\n",siz[t1]+1),merge(t1,t2,root);break; 52 case 4:printf("%d\n",kth(root,t));break; 53 case 5:split(root,t-1,t1,t2),printf("%d\n",kth(t1,siz[t1])),merge(t1,t2,root);break; 54 case 6:split(root,t,t1,t2),printf("%d\n",kth(t2,1)),merge(t1,t2,root);break; 55 } 56 } 57 return 0; 58 }
(2).带有区间操作的平衡树:
比一般的平衡树加了个pushdwon(下传标记)以及各自需要支持的操作,
在merge和split中加入pushdown操作,
并且split修改为将一棵树分为<=size和>size两部分。
pushup加了许多新东西维护。
1 inline void equal(int x,int y){if(!x) return; w[x]=lazy[x]=y,sum[x]=siz[x]*y,ml[x]=mr[x]=mx[x]=(y>=0?sum[x]:y);} 2 inline void ress(int x){if(!x) return; re[x]^=1,swap(ml[x],mr[x]),swap(son[x][0],son[x][1]);} 3 inline void pushdown(int x) 4 { 5 if(!x) return; 6 int lc=son[x][0],rc=son[x][1]; 7 if(re[x]) re[x]=0,ress(lc),ress(rc); 8 if(lazy[x]!=inf2) equal(son[x][0],lazy[x]),equal(son[x][1],lazy[x]),lazy[x]=inf2; 9 }
1 inline void pushup(int x){ 2 int lc=son[x][0],rc=son[x][1]; 3 siz[x]=siz[lc]+siz[rc]+1; 4 sum[x]=sum[lc]+sum[rc]+w[x]; 5 ml[x]=max(ml[lc],max(sum[lc]+w[x],sum[lc]+w[x]+ml[rc])); 6 mr[x]=max(mr[rc],max(sum[rc]+w[x],sum[rc]+w[x]+mr[lc])); 7 mx[x]=max(mx[lc],max(mx[rc],max(mr[lc],0)+w[x]+max(ml[rc],0))); 8 }
1 void split(int x,int k,int &l,int &r){ 2 if(!x){l=r=0; return;} 3 pushdown(x); p=siz[son[x][0]]+1; 4 if(p<=k) l=x,split(son[x][1],k-p,son[x][1],r),pushup(x); 5 else r=x,split(son[x][0],k,l,son[x][0]),pushup(x); 6 } 7 void merge(int l,int r,int &o){ 8 if(!l||!r){o=(l|r); pushdown(o); return;} 9 if(rnd[l]<rnd[r]) pushdown(l),o=l,merge(son[l][1],r,son[l][1]),pushup(l); 10 else pushdown(r),o=r,merge(l,son[r][0],son[r][0]),pushup(r); 11 }
解释一下数组含义:
siz[x]:子树大小
rnd[x]:随机值
w[x]:权值
sum[x]:子树内权值总和
lazy[x]:懒标记,代表子树内所有点被修改为lazy[x]
re[x]:懒标记,代表子树内所有点都被翻转/没被翻转
son[x][0/1]:左右儿子
ml[x]:从子树内最左端点开始的最大连续子段和
mr[x]:从子树内最右端点开始的最大连续子段和
mx[x]:子树内最大连续子段和
我们可以发现:

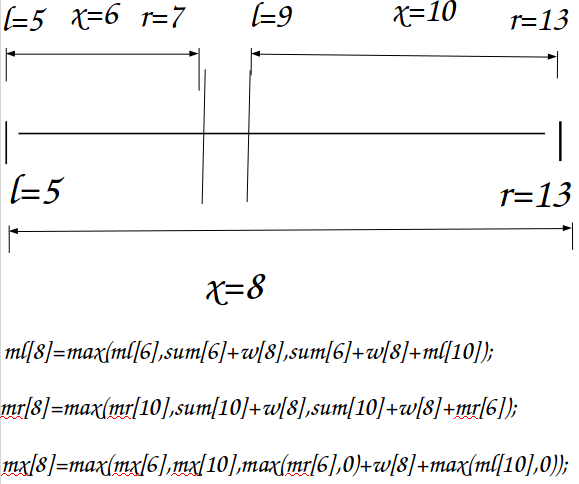
对于每一个区间[l,r],我们将root分为[1,l-1],[l,r],[r+1,n]三部分,操作完再合并。
1 split(root,r,t1,t3),split(t1,l-1,t1,t2); 2 //bula bula bula~~~; 3 merge(t2,t3,t2),merge(t1,t2,root); 4 //注意:split(root,l-1,t1,t2),split(t2,r,t2,t3)是错误的 5 //在将root分为树t1、t2后,r在t2中处于第r-l+1个位置 6 //split(root,l-1,t1,t2),split(t2,r-l+1,t2,t3);
<1>.翻转:
1 void res(int x,int k){split(root,x+k-1,t2,t3),split(t2,x-1,t1,t2),ress(t2),merge(t1,t2,t1),merge(t1,t3,root);}
<2>.修改:
1 void chg(int x,int k,int y){split(root,x+k-1,t2,t3),split(t2,x-1,t1,t2),equal(t2,y),merge(t1,t2,t1),merge(t1,t3,root);}
<3>.求和:
1 void gtsum(int x,int k){split(root,x+k-1,t2,t3),split(t2,x-1,t1,t2),printf("%d\n",sum[t2]),merge(t1,t2,t1),merge(t1,t3,root);}
<4>.插入:
要求线性建树,因此要用到笛卡尔树建树法:
笛卡尔树:
满足Treap,key值左儿子小于本身小于右儿子,val值祖先大/小于孙辈的性质,(不妨设val值越大,深度越高)。
因此常用于线性建Treap。
其方法大致如下:
首先将点按key值排序,后插入的点一定为先插入的点的右儿子
维护一个关于val的单调栈,依次存放根,根的右儿子,根的右儿子的右儿子,根的右儿子的右儿子的右儿子………
每次新加入节点x,将val值大于x的点从栈里清除,x变为val值小于x且相差x最小的点y的右儿子,y点原先的右儿子z变为x的左儿子。
我们可以发现:x、y、z间恰好满足:val[z]>val[x]>val[y],key[x]>key[z]>key[y],符合Treap的性质。
1 void ins(int x,int k){ 2 rt=0,t=0; 3 for(int i=1;i<=k;++i){ 4 t1=read(),new_point(t1); 5 while(rnd[num]<rnd[s[t]]&&t>=1) pushup(s[t]),son[num][0]=s[t],--t; 6 if(t) son[s[t]][1]=num; 7 else rt=num; 8 s[++t]=num; 9 } 10 while(t>=1) pushup(s[t]),--t; 11 split(root,x,t1,t2); 12 merge(t1,rt,t1); 13 merge(t1,t2,root); 14 }
<5>.删除:
1 void del(int x,int k){split(root,x+k-1,t2,t3),split(t2,x-1,t1,t2),merge(t1,t3,root),add(t2);}
<6>.最大连续子段和:
1 void mxsum(int x,int k){split(root,x+k-1,t2,t3),split(t2,x-1,t1,t2),printf("%d\n",mx[t2]),merge(t1,t2,t1),merge(t1,t3,root);}
总代码:
1 // luogu-judger-enable-o2 2 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 3 #define reg register 4 using namespace std; 5 const int N=5e5+6,inf=-(1<<30),inf2=-1006; 6 int n,m,tot=0,top=0,num,t,root=0,rt,t1,t2,t3,p,s[N],re[N],son[N][2],bin[N],siz[N],sum[N],w[N],ml[N],mr[N],mx[N],rnd[N],lazy[N]; 7 bool flag=0; 8 char c[33]; 9 inline int read(){ 10 int T=0,F=1; char ch=getchar(); 11 while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-') F=-1; ch=getchar();} 12 while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') T=(T<<3)+(T<<1)+(ch-48),ch=getchar(); 13 return F*T; 14 } 15 inline void new_point(int x){ 16 if(top) num=bin[top],--top; 17 else num=++tot; 18 lazy[num]=inf2,re[num]=0,siz[num]=1,son[num][0]=son[num][1]=0,ml[num]=mr[num]=mx[num]=sum[num]=w[num]=x,rnd[num]=((rand()<<15)|rand()); 19 } 20 inline void pushup(int x){ 21 int lc=son[x][0],rc=son[x][1]; 22 siz[x]=siz[lc]+siz[rc]+1; 23 sum[x]=sum[lc]+sum[rc]+w[x]; 24 ml[x]=max(ml[lc],max(sum[lc]+w[x],sum[lc]+w[x]+ml[rc])); 25 mr[x]=max(mr[rc],max(sum[rc]+w[x],sum[rc]+w[x]+mr[lc])); 26 mx[x]=max(mx[lc],max(mx[rc],max(mr[lc],0)+w[x]+max(ml[rc],0))); 27 } 28 inline void equal(int x,int y){if(!x) return; w[x]=lazy[x]=y,sum[x]=siz[x]*y,ml[x]=mr[x]=mx[x]=(y>=0?sum[x]:y);} 29 inline void ress(int x){if(!x) return; re[x]^=1,swap(ml[x],mr[x]),swap(son[x][0],son[x][1]);} 30 inline void pushdown(int x) 31 { 32 if(!x) return; 33 int lc=son[x][0],rc=son[x][1]; 34 if(re[x]) re[x]=0,ress(lc),ress(rc); 35 if(lazy[x]!=inf2) equal(son[x][0],lazy[x]),equal(son[x][1],lazy[x]),lazy[x]=inf2; 36 } 37 void split(int x,int k,int &l,int &r){ 38 if(!x){l=r=0; return;} 39 pushdown(x); p=siz[son[x][0]]+1; 40 if(p<=k) l=x,split(son[x][1],k-p,son[x][1],r),pushup(x); 41 else r=x,split(son[x][0],k,l,son[x][0]),pushup(x); 42 } 43 void merge(int l,int r,int &o){ 44 if(!l||!r){o=(l|r); pushdown(o); return;} 45 if(rnd[l]<rnd[r]) pushdown(l),o=l,merge(son[l][1],r,son[l][1]),pushup(l); 46 else pushdown(r),o=r,merge(l,son[r][0],son[r][0]),pushup(r); 47 } 48 void ins(int x,int k){ 49 rt=0,t=0; 50 for(int i=1;i<=k;++i){ 51 t1=read(),new_point(t1); 52 while(rnd[num]<rnd[s[t]]&&t>=1) pushup(s[t]),son[num][0]=s[t],--t; 53 if(t) son[s[t]][1]=num; 54 else rt=num; 55 s[++t]=num; 56 } 57 while(t>=1) pushup(s[t]),--t; 58 split(root,x,t1,t2); 59 merge(t1,rt,t1); 60 merge(t1,t2,root); 61 } 62 void add(int x){if(!x) return; bin[++top]=x,add(son[x][0]),add(son[x][1]);} 63 void del(int x,int k){split(root,x+k-1,t2,t3),split(t2,x-1,t1,t2),merge(t1,t3,root),add(t2);} 64 void chg(int x,int k,int y){split(root,x+k-1,t2,t3),split(t2,x-1,t1,t2),equal(t2,y),merge(t1,t2,t1),merge(t1,t3,root);} 65 void res(int x,int k){split(root,x+k-1,t2,t3),split(t2,x-1,t1,t2),ress(t2),merge(t1,t2,t1),merge(t1,t3,root);} 66 void gtsum(int x,int k){split(root,x+k-1,t2,t3),split(t2,x-1,t1,t2),printf("%d\n",sum[t2]),merge(t1,t2,t1),merge(t1,t3,root);} 67 void mxsum(int x,int k){split(root,x+k-1,t2,t3),split(t2,x-1,t1,t2),printf("%d\n",mx[t2]),merge(t1,t2,t1),merge(t1,t3,root);} 68 int main(){ 69 n=read(),m=read(); 70 ins(0,n); ml[0]=mr[0]=mx[0]=-(1<<30); w[0]=sum[0]=siz[0]=0; lazy[0]=-1006; 71 for(reg int i=1;i<=m;++i){ 72 scanf("%s",c); t=strlen(c); 73 if(c[0]=='I') t1=read(),t2=read(),ins(t1,t2); 74 else if(c[0]=='D') t1=read(),t2=read(),del(t1,t2); 75 else if(c[0]=='R') t1=read(),t2=read(),res(t1,t2); 76 else if(c[0]=='cG'&&t>3) t1=read(),t2=read(),gtsum(t1,t2); 77 else if(c[0]=='G') t1=read(),gtsum(t1,1); 78 else if(c[2]=='K') t1=read(),t2=read(),t3=read(),chg(t1,t2,t3); 79 else t1=read(),t2=read(),mxsum(t1,t2); 80 } 81 return 0; 82 }
(3).可持久化:(有多个历史版本,每一次修改基于指定的版本)
运用了主席树的思想,如有不懂可以先看我的博客: 主席树
我们每一次操作最多只会改变一条链。
因此,我们每次操作只要复制那条链,并在上面进行修改,其它的点只要沿用之前的即可,时间和空间被大大优化。
重点:copy(复制)函数和加了copy函数的split和merge
1 inline void copy(int x){w[++n]=w[x],son[n][0]=son[x][0],son[n][1]=son[x][1],rnd[n]=rnd[x];} 2 void split(int x,int k,int &l,int &r) 3 { 4 if(!x){l=0,r=0; return;} 5 if(w[x]<=k) copy(x),l=x=n,split(son[x][1],k,son[x][1],r),pushup(x); 6 else copy(x),r=x=n,split(son[x][0],k,l,son[x][0]),pushup(x); 7 } 8 void merge(int l,int r,int &o) 9 { 10 if(!l||!r){o=l+r; return;} 11 if(rnd[l]<rnd[r]) copy(l),o=l=n,merge(son[l][1],r,son[l][1]),pushup(l); 12 else copy(r),o=r=n,merge(l,son[r][0],son[r][0]),pushup(r); 13 }
<1>.普通平衡树:
代码:
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 #define re register 3 using namespace std; 4 const int N=5e5+6; 5 int n=0,m,siz[N<<6],w[N<<6],rnd[N<<6],son[N<<6][2],rt[N],t1,t2,t3,p,opt; 6 inline int read() 7 { 8 int T=0,F=1; char ch=getchar(); 9 while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-') F=-1; ch=getchar();} 10 while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') T=(T<<3)+(T<<1)+(ch-48),ch=getchar(); 11 return F*T; 12 } 13 inline void pushup(int x){siz[x]=siz[son[x][0]]+siz[son[x][1]]+1;} 14 inline void new_point(int x){siz[++n]=1; w[n]=x; rnd[n]=((rand()<<15)|rand());} 15 inline void copy(int x){w[++n]=w[x],son[n][0]=son[x][0],son[n][1]=son[x][1],rnd[n]=rnd[x];} 16 void split(int x,int k,int &l,int &r) 17 { 18 if(!x){l=0,r=0; return;} 19 if(w[x]<=k) copy(x),l=x=n,split(son[x][1],k,son[x][1],r),pushup(x); 20 else copy(x),r=x=n,split(son[x][0],k,l,son[x][0]),pushup(x); 21 } 22 void merge(int l,int r,int &o) 23 { 24 if(!l||!r){o=l+r; return;} 25 if(rnd[l]<rnd[r]) copy(l),o=l=n,merge(son[l][1],r,son[l][1]),pushup(l); 26 else copy(r),o=r=n,merge(l,son[r][0],son[r][0]),pushup(r); 27 } 28 void ins(int &root,int x){split(root,x,t1,t2),new_point(x),merge(t1,n,t1),merge(t1,t2,root);} 29 void del(int &root,int x){split(root,x,t1,t2),split(t1,x-1,t1,t3),merge(son[t3][0],son[t3][1],t3),merge(t1,t3,t1),merge(t1,t2,root);} 30 int kth(int x,int k) 31 { 32 while(k) 33 { 34 p=siz[son[x][0]]; 35 if(k<=p) x=son[x][0]; 36 else if(k==p+1) return w[x]; 37 else x=son[x][1],k=k-p-1; 38 } 39 } 40 int main() 41 { 42 m=read(); 43 for(re int i=1;i<=m;++i) 44 { 45 t1=read(),opt=read(),t3=read(); 46 rt[i]=rt[t1]; 47 switch(opt) 48 { 49 case 1:ins(rt[i],t3);break; 50 case 2:del(rt[i],t3);break; 51 case 3:split(rt[i],t3-1,t1,t2),printf("%d\n",siz[t1]+1),merge(t1,t2,rt[i]);break; 52 case 4:printf("%d\n",kth(rt[i],t3));break; 53 case 5:split(rt[i],t3-1,t1,t2),printf("%d\n",kth(t1,siz[t1])),merge(t1,t2,rt[i]);break; 54 case 6:split(rt[i],t3,t1,t2),printf("%d\n",kth(t2,1)),merge(t1,t2,rt[i]);break; 55 } 56 } 57 return 0; 58 }
<2>.带有区间操作的平衡树:
目前只知道带翻转的例题:
除copy函数外,pushdown函数也有较大变化:
若re[x]=1,则左右儿子的re值都会改变,但分裂或者合并时只会遍历一个儿子,故在pushdown时也进行copy。
1 inline void pushdown(int x){ 2 if(re[x]){ 3 int lc=son[x][0],rc=son[x][1]; 4 if(lc) copy(lc),lc=son[x][0]=n; 5 if(rc) copy(rc),rc=son[x][1]=n; 6 re[lc]^=1,re[rc]^=1; 7 swap(son[x][0],son[x][1]); re[x]=0; 8 } 9 } 10 void split(int x,int k,int &l,int &r) 11 { 12 if(!x){l=r=0; return;} 13 pushdown(x),p=siz[son[x][0]]; 14 //if(siz[x]==k){copy(x); l=x=n,r=0; return;} 15 if(p<k) copy(x),l=x=n,split(son[x][1],k-p-1,son[x][1],r),pushup(x); 16 else copy(x),r=x=n,split(son[x][0],k,l,son[x][0]),pushup(x); 17 } 18 void merge(int l,int r,int &o){ 19 if(!l||!r){o=l+r; return;} 20 if(rnd[l]<rnd[r]) pushdown(l),o=l,merge(son[l][1],r,son[l][1]),pushup(l); 21 else pushdown(r),o=r,merge(l,son[r][0],son[r][0]),pushup(r); 22 }
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 #define reg register 3 using namespace std; 4 const int N=2e5+6; 5 int n=0,m,p,opt,t1,t2,t3,siz[N<<6],son[N<<6][2],w[N<<6],re[N<<6],rnd[N<<6],rt[N]; 6 long long sum[N<<6],t=0; 7 inline int read() 8 { 9 int T=0,F=1; char ch=getchar(); 10 while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-') F=-1; ch=getchar();} 11 while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') T=(T<<3)+(T<<1)+(ch-48),ch=getchar(); 12 return F*T; 13 } 14 inline void new_point(int x){++n,siz[n]=1,sum[n]=w[n]=x,rnd[n]=((rand()<<15)|rand());} 15 inline void copy(int x){++n,w[n]=w[x],sum[n]=sum[x],siz[n]=siz[x],son[n][0]=son[x][0],son[n][1]=son[x][1],re[n]=re[x],rnd[n]=rnd[x];} 16 inline void pushup(int x){siz[x]=siz[son[x][0]]+siz[son[x][1]]+1,sum[x]=sum[son[x][0]]+sum[son[x][1]]+w[x];} 17 inline void pushdown(int x){ 18 if(re[x]){ 19 int lc=son[x][0],rc=son[x][1]; 20 if(lc) copy(lc),lc=son[x][0]=n; 21 if(rc) copy(rc),rc=son[x][1]=n; 22 re[lc]^=1,re[rc]^=1; 23 swap(son[x][0],son[x][1]); re[x]=0; 24 } 25 } 26 void split(int x,int k,int &l,int &r) 27 { 28 if(!x){l=r=0; return;} 29 pushdown(x),p=siz[son[x][0]]; 30 //if(siz[x]==k){copy(x); l=x=n,r=0; return;} 31 if(p<k) copy(x),l=x=n,split(son[x][1],k-p-1,son[x][1],r),pushup(x); 32 else copy(x),r=x=n,split(son[x][0],k,l,son[x][0]),pushup(x); 33 } 34 void merge(int l,int r,int &o){ 35 if(!l||!r){o=l+r; return;} 36 if(rnd[l]<rnd[r]) pushdown(l),o=l,merge(son[l][1],r,son[l][1]),pushup(l); 37 else pushdown(r),o=r,merge(l,son[r][0],son[r][0]),pushup(r); 38 } 39 void ins(int x,int y,int &root){split(root,x,t1,t2),new_point(y),merge(t1,n,t1),merge(t1,t2,root);} 40 void del(int x,int &root){split(root,x,t1,t2),split(t1,x-1,t1,t3),merge(t1,t2,root);} 41 void res(int l,int r,int &root){split(root,r,t1,t3),split(t1,l-1,t1,t2),re[t2]^=1,merge(t1,t2,t1),merge(t1,t3,root);} 42 long long query(int l,int r,int &root){split(root,r,t1,t3),split(t1,l-1,t1,t2),t=sum[t2],merge(t1,t2,t1),merge(t1,t3,root); return t;} 43 int main() 44 { 45 m=read(); long long e,f; 46 for(reg int i=1;i<=m;++i){ 47 t1=read(),opt=read(),e=read(),e^=t,rt[i]=rt[t1]; 48 switch(opt){ 49 case 1:f=read(),f^=t,ins(e,f,rt[i]);break; 50 case 2:del(e,rt[i]);break; 51 case 3:f=read(),f^=t,res(e,f,rt[i]);break; 52 case 4:f=read(),f^=t,printf("%lld\n",query(e,f,rt[i]));break; 53 } 54 } 55 return 0; 56 }
四.splay:
1.介绍:老牌平衡树算法,由tarjan大神发明,用神奇的伸展操作维护平衡并进行操作。
2.特点:
<1>.很多操作后都喜欢伸展维护平衡,故常数巨大。
<2>.splay操作,splay(x),将x变为根。
操作如图:
[1].三点不一线:将4连续旋转两次。
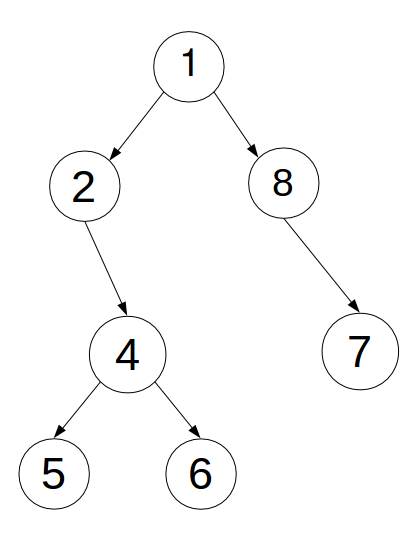
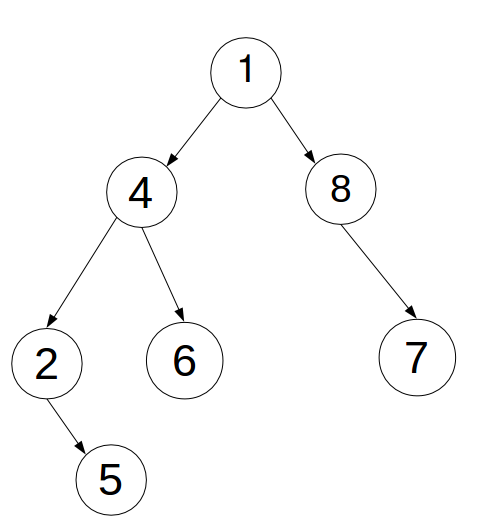
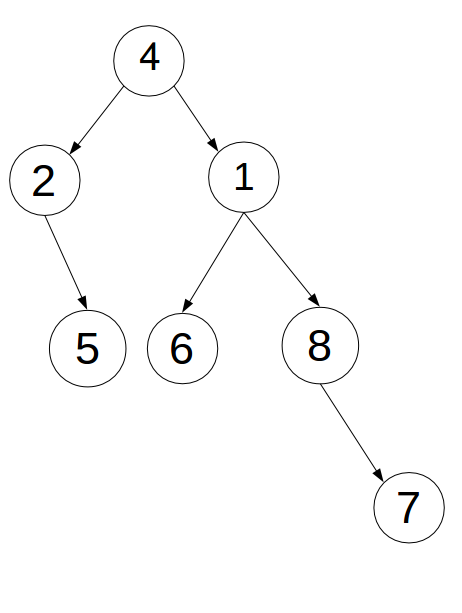
[2].三点一线:先转父亲2再转儿子3。
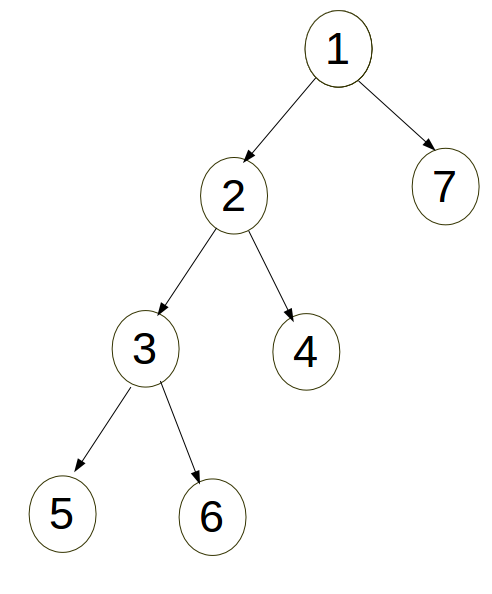
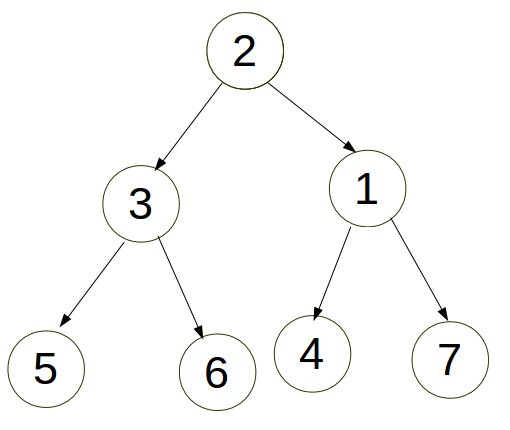
3.代码:
区间操作跟fhq treap差不多,其它操作跟treap差不多。
不过,处理区间时一般将l-1旋到根,r+1旋到右儿子,r+1的左子树就是区间[l,r];
这样万一遇到l=1时,l-1=0,f[0]=0,root会为0,而son[0][0]=son[0][1]=0,易出错,
同理r=n时也是如此,所以新增0和n+1两个点,但为防止误判点0不存在,0到n+1的编号就都右移一位,对应1到n+2,
读入l,r,却splay(l,0),splay(r+2,l)便是因此。
<1>.普通平衡树:
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 #define re register 3 using namespace std; 4 const int N=2e5+6; 5 int n,w[N],son[N][2],f[N],siz[N],num[N],cnt=0,head[N],t1,opt,o,root; 6 inline int read() 7 { 8 int T=0,F=1; char ch=getchar(); 9 while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-') F=-1; ch=getchar();} 10 while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') T=(T<<3)+(T<<1)+(ch-48),ch=getchar(); 11 return F*T; 12 } 13 inline void pushup(int x){siz[x]=siz[son[x][0]]+siz[son[x][1]]+num[x];} 14 inline void rotate(int x) 15 { 16 int y=f[x]; int z=f[y],k=(son[y][1]==x); 17 if(z) son[z][son[z][1]==y]=x; 18 f[x]=z; 19 son[y][k]=son[x][k^1],f[son[y][k]]=y; 20 son[x][k^1]=y,f[y]=x; 21 pushup(y),pushup(x); 22 } 23 void splay(int x,int u) 24 { 25 while(f[x]!=u) 26 { 27 int y=f[x]; int z=f[y]; 28 if(z!=u) rotate(((son[y][1]==x)^(son[z][1]==y))?x:y); 29 rotate(x); 30 } 31 if(!u) root=x; 32 } 33 int fnd(int x,int u) 34 { 35 while(w[x]!=u&&x) x=son[x][u>w[x]]; 36 return x; 37 } 38 void ins(int x,int u) 39 { 40 if(!x){++o,w[1]=u,siz[1]=num[1]=1,f[1]=0,root=1; return;} 41 int t=son[x][w[x]<u]; 42 while(w[x]!=u&&t) ++siz[x],x=t,t=son[x][w[x]<u]; 43 if(w[x]!=u) ++siz[x],++o,w[o]=u,siz[o]=num[o]=1,son[x][w[x]<u]=o,f[o]=x,splay(o,0); 44 else ++num[x],splay(x,0); 45 } 46 int rak(int u){u=fnd(root,u); splay(u,0); return siz[son[u][0]]+1;} 47 int kth(int x,int u) 48 { 49 int t; 50 while(1) 51 { 52 t=siz[son[x][0]]+num[x]; 53 if(u>t) u-=t,x=son[x][1]; 54 else if(u>siz[son[x][0]]&&u<=t) return w[x]; 55 else x=son[x][0]; 56 } 57 } 58 int lat(int u) 59 { 60 u=son[u][0]; 61 if(!u) return -1; 62 while(son[u][1]) u=son[u][1]; 63 return u; 64 } 65 void del(int u) 66 { 67 int t=fnd(root,u); 68 splay(t,0); 69 if(num[t]>1) --num[t],--siz[t]; 70 else 71 { 72 t=lat(t); 73 if(t==-1){root=son[root][1],f[root]=0; return;} 74 splay(t,0); 75 son[t][1]=son[son[t][1]][1],f[son[t][1]]=t; 76 --siz[t]; 77 } 78 } 79 int pre(int u) 80 { 81 int t; 82 ins(root,u),t=lat(root),del(w[root]); 83 return w[t]; 84 } 85 int nxt(int u) 86 { 87 int t; 88 ins(root,u); 89 t=son[root][1]; 90 while(son[t][0]) t=son[t][0]; 91 del(w[root]); 92 return w[t]; 93 } 94 int main() 95 { 96 n=read(); o=0; root=0; 97 for(re int i=1;i<=n;++i) 98 { 99 opt=read(),t1=read(); 100 switch(opt) 101 { 102 case 1:ins(root,t1);break; 103 case 2:del(t1);break; 104 case 3:printf("%d\n",rak(t1));break; 105 case 4:printf("%d\n",kth(root,t1));break; 106 case 5:printf("%d\n",pre(t1));break; 107 case 6:printf("%d\n",nxt(t1));break; 108 } 109 } 110 return 0; 111 }
<2>.文艺平衡树:
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 #define reg register 3 using namespace std; 4 const int N=2e5+6; 5 int n,w[N],son[N][2],f[N],siz[N],t1,t2,o,root,m,re[N]; 6 inline int read() 7 { 8 int T=0,F=1; char ch=getchar(); 9 while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-') F=-1; ch=getchar();} 10 while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') T=(T<<3)+(T<<1)+(ch-48),ch=getchar(); 11 return F*T; 12 } 13 inline void pushup(int x){siz[x]=siz[son[x][0]]+siz[son[x][1]]+1;} 14 inline void rotate(int x) 15 { 16 int y=f[x]; int z=f[y],k=(son[y][1]==x); 17 if(z) son[z][son[z][1]==y]=x; 18 f[x]=z; 19 son[y][k]=son[x][k^1],f[son[y][k]]=y; 20 son[x][k^1]=y,f[y]=x; 21 pushup(y),pushup(x); 22 } 23 void splay(int x,int u) 24 { 25 while(f[x]!=u) 26 { 27 int y=f[x]; int z=f[y]; 28 if(z!=u) rotate((son[y][1]==x)^(son[z][1]==y)?x:y); 29 rotate(x); 30 } 31 if(!u) root=x; 32 } 33 void ins(int x,int u) 34 { 35 if(!x){++o,w[1]=u,siz[1]=1,f[1]=0,root=1; return;} 36 int t=son[x][w[x]<u]; 37 while(t) ++siz[x],x=t,t=son[x][w[x]<u]; 38 ++siz[x],++o,w[o]=u,siz[o]=1,son[x][w[x]<u]=o,f[o]=x,splay(o,0); 39 } 40 int kth(int x,int u) 41 { 42 int t; 43 while(1) 44 { 45 if(re[x]) re[x]=0,re[son[x][0]]^=1,re[son[x][1]]^=1,swap(son[x][0],son[x][1]); 46 t=siz[son[x][0]]+1; 47 if(u>t) u-=t,x=son[x][1]; 48 else if(u==t) return w[x]; 49 else x=son[x][0]; 50 } 51 } 52 void res(int l,int r) 53 { 54 l=kth(root,l),r=kth(root,r+2); 55 splay(l,0),splay(r,l); 56 l=son[r][0],re[l]^=1; 57 } 58 void output(int x) 59 { 60 if(!x) return; 61 if(re[x]) swap(son[x][0],son[x][1]),re[son[x][0]]^=1,re[son[x][1]]^=1; 62 output(son[x][0]); 63 if(x!=1&&x!=n+2) printf("%d ",x-1); 64 output(son[x][1]); 65 } 66 int main() 67 { 68 n=read(),m=read(); o=0; root=0; 69 for(reg int i=1;i<=n+2;++i) ins(root,i); 70 for(reg int i=1;i<=m;++i) t1=read(),t2=read(),res(t1,t2); 71 output(root); 72 return 0; 73 }

