2 Python 面向对象
1 类
用来描述具有相同的属性和方法的对象的集合。它定义了该集合中每个对象所共有的属性和方法。对象是类的实例。
1.1 类的基本介绍

1 class Person(object): #类关键字class 2 3 #类变量,在所有实例之间共享 4 head = '头' 5 body = '身体' 6 arm = '胳膊' 7 leg = '腿' 8 9 #无参构造函数,类被实例化时调用 10 def __init__(self): 11 self.__name = '张飞' #self指类的实例 12 self.__age = 0 #__表示私有变量 13 14 #自定义函数,获取名字 15 def getName(self): 16 return self.__name 17 18 #自定义函数,获取年龄 19 def getAge(self): 20 return self.__age 21 22 #类的实例化 23 zhang = Person() 24 print '张有 ' + zhang.head + zhang.body + zhang.arm + zhang.leg #类变量使用 25 print '张的名字是: ' + zhang.getName() #自定义函数使用 26 print '张的年龄是: ' + str(zhang.getAge()) 27 28 #结果 29 张有: 头身体胳膊腿 30 张的名字是: 张飞 31 张的年龄是: 0
1.2 静态属性及方法

1 class Person(object): 2 3 #静态变量 4 head = '头' 5 body = '身体' 6 arm = '胳膊' 7 leg = '腿' 8 9 #有参构造函数,类被实例化时调用 10 def __init__(self , name , age): 11 self.__name = name #self指类的实例 12 self.__age = age #__表示私有变量 13 14 #自定义函数,获取名字 15 def getName(self): 16 return self.__name 17 18 #自定义函数,获取年龄 19 def getAge(self): 20 return self.__age 21 22 #静态方法 23 @staticmethod 24 def eat(): 25 return '开始吃饭' 26 27 #类的实例化 28 zhao = Person('赵云' , 20) 29 print '张的名字是: ' + zhao.getName() #自定义函数使用 30 print '张的年龄是: ' + str(zhao.getAge()) 31 print Person.head #静态变量使用 32 print Person.eat() #静态方法使用 33 34 #结果 35 张的名字是: 赵云 36 张的年龄是: 20 37 头 38 开始吃饭
1.3 property装饰器
可以把一个 方法 变成 属性 来调用

1 class Person(object): 2 3 def __init__(self): 4 self.__name = '张飞' 5 6 @property 7 def name(self): 8 return self.__name 9 10 @name.setter 11 def name(self , name): 12 self.__name = name 13 14 #类的实例化 15 zhao = Person() 16 print '名字是: ' + zhao.name #property get方法 17 zhao.name = '赵云' #property set方法 18 print '名字是: ' + zhao.name 19 20 #结果 21 名字是: 张飞 22 名字是: 赵云
1.4 构造函数和析构函数
构造函数:新建对象时做初始化工作
析构函数:销毁对象时做清理工作,如:释放内存等
当对象被创建时, 就创建了一个引用计数, 当这个对象不再需要时, 也就是说, 这个对象的引用计数变为0 时, 它被垃圾回收。
但是回收不是"立即"的, 由解释器在适当的时机,将垃圾对象占用的内存空间回收。

1 class Person(object): 2 3 def __init__(self): 4 print '构造函数' 5 6 def __del__(self): 7 print '析构函数' 8 9 #类的实例化 10 p = Person() 11 12 #结果 13 构造函数 14 析构函数
1.5 继承

1 #构造函数无参-------------------------------------------------- 2 class Person(object): 3 4 #类变量,在所有实例之间共享 5 head = '头' 6 body = '身体' 7 arm = '胳膊' 8 leg = '腿' 9 10 def __init__(self): 11 print 'Person class' 12 13 #自定义函数,获取名字 14 def getName(self): 15 return '赵云' 16 17 #自定义函数,获取年龄 18 def getAge(self): 19 return 18 20 21 #习惯类 22 def habit(self): 23 print '父类坏习惯:喝酒' 24 25 class Student(Person): #继承Person类 26 27 def __init__(self): 28 super(Student , self).__init__() #调用父类构造方法 29 print 'Student class' 30 31 #子类习惯类 32 def habit(self): 33 Person.habit(self) #调用父类方法 34 print '子类坏习惯:抽烟' 35 36 #类的实例化 37 s = Student() 38 print Student.head 39 print s.getName() 40 s.habit() 41 42 #结果 43 Person class 44 Student class 45 头 46 赵云 47 父类坏习惯:喝酒 48 子类坏习惯:抽烟 49 50 #构造函数有参-------------------------------------------------- 51 class Person(object): 52 53 def __init__(self , name , age): 54 self.__name = name 55 self.__age = age 56 print 'Person class' 57 58 #自定义函数,获取名字 59 def getName(self): 60 return self.__name 61 62 #自定义函数,获取年龄 63 def getAge(self): 64 return self.__age 65 66 #习惯类 67 def habit(self): 68 print '父类坏习惯:喝酒' 69 70 class Student(Person): #继承Person类 71 72 def __init__(self , name , age): 73 print 'Student class' 74 super(Student , self).__init__(name , age) #调用父类构造函数 75 76 #子类习惯类 77 def habit(self): 78 Person.habit(self) #调用父类方法 79 print '子类坏习惯:抽烟' 80 81 #类的实例化 82 s = Student('小明' , 20) 83 s.habit() 84 85 #结果 86 Student class 87 Person class 88 父类坏习惯:喝酒 89 子类坏习惯:抽烟
1.6 多继承
经典类:深度优先
新式类:广度优先

1 #经典类---------------------------------------------------------------- 2 #实例调用say(),python搜索顺序grandson->father 3 #实例调用eat(),python搜索顺序grandson->father->grandfather 4 #虽然grandson也继承uncle,但是并没有调用uncle的eat() 5 class grandfather(): #经典类 6 def say(self): 7 print 'grandfather say' 8 9 def eat(self): 10 print 'grandfather eat' 11 12 class father(grandfather): 13 def say(self): 14 print 'father say' 15 16 class uncle(grandfather): 17 def eat(self): 18 print 'uncle eat' 19 20 class grandson(father , uncle): 21 pass 22 23 gs = grandson() 24 gs.say() 25 gs.eat() 26 27 #结果 28 father say 29 grandfather eat 30 31 #新式类---------------------------------------------------------------- 32 #实例调用say(),python搜索顺序grandson->father 33 #实例调用eat(),python搜索顺序grandson->father->uncle 34 class grandfather(object): #新式类 35 def say(self): 36 print 'grandfather say' 37 38 def eat(self): 39 print 'grandfather eat' 40 41 class father(grandfather): 42 def say(self): 43 print 'father say' 44 45 class uncle(grandfather): 46 def eat(self): 47 print 'uncle eat' 48 49 class grandson(father , uncle): 50 pass 51 52 gs = grandson() 53 gs.say() 54 gs.eat() 55 56 #结果 57 father say 58 uncle eat
1.7 接口
python 没有抽象类、接口的概念,需要abc.py 这个类库来帮助实现

1 from abc import ABCMeta, abstractmethod 2 3 class father(): 4 __metaclass__ = ABCMeta 5 6 @abstractmethod 7 def say(self):pass 8 9 class son(father): 10 def say(self): 11 print 'son say' 12 13 son = son() 14 son.say() 15 16 #结果 17 son say
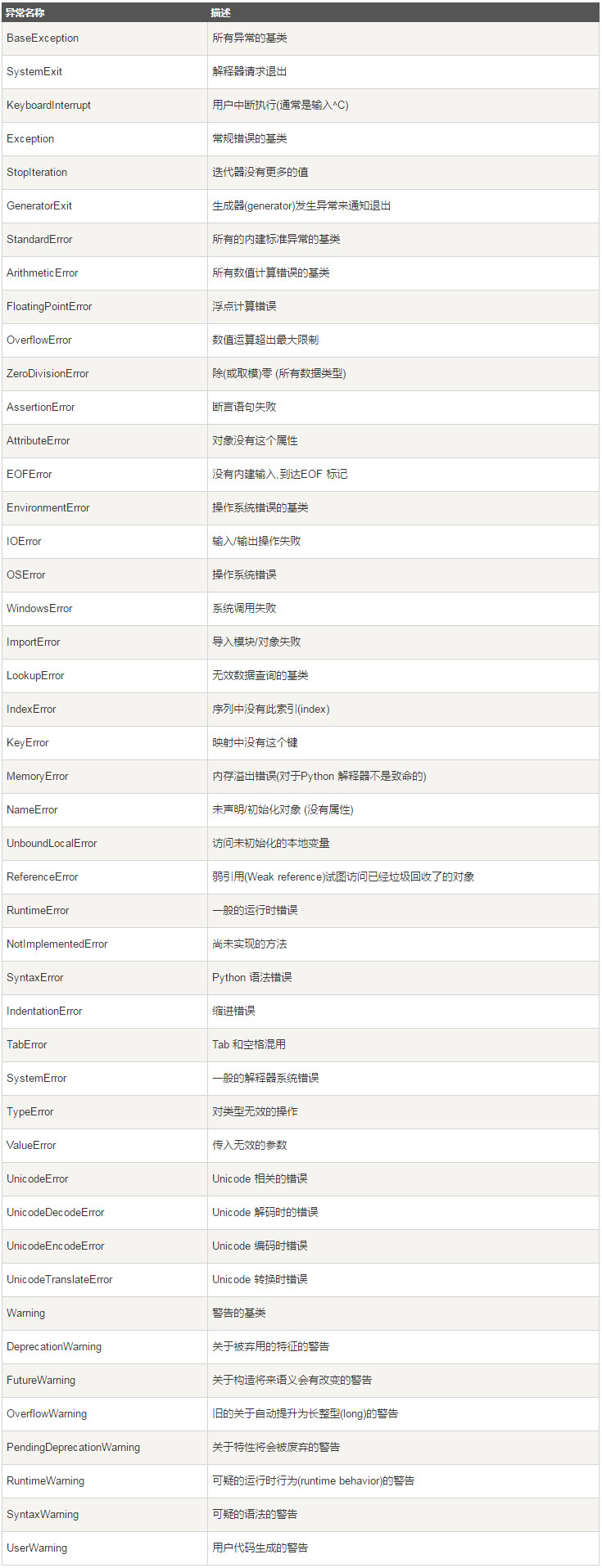
2 异常
在Python中,无法正常处理程序时就会发生一个异常。发生异常时我们需要捕获处理它,否则程序会终止执行。