电子公文传输系统验收(MD5加密改为SM3加密)
原本的功能实现
用MD5加密算法对用户输入的密码进行加密,并存储在数据库中,以123456为例
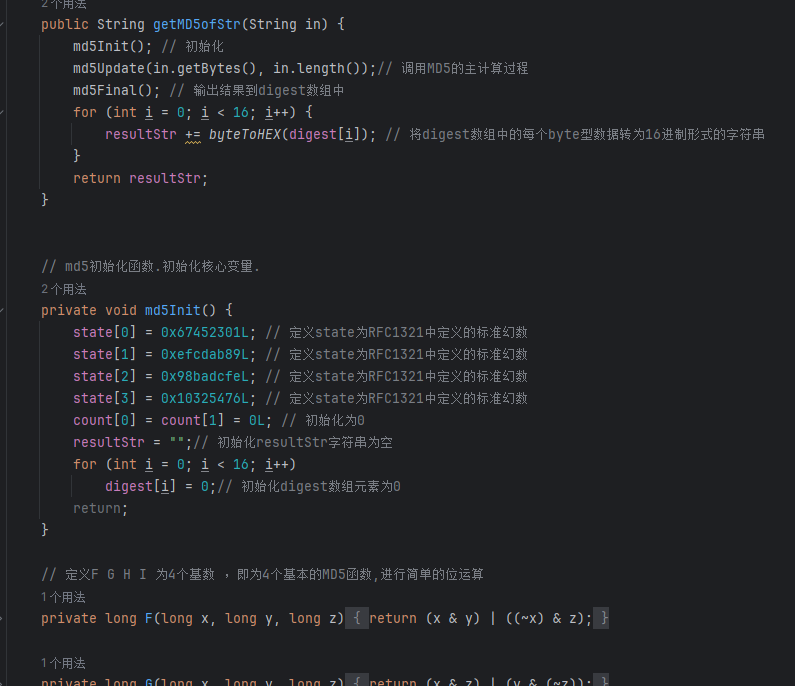
这部分加密源代码如下:
package cn.edu.nuc.article.util; /** * 采用MD5加密解密 * @author 仰望星空 * @datetime 2023 12 20 */ public class MD5Helper { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(new MD5Helper().getTwiceMD5ofString("123456")); } // 标准的构造函数,调用md5Init函数进行初始化工作 public MD5Helper() { md5Init(); return; } // RFC1321中定义的标准4*4矩阵的常量定义。 static final int S11 = 7, S12 = 12, S13 = 17, S14 = 22; static final int S21 = 5, S22 = 9, S23 = 14, S24 = 20; static final int S31 = 4, S32 = 11, S33 = 16, S34 = 23; static final int S41 = 6, S42 = 10, S43 = 15, S44 = 21; // 按RFC1321标准定义不可变byte型数组PADDING static final byte[] PADDING = { -128, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }; // MD5计算过程中的3组核心数据,采用数组形式存放 private long[] state = new long[4]; // 计算状态(分别对应a b c d) private byte[] buffer = new byte[64]; // 分配64个字节私有缓冲区 private long[] count = new long[2]; // 位个数 // 最新一次计算结果的16进制ASCII字符串表示,代表了16个字符串形式的MD5值 public String resultStr; // 最新一次计算结果的2进制数组表示,一共16个字节,代表了128bit形式的MD5值 public byte[] digest = new byte[16]; /** * 获得两次MD5加密的字符串 * @param str * @return */ public String getTwiceMD5ofString(String str){ return getMD5ofStr(getMD5ofStr(str)); } /** * MD5_Encoding类提供的主要的接口函数getMD5ofStr,用来进行数据加密变换。调用其可对任意字符串进行加密运算,并以字符串形式返回加密结果。 * @param in * @return */ public String getMD5ofStr(String in) { md5Init(); // 初始化 md5Update(in.getBytes(), in.length());// 调用MD5的主计算过程 md5Final(); // 输出结果到digest数组中 for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) { resultStr += byteToHEX(digest[i]); // 将digest数组中的每个byte型数据转为16进制形式的字符串 } return resultStr; } // md5初始化函数.初始化核心变量. private void md5Init() { state[0] = 0x67452301L; // 定义state为RFC1321中定义的标准幻数 state[1] = 0xefcdab89L; // 定义state为RFC1321中定义的标准幻数 state[2] = 0x98badcfeL; // 定义state为RFC1321中定义的标准幻数 state[3] = 0x10325476L; // 定义state为RFC1321中定义的标准幻数 count[0] = count[1] = 0L; // 初始化为0 resultStr = "";// 初始化resultStr字符串为空 for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) digest[i] = 0;// 初始化digest数组元素为0 return; } // 定义F G H I 为4个基数 ,即为4个基本的MD5函数,进行简单的位运算 private long F(long x, long y, long z) { return (x & y) | ((~x) & z); } private long G(long x, long y, long z) { return (x & z) | (y & (~z)); } private long H(long x, long y, long z) { return x ^ y ^ z; } private long I(long x, long y, long z) { return y ^ (x | (~z)); } // FF,GG,HH和II调用F,G,H,I函数进行进一步变换 private long FF(long a, long b, long c, long d, long x, long s, long ac) { a += F(b, c, d) + x + ac; a = ((int) a << s) | ((int) a >>> (32 - s)); // 这里long型数据右移时使用无符号右移运算符>>> a += b; return a; } private long GG(long a, long b, long c, long d, long x, long s, long ac) { a += G(b, c, d) + x + ac; a = ((int) a << s) | ((int) a >>> (32 - s)); // 这里long型数据右移时使用无符号右移运算符>>> a += b; return a; } private long HH(long a, long b, long c, long d, long x, long s, long ac) { a += H(b, c, d) + x + ac; a = ((int) a << s) | ((int) a >>> (32 - s));// 这里long型数据右移时使用无符号右移运算符>>> a += b; return a; } private long II(long a, long b, long c, long d, long x, long s, long ac) { a += I(b, c, d) + x + ac; a = ((int) a << s) | ((int) a >>> (32 - s));// 这里long型数据右移时使用无符号右移运算符>>> a += b; return a; } // MD5的主计算过程,input是需要变换的二进制字节串,inputlen是长度 private void md5Update(byte[] input, int inputLen) { int i = 0, index, partLen; byte[] block = new byte[64]; // 分配64个字节缓冲区 // 根据count计算index值。这里long型数据右移时使用无符号右移运算符>>> index = (int) (count[0] >>> 3) & 0x3F; if ((count[0] += (inputLen << 3)) < (inputLen << 3)) count[1]++; count[1] += (inputLen >>> 29); // 这里int型数据右移时使用无符号右移运算符>>> partLen = 64 - index; // 计算partLen值 if (inputLen >= partLen) { md5Memcpy(buffer, input, index, 0, partLen); md5Transform(buffer); for (i = partLen; i + 63 < inputLen; i += 64) { md5Memcpy(block, input, 0, i, 64); md5Transform(block); } index = 0; } else i = 0; md5Memcpy(buffer, input, index, i, inputLen - i); } // 整理和填写输出结果,结果放到数组digest中。 private void md5Final() { byte[] bits = new byte[8]; int index, padLen; Encode(bits, count, 8); index = (int) (count[0] >>> 3) & 0x3f; // 这里long型数据右移时使用无符号右移运算符>>> padLen = (index < 56) ? (56 - index) : (120 - index); md5Update(PADDING, padLen); md5Update(bits, 8); Encode(digest, state, 16); } // byte数组的块拷贝函数,将input数组中的起始位置为inpos,长度len的数据拷贝到output数组起始位置outpos处。 private void md5Memcpy(byte[] output, byte[] input, int outpos, int inpos, int len) { int i; for (i = 0; i < len; i++) output[outpos + i] = input[inpos + i]; } // MD5核心变换计算程序,由md5Update函数调用,block是分块的原始字节数组 private void md5Transform(byte block[]) { long a = state[0], b = state[1], c = state[2], d = state[3]; long[] x = new long[16]; Decode(x, block, 64); // 进行4级级联运算 // 第1级 a = FF(a, b, c, d, x[0], S11, 0xd76aa478L); /* 1 */ d = FF(d, a, b, c, x[1], S12, 0xe8c7b756L); /* 2 */ c = FF(c, d, a, b, x[2], S13, 0x242070dbL); /* 3 */ b = FF(b, c, d, a, x[3], S14, 0xc1bdceeeL); /* 4 */ a = FF(a, b, c, d, x[4], S11, 0xf57c0fafL); /* 5 */ d = FF(d, a, b, c, x[5], S12, 0x4787c62aL); /* 6 */ c = FF(c, d, a, b, x[6], S13, 0xa8304613L); /* 7 */ b = FF(b, c, d, a, x[7], S14, 0xfd469501L); /* 8 */ a = FF(a, b, c, d, x[8], S11, 0x698098d8L); /* 9 */ d = FF(d, a, b, c, x[9], S12, 0x8b44f7afL); /* 10 */ c = FF(c, d, a, b, x[10], S13, 0xffff5bb1L); /* 11 */ b = FF(b, c, d, a, x[11], S14, 0x895cd7beL); /* 12 */ a = FF(a, b, c, d, x[12], S11, 0x6b901122L); /* 13 */ d = FF(d, a, b, c, x[13], S12, 0xfd987193L); /* 14 */ c = FF(c, d, a, b, x[14], S13, 0xa679438eL); /* 15 */ b = FF(b, c, d, a, x[15], S14, 0x49b40821L); /* 16 */ // 第2级 a = GG(a, b, c, d, x[1], S21, 0xf61e2562L); /* 17 */ d = GG(d, a, b, c, x[6], S22, 0xc040b340L); /* 18 */ c = GG(c, d, a, b, x[11], S23, 0x265e5a51L); /* 19 */ b = GG(b, c, d, a, x[0], S24, 0xe9b6c7aaL); /* 20 */ a = GG(a, b, c, d, x[5], S21, 0xd62f105dL); /* 21 */ d = GG(d, a, b, c, x[10], S22, 0x2441453L); /* 22 */ c = GG(c, d, a, b, x[15], S23, 0xd8a1e681L); /* 23 */ b = GG(b, c, d, a, x[4], S24, 0xe7d3fbc8L); /* 24 */ a = GG(a, b, c, d, x[9], S21, 0x21e1cde6L); /* 25 */ d = GG(d, a, b, c, x[14], S22, 0xc33707d6L); /* 26 */ c = GG(c, d, a, b, x[3], S23, 0xf4d50d87L); /* 27 */ b = GG(b, c, d, a, x[8], S24, 0x455a14edL); /* 28 */ a = GG(a, b, c, d, x[13], S21, 0xa9e3e905L); /* 29 */ d = GG(d, a, b, c, x[2], S22, 0xfcefa3f8L); /* 30 */ c = GG(c, d, a, b, x[7], S23, 0x676f02d9L); /* 31 */ b = GG(b, c, d, a, x[12], S24, 0x8d2a4c8aL); /* 32 */ // 第3级 a = HH(a, b, c, d, x[5], S31, 0xfffa3942L); /* 33 */ d = HH(d, a, b, c, x[8], S32, 0x8771f681L); /* 34 */ c = HH(c, d, a, b, x[11], S33, 0x6d9d6122L); /* 35 */ b = HH(b, c, d, a, x[14], S34, 0xfde5380cL); /* 36 */ a = HH(a, b, c, d, x[1], S31, 0xa4beea44L); /* 37 */ d = HH(d, a, b, c, x[4], S32, 0x4bdecfa9L); /* 38 */ c = HH(c, d, a, b, x[7], S33, 0xf6bb4b60L); /* 39 */ b = HH(b, c, d, a, x[10], S34, 0xbebfbc70L); /* 40 */ a = HH(a, b, c, d, x[13], S31, 0x289b7ec6L); /* 41 */ d = HH(d, a, b, c, x[0], S32, 0xeaa127faL); /* 42 */ c = HH(c, d, a, b, x[3], S33, 0xd4ef3085L); /* 43 */ b = HH(b, c, d, a, x[6], S34, 0x4881d05L); /* 44 */ a = HH(a, b, c, d, x[9], S31, 0xd9d4d039L); /* 45 */ d = HH(d, a, b, c, x[12], S32, 0xe6db99e5L); /* 46 */ c = HH(c, d, a, b, x[15], S33, 0x1fa27cf8L); /* 47 */ b = HH(b, c, d, a, x[2], S34, 0xc4ac5665L); /* 48 */ // 第4级 a = II(a, b, c, d, x[0], S41, 0xf4292244L); /* 49 */ d = II(d, a, b, c, x[7], S42, 0x432aff97L); /* 50 */ c = II(c, d, a, b, x[14], S43, 0xab9423a7L); /* 51 */ b = II(b, c, d, a, x[5], S44, 0xfc93a039L); /* 52 */ a = II(a, b, c, d, x[12], S41, 0x655b59c3L); /* 53 */ d = II(d, a, b, c, x[3], S42, 0x8f0ccc92L); /* 54 */ c = II(c, d, a, b, x[10], S43, 0xffeff47dL); /* 55 */ b = II(b, c, d, a, x[1], S44, 0x85845dd1L); /* 56 */ a = II(a, b, c, d, x[8], S41, 0x6fa87e4fL); /* 57 */ d = II(d, a, b, c, x[15], S42, 0xfe2ce6e0L); /* 58 */ c = II(c, d, a, b, x[6], S43, 0xa3014314L); /* 59 */ b = II(b, c, d, a, x[13], S44, 0x4e0811a1L); /* 60 */ a = II(a, b, c, d, x[4], S41, 0xf7537e82L); /* 61 */ d = II(d, a, b, c, x[11], S42, 0xbd3af235L); /* 62 */ c = II(c, d, a, b, x[2], S43, 0x2ad7d2bbL); /* 63 */ b = II(b, c, d, a, x[9], S44, 0xeb86d391L); /* 64 */ // 分别累加到state[0],state[1],state[2],state[3] state[0] += a; state[1] += b; state[2] += c; state[3] += d; } // 把byte型数据转换为无符号long型数据 private static long byteToul(byte b) { return b > 0 ? b : (b & 0x7F + 128); } // 把byte类型的数据转换成十六进制ASCII字符表示 private static String byteToHEX(byte in) { char[] DigitStr = { '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F' }; char[] out = new char[2]; out[0] = DigitStr[(in >> 4) & 0x0F]; // 取高4位 out[1] = DigitStr[in & 0x0F]; // 取低4位 String s = new String(out); return s; } // 将long型数组按顺序拆成byte型数组,长度为len private void Encode(byte[] output, long[] input, int len) { int i, j; for (i = 0, j = 0; j < len; i++, j += 4) { output[j] = (byte) (input[i] & 0xffL); output[j + 1] = (byte) ((input[i] >>> 8) & 0xffL); output[j + 2] = (byte) ((input[i] >>> 16) & 0xffL); output[j + 3] = (byte) ((input[i] >>> 24) & 0xffL); } } // 将byte型数组按顺序合成long型数组,长度为len private void Decode(long[] output, byte[] input, int len) { int i, j; for (i = 0, j = 0; j < len; i++, j += 4) output[i] = byteToul(input[j]) | (byteToul(input[j + 1]) << 8) | (byteToul(input[j + 2]) << 16) | (byteToul(input[j + 3]) << 24); return; } }
-
代码中的 md5Update、md5Final 和 md5Transform 等方法实现了MD5算法的核心计算过程。
-
初始化: md5Init 方法对MD5算法的状态进行初始化,包括设置初始的计算状态、缓冲区和计数器等。
-
数据更新: md5Update 方法用于更新MD5算法的内部状态,将输入数据按照一定规则进行分块处理。
-
计算最终结果: md5Final 方法用于整理和填写输出结果,将最终的哈希值存储在 digest 数组中。
-
字符串表示: getMD5ofStr 方法将字节数组表示的MD5值转换为字符串形式。
-
Twice MD5: getTwiceMD5ofString 方法对输入字符串进行两次MD5加密,返回最终的加密结果。
实际加密结果
123456的MD5一次加密:E10ADC3949BA59ABBE56E057F20F883E。
123456的MD5二次加密:F59BD65F7EDAFB087A81D4DCA06C4910。
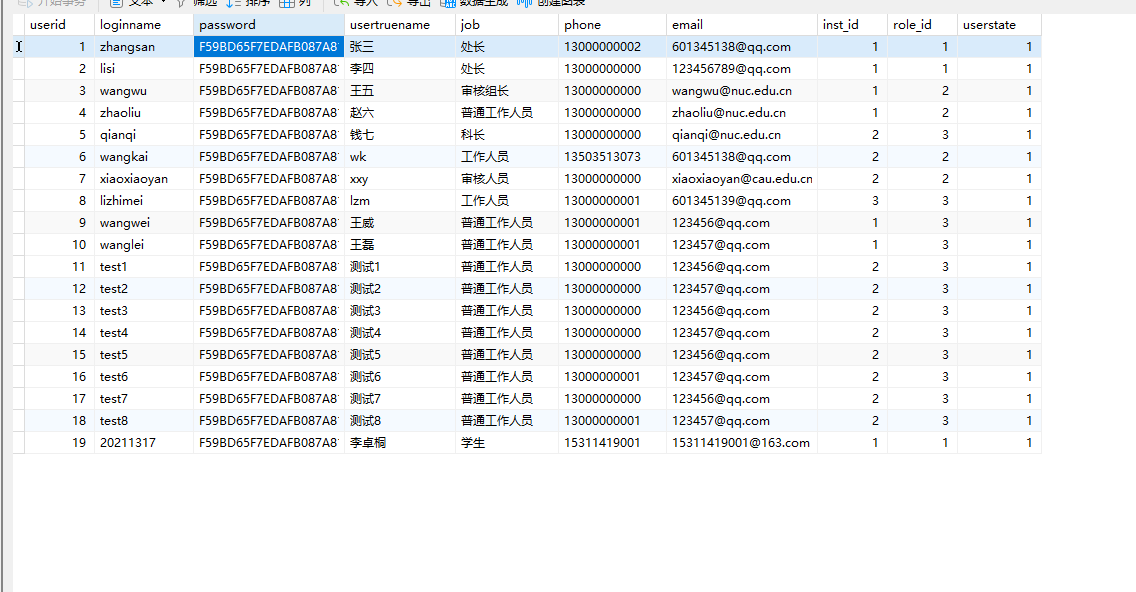
数据库中密码显示如下
改为用SM3实现
代码文件名修改
类名修改
调用名修改(MD5Helper改为SM3Helper)
源代码如下
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; public class SM3Helper { private static final int[] Tj = new int[64]; static { for (int j = 0; j < 16; j++) { Tj[j] = 0x79cc4519; } for (int j = 16; j < 64; j++) { Tj[j] = 0x7a879d8a; } } private static int FF(int X, int Y, int Z, int j) { if (j < 16) { return X ^ Y ^ Z; } else { return (X & Y) | (X & Z) | (Y & Z); } } private static int GG(int X, int Y, int Z, int j) { if (j < 16) { return X ^ Y ^ Z; } else { return (X & Y) | (~X & Z); } } private static int P0(int X) { return X ^ (X << 9 | X >>> 23) ^ (X << 17 | X >>> 15); } private static int P1(int X) { return X ^ (X << 15 | X >>> 17) ^ (X << 23 | X >>> 9); } private static byte[] sm3(byte[] input) { int[] v = new int[8]; System.arraycopy(SM3Consts.IV, 0, v, 0, v.length); // 对消息进行填充 byte[] paddedInput = padInput(input); // 进行消息处理 for (int offset = 0; offset < paddedInput.length; offset += 64) { int[] block = new int[16]; for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) { block[i] = (paddedInput[offset + i * 4] & 0xFF) << 24 | (paddedInput[offset + i * 4 + 1] & 0xFF) << 16 | (paddedInput[offset + i * 4 + 2] & 0xFF) << 8 | (paddedInput[offset + i * 4 + 3] & 0xFF); } sm3ProcessBlock(v, block); } // 返回计算结果 byte[] result = new byte[32]; for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) { result[i * 4] = (byte) (v[i] >>> 24); result[i * 4 + 1] = (byte) (v[i] >>> 16); result[i * 4 + 2] = (byte) (v[i] >>> 8); result[i * 4 + 3] = (byte) v[i]; } return result; } private static byte[] padInput(byte[] input) { // 具体的填充实现,这里只是简化版本,实际中需要考虑消息长度的处理等 // 这里假设输入的长度不超过 2^61 - 1 个字节 int originalLength = input.length; int paddedLength = originalLength + 1 + 8; int paddingBytes = 64 - paddedLength % 64; byte[] paddedInput = new byte[paddedLength + paddingBytes]; System.arraycopy(input, 0, paddedInput, 0, originalLength); paddedInput[originalLength] = (byte) 0x80; long bitLength = (long) originalLength * 8; for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) { paddedInput[paddedLength + i] = (byte) (bitLength >>> (56 - i * 8)); } return paddedInput; } private static void sm3ProcessBlock(int[] v, int[] block) { int[] w = new int[68]; int[] w1 = new int[64]; for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) { w[i] = block[i]; } for (int i = 16; i < 68; i++) { w[i] = P1(w[i - 16] ^ w[i - 9] ^ (w[i - 3] << 15 | w[i - 3] >>> 17)) ^ (w[i - 13] << 7 | w[i - 13] >>> 25) ^ w[i - 6]; } for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++) { w1[i] = w[i] ^ w[i + 4]; } int a = v[0]; int b = v[1]; int c = v[2]; int d = v[3]; int e = v[4]; int f = v[5]; int g = v[6]; int h = v[7]; for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++) { int ss1 = (a << 12 | a >>> 20) + e + (Tj[i] << 12 | Tj[i] >>> 20); ss1 = (ss1 << 7 | ss1 >>> 25) ^ ((ss1 << 12 | ss1 >>> 20) & (ss1 << 17 | ss1 >>> 15)); int ss2 = FF(a, b, c, i) + d + ss1 + w1[i]; int tt1 = GG(e, f, g, i) + h + ss2 + w[i]; int tt2 = P0(e) + FF(e, f, g, i) + tt1; d = c; c = (b << 9 | b >>> 23); b = a; a = tt2; h = g; g = (f << 19 | f >>> 13); f = e; e = P0(tt1); } v[0] ^= a; v[1] ^= b; v[2] ^= c; v[3] ^= d; v[4] ^= e; v[5] ^= f; v[6] ^= g; v[7] ^= h; } public static String getSM3ofStr(String str) { byte[] data = str.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8); byte[] result = sm3(data); return bytesToHexString(result); } private static String bytesToHexString(byte[] bytes) { StringBuilder hexString = new StringBuilder(); for (byte b : bytes) { String hex = Integer.toHexString(0xFF & b); if (hex.length() == 1) { hexString.append('0'); } hexString.append(hex); } return hexString.toString(); } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(getSM3ofStr("123456")); } } class SM3Consts { static final int[] IV = { 0x7380166F, 0x4914B2B9, 0x172442D7, 0xDA8A0600, 0xA96F30BC, 0x163138AA, 0xE38DEE4D, 0xB0FB0E4E }; }
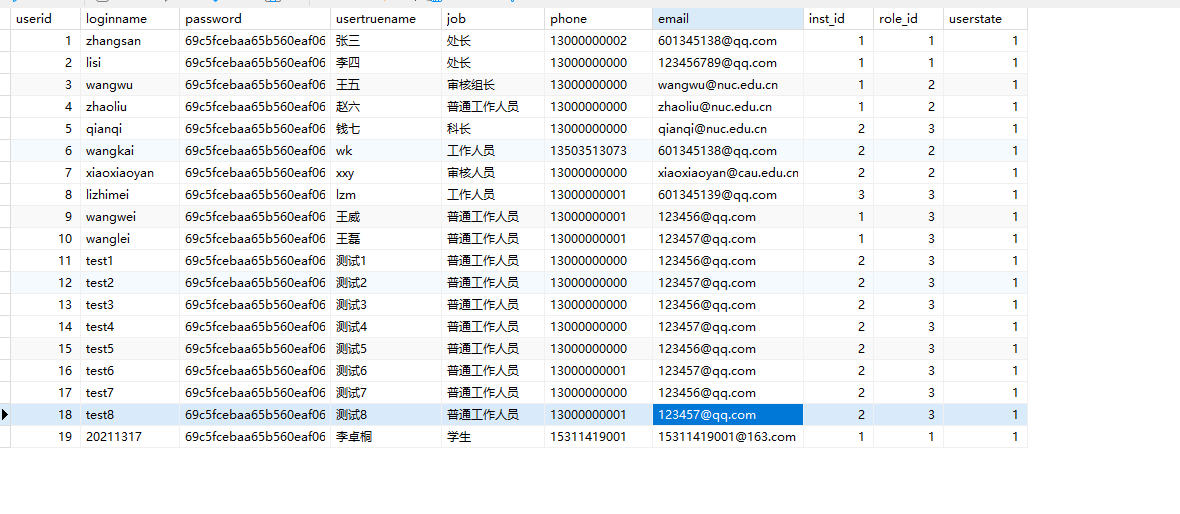
加密结果数据库截图







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 如何调用 DeepSeek 的自然语言处理 API 接口并集成到在线客服系统