1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <time.h> 4 #include <windows.h> 5 #define N 80 6 void printText(int line, int col, char text[]); 7 void printSpaces(int n); 8 void printBlankLines(int n);
9 int main() 10 { 11 int line, col, i; 12 char text[N] = "hi, May~"; 13 14 srand(time(0)); 15 16 for (i = 1; i <= 10; ++i) 17 { 18 line = rand() % 25; 19 col = rand() % 80; 20 printText(line, col, text); 21 Sleep(1000); 22 } 23 24 return 0; 25 } 26 27 void printSpaces(int n) 28 { 29 int i; 30 31 for (i = 1; i <= n; ++i) 32 printf(" "); 33 } 34 35 void printBlankLines(int n) 36 { 37 int i; 38 for (i = 1; i <= n; ++i) 39 printf("\n"); 40 } 41 42 void printText(int line, int col, char text[]) 43 { 44 printBlankLines(line - 1); 45 printSpaces(col - 1); 46 printf("%s", text); 47 }
每隔一秒在后续位置随机打印一个“hi,May~”,一共十次。
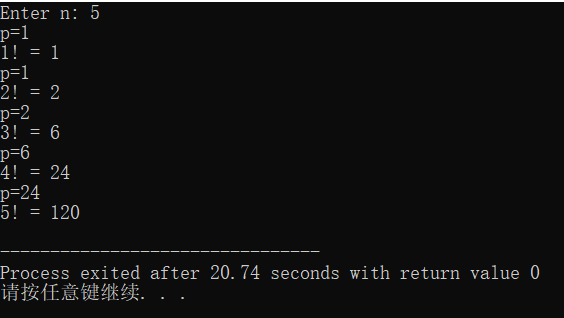
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 long long fac(int n); 3 int main() 4 { 5 int i, n; 6 printf("Enter n: "); 7 scanf("%d", &n); 8 for (i = 1; i <= n; ++i) printf("%d! = %lld\n", i, fac(i)); 9 return 0; 10 } 11 long long fac(int n) 12 { 13 static long long p = 1; 14 printf("p=%lld\n",p); 15 p = p * n; 16 return p; 17 }
#include <stdio.h> int func(int, int); int main() { int k = 4, m = 1, p1, p2; p1 = func(k, m); p2 = func(k, m); printf("%d,%d\n", p1, p2); return 0; } int func(int a, int b) { static int m = 0, i = 2; i += m + 1; m = i + a + b; return m; }
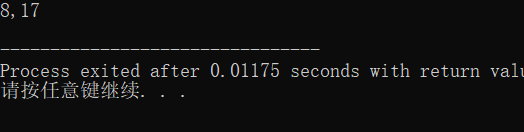
总结:静态局部变量只赋初值一次,之后每次调用函数时不再重新赋初值而是保留上次函数调用结束时的值。
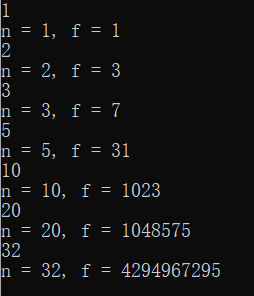
#include <stdio.h> long long fun(int n); int main() { int n; long long f; while (scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) { f = fun(n); printf("n = %d, f = %lld\n", n, f); } return 0; } long long fun(int n) { long long s; if(n==0) s=0; else s=2*fun(n-1)+1; return s; }
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<math.h> 3 void hanoi(unsigned int n,char from,char temp,char to); 4 void moveplate(unsigned int n,char from,char to); 5 int main() 6 { 7 unsigned int n,t; 8 while(scanf("%u",&n)!=EOF) 9 { 10 hanoi(n,'A','B','C'); 11 t = pow(2,n)-1; 12 printf("\n一共移动了%d次.\n\n",t); 13 } 14 return 0; 15 } 16 void hanoi(unsigned int n,char from,char temp,char to) 17 { 18 if(n==1) moveplate(n,from,to); 19 else 20 { 21 hanoi(n-1,from,to,temp); 22 moveplate(n,from,to); 23 hanoi(n-1,temp,from,to); 24 } 25 } 26 void moveplate(unsigned int n,char from,char to) 27 { 28 printf("第%u个盘子:%c-->%c\n",n,from,to); 29 }

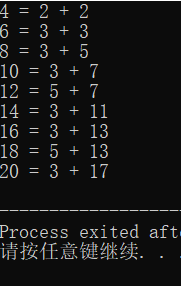
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<math.h> 3 int is_prime(int n); 4 int main() 5 { 6 for(int j=4;j<=20;j+=2) 7 { 8 for(int k=2;k<=j/2;k++) 9 { 10 if(is_prime(k)==0&&is_prime(j-k)==0) 11 { 12 printf("%d = %d + %d\n",j,k,j-k); 13 break; 14 } 15 16 } 17 } 18 return 0; 19 } 20 int is_prime(int n) 21 { 22 for(int i=2;i<=sqrt(n);i++) 23 if(n%i==0) return 1; 24 return 0; 25 }
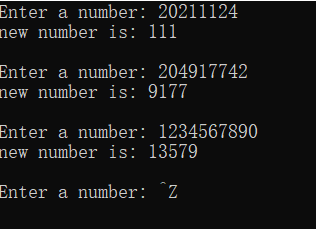
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<math.h> 3 long fun(long s); 4 int main() 5 { 6 long s, t; 7 printf("Enter a number: "); 8 while (scanf("%ld", &s) != EOF) 9 { 10 t = fun(s); 11 printf("new number is: %ld\n\n", t); 12 printf("Enter a number: "); 13 } 14 return 0; 15 } 16 long fun(long s) 17 { 18 int result=0,i; 19 for(int j=0;s!=0;s=s/10) 20 { 21 i = s%10; 22 if(i%2!=0) 23 { 24 result = i*pow(10,j)+result; 25 j = j+1; 26 } 27 } 28 return result; 29 }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号