python | 算法-二叉树宽度、判断以及各种实际问题
针对b站视频左神算法与数据结构,自己练习对应的python代码
相关链接:
1️⃣b站视频地址
2️⃣视频笔记(其实主要是题目截图)
1. 二叉树宽度
📝用hash表
# 用hash表
def BTWidth2(self, root):
if root is None:
return 0
ht = {} # hash table
ht[root] = 1
que = [] # queue
que.append(root)
width = 0 # save max width
count = 0 # save cur level nodes number
cur_level = 1
while len(que) != 0:
cur = que.pop(0)
node_level = ht[cur]
if node_level == cur_level:
count += 1
else:
width = max(width, count)
count = 1
cur_level += 1
if cur.lchild is not None:
que.append(cur.lchild)
ht[cur.lchild] = cur_level + 1
if cur.rchild is not None:
que.append(cur.rchild)
ht[cur.rchild] = cur_level + 1
else:
width = max(width, count)
return width
📝不用hash表
# 不用hash表
def BTWidth1(self, root):
if root is None:
return 0
width = 0
now_last = root # save cur level's last node
next_last = None # save next level's last node
queue = []
queue.append(root)
count = 0 # count cur level nodes num
while len(queue) != 0:
p = queue.pop(0)
count += 1
if p.lchild is not None:
queue.append(p.lchild)
next_last = p.lchild
if p.rchild is not None:
queue.append(p.rchild)
next_last = p.rchild
if p == now_last:
width = max(width, count)
count = 0
now_last = next_last
return width
完整版代码测试结果:(与上一篇同样的例子)
点击查看代码
class BTNode():
def __init__(self, key=None, lchild=None, rchild=None):
self.key = key
self.lchild = lchild
self.rchild = rchild
class BiTree():
def __init__(self, data_list):
self.data = iter(data_list)
def createBiTree(self, root=None):
try:
nextone = next(self.data)
if nextone == '#':
root = None
else:
root = BTNode(nextone)
root.lchild = self.createBiTree(root.lchild)
root.rchild = self.createBiTree(root.rchild)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
return root
# 不用hash表
def BTWidth1(self, root):
if root is None:
return 0
width = 0
now_last = root # save cur level's last node
next_last = None # save next level's last node
queue = []
queue.append(root)
count = 0 # count cur level nodes num
while len(queue) != 0:
p = queue.pop(0)
count += 1
if p.lchild is not None:
queue.append(p.lchild)
next_last = p.lchild
if p.rchild is not None:
queue.append(p.rchild)
next_last = p.rchild
if p == now_last:
width = max(width, count)
count = 0
now_last = next_last
return width
# 用hash表
def BTWidth2(self, root):
if root is None:
return 0
ht = {} # hash table
ht[root] = 1
que = [] # queue
que.append(root)
width = 0 # save max width
count = 0 # save cur level nodes number
cur_level = 1
while len(que) != 0:
cur = que.pop(0)
node_level = ht[cur]
if node_level == cur_level:
count += 1
else:
width = max(width, count)
count = 1
cur_level += 1
if cur.lchild is not None:
que.append(cur.lchild)
ht[cur.lchild] = cur_level + 1
if cur.rchild is not None:
que.append(cur.rchild)
ht[cur.rchild] = cur_level + 1
else:
width = max(width, count)
return width
# test
data_list = [1, 2, '#', 4, '#', '#', 3, 5, '#', '#', 6, '#', '#']
biTree = BiTree(data_list) # biTree -> BiTree class, iter
root = biTree.createBiTree() # root -> createBiTree()'s return
print(biTree.BTWidth1(root))
print(biTree.BTWidth2(root))
# output:
# 3
# 3
2. 二叉树的相关概念及其实现判断
2.1 判断一棵二叉树是不是搜索二叉树
1️⃣搜索二叉树:
对于每一棵子树来说,它的左树的节点比它小,右树都比它大
2️⃣判断一棵树是不是搜索二叉树:
中序遍历是依次升序就是搜索二叉树
📝递归方法:
# 判断搜索二叉树 -> 递归
def searchBT1(self, root):
if root is None:
return True
if root.lchild is not None:
left = self.GetRightMost(root.lchild) # 取左边子树的最后一点(中序遍历的角度)
if not self.searchBT1(root.lchild) or left.key > root.key:
return False
if root.rchild is not None:
right = self.GetLeftMost(root.rchild) #取右边子树的第一点(中序遍历的角度)
if not self.searchBT1(root.rchild) or root.key > right.key:
return False
return True
def GetLeftMost(self, node):
while node is not None and node.lchild is not None:
node = node.lchild
return node
def GetRightMost(self, node):
while node is not None and node.rchild is not None:
node = node.rchild
return node
📝非递归方法:
# 判断搜索二叉树 -> 非递归
def searchBT2(self, root):
if root is None: return True
help = [] # save results
stack = [] # save path
while len(stack) != 0 or root is not None:
if root is not None:
stack.append(root)
root = root.lchild
else:
root = stack.pop()
help.append(root.key)
root = root.rchild
post = help.pop()
while len(help) != 0:
pre = help.pop()
if pre > post: return False
post = pre
return True
📝测试结果:
# test
data_list = [1, 2, '#', 4, '#', '#', 3, 5, '#', '#', 6, '#', '#']
biTree = BiTree(data_list) # biTree -> BiTree class, iter
root = biTree.createBiTree() # root -> createBiTree()'s return
print(biTree.searchBT1(root))
print(biTree.searchBT2(root))
# output:
# False
# False
2.2 判断一棵二叉树是不是完全二叉树
1️⃣完全二叉树
一棵深度为k的有n个结点的二叉树,对树中的结点按从上至下、从左到右的顺序进行编号,如果编号为i(1≤i≤n)的结点与满二叉树中编号为i的结点在二叉树中的位置相同,则这棵二叉树称为完全二叉树。
2️⃣判断完全二叉树
宽度优先遍历
# 判断完全二叉树
def isCBT(self, root):
if root is None: return True
queue = []
queue.append(root)
leaf = False # leaf -> pre leaf that has left but no right child
while len(queue) != 0:
now = queue.pop(0)
l, r = now.lchild, now.rchild
if (l is None and r is not None) or \
(leaf and (l is not None or r is not None)):
return False
if l is not None:
queue.append(l)
if r is not None:
queue.append(r)
if (l is None or r is None):
leaf = True
return True
# test
data_list = [1, 2, 4, 8, '#', '#', '#', 5, '#', '#', 3, 6, '#', '#', 7, '#', '#']
biTree = BiTree(data_list) # biTree -> BiTree class, iter
root = biTree.createBiTree() # root -> createBiTree()'s return
print(biTree.isCBT(root))
# True
代码中二叉树结构和创建,记录在python | 算法大神左神(左程云)算法课程 二叉树部分【上】
2.3 判断一棵二叉树是不是满二叉树
1️⃣树的最大深度L和节点个数N之间有等量关系:$N=2^L-1$,满足,则是满二叉树。
2️⃣宽度优先遍历,同时记录节点数和树的深度,最后判断上述等式是否成立。
#判断满二叉树 F-full
def isFBT(self, root):
if root is None: return True
queue = []
queue.append(root)
cur_last = root
next_last = None
level = 0 # save height of BiTree
n = 0 # count number of node
while len(queue) != 0:
cur = queue.pop(0)
n += 1
if cur.lchild is not None:
queue.append(cur.lchild)
next_last = cur.lchild
if cur.rchild is not None:
queue.append(cur.rchild)
next_last = cur.rchild
if cur == cur_last:
level += 1
cur_last = next_last
if 2 ** level - 1 == n:
return True
return False
# test
# data_list = [1, 2, 4, '#', '#', 5, '#', '#', 3, 6, '#', '#', 7, '#', '#']
# True
2.4 判断一棵二叉树是否是平衡二叉树
1️⃣平衡二叉树
对于任何子树来说,其左子树和右子树的高度差不超过1
2️⃣判断平衡二叉树
递归,分别判断左右子树,再判断整棵树,递归函数有两个返回值:是否是平衡二叉树以及树高
# 判断平衡二叉树 B-balanced
def isBBT(self, root):
return self.process(root)[0]
def process(self, root):
if root is None:
return [True, 0]
left = self.process(root.lchild)
right = self.process(root.rchild)
height = max(left[1], right[1])
isBalanced = left[0] and right[0] and abs(left[1] - right[1]) < 2
return [isBalanced, height]
# test
# data_list = [1, 2, 4, '#', '#', 5, '#', '#', 3, 6, '#', '#', 7, '#', '#']
# True
3. 二叉树问题实际训练
3.1 最低公共祖先
给定两个二叉树的节点node1和node2,找到他们的最低公共祖先节点
1️⃣ 设置一个 HashMap 保存节点与该节点的父节点(设根节点的父节点为本身),然后再用一个集合 set1 保存 node1 的全部祖先节点,对node2往上求祖先节点,看是否在 set1 中,若在,则这个节点即为最低公共祖先节点。
class BTNode():
def __init__(self, key=None, lchild=None, rchild=None):
self.key = key
self.lchild = lchild
self.rchild = rchild
class BiTree():
def __init__(self, data_list):
self.len = len(data_list)
self.data = iter(data_list)
def createBiTree(self, root=None):
try:
nextone = next(self.data)
if nextone == '#':
root = None
else:
root = BTNode(nextone)
root.lchild = self.createBiTree(root.lchild)
root.rchild = self.createBiTree(root.rchild)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
return root
# Lowest Common Ancestor
def lca(head=None, node1=None, node2=None):
"""Here we assume that node1 and node2 must belong to the tree headed by head"""
# Get a hash table of all nodes mapped to their parents
father_map = {}
father_map[head] = head
process(head, father_map)
# Get all ancestor node of node1, and put them in list1
list1 = []
cur = node1
while(cur is not father_map[cur]):
list1.append(cur)
cur = father_map[cur]
else:
list1.append(cur)
# Get ancestor of node2, and judge weather it is in list1 -> find the target ancestor
cur = node2
while(cur not in list1):
cur = father_map[cur]
return cur # this is the lowest common ancestor
def process(head, father_map):
if head is None:
return
father_map[head.lchild] = head
father_map[head.rchild] = head
process(head.lchild, father_map)
process(head.rchild, father_map)
2️⃣ 递归操作
-
基本事件是当一棵子树的头节点为 null 或 为 node1 或 node2 时,就返回这个头节点。
-
对左右子树作递归,获得左右子树的返回值。递归的返回值只有四种可能:null 、node1 、node2,两节点的最低公共祖先节点。
-
当左子树返回值不空,右子树返回值不空(即两节点分别落于左右子树上),返回头节点(该头节点即为最低公共祖先节点)。
-
当不满足左右子树返回值均不空这个条件时,若左子树返回值不空时返回该值(可能为node1 、node2,两节点的最低公共祖先节点),否则返回右子树的值(可能为null 、node1 、node2,两节点的最低公共祖先节点)。
def lca2(head=None, node1=None, node2=None):
if head is None or head == node1 or head == node2:
return head
left = lca2(head.lchild, node1, node2)
right = lca2(head.rchild, node1, node2)
if left is not None and right is not None:
return head
else:
return left if (left is not None) else right
3.2 在二叉树中找到一个节点的后继节点

1️⃣ node有右子树时,其后继节点一定是右子树的中序遍历第一个节点
2️⃣ node没有右子树时,一路向上,找到某个节点是其父亲节点的左孩子,那么该父亲节点就是node的后继节点
def SuccessorNode(node):
if node is None:
return node
if node.right is not None: # node有右子树
return GetLeftMost(node.right) #寻找右子树的中序遍历第一个节点
else: # node没有右子树
parent = node.parent # 向祖先寻找后继节点
while parent is not None and parent.left != node: # 循环找当前节点是其父节点的左子树
node = parent
parent = node.parent
return parent
def GetLeftMost(node):
while node is not None:
node = node.left
return node.parent
3.3 二叉树的序列化和反序列化
# Definition for a binary tree node
class BTNode():
def __init__(self, value=None, left=None, right=None):
self.value = value
self.left = left
self.right = right
class Solution():
def serialize(self, root):
"""
Encodes a tree to a single string
:param root: BTNode
:return: str
"""
if root is None:
return 'null,'
left_serialize = self.serialize(root.left)
right_serialize = self.serialize(root.right)
return str(root.value) + ',' + left_serialize + right_serialize
def deserialize(self, data):
"""
Decodes your encoded data to a binary tree
:param data: str
:return: BTNode
"""
def dfs(queue): # dfs -> Deep First Search
val = queue.popleft()
if val == "null":
return None
node = BTNode(value=val)
node.left = dfs(queue)
node.right = dfs(queue)
return node
from collections import deque
queue = deque(data.split(','))
return dfs(queue)
3.4 折纸问题

分析折纸过程,发现所求是如下二叉树的中序遍历:
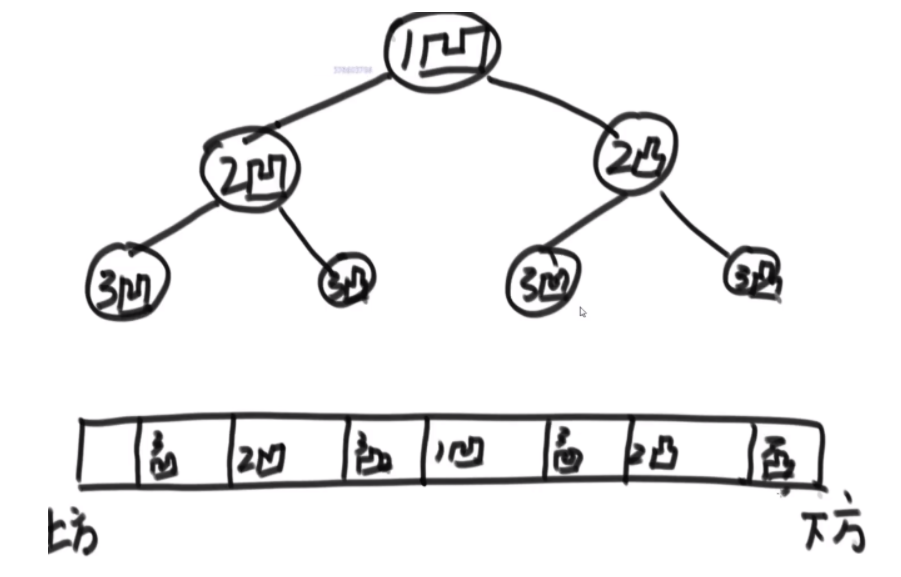
def PrintAllFolds(N):
PrintProcess(1, N, True)
def PrintProcess(i, N, down=True):
# i 是节点层数, N是一共的层数, down == true 代表凹,打印down, down == false 代表凸 打印up
if i > N: return
PrintProcess(i+1, N, True)
print("down" if down else "up")
PrintProcess(i+1, N, False)





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!