C++ 相关系数的计算以及在图像配准领域应用演示
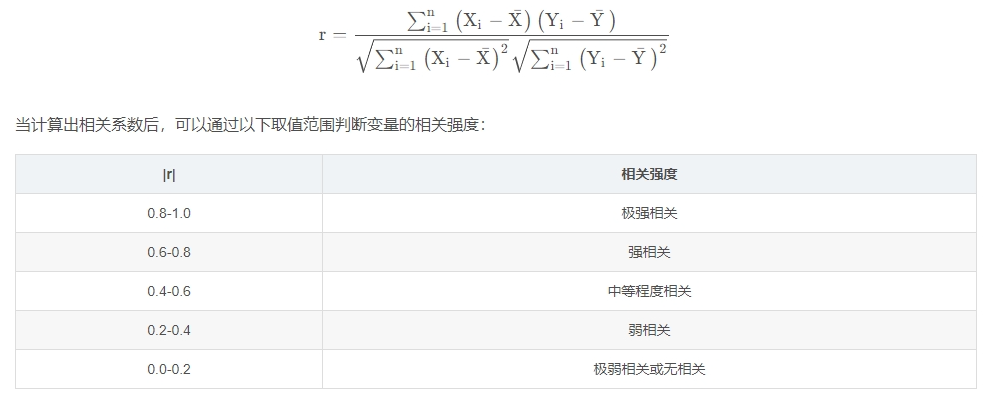
相关系数(皮尔逊相关系数)公式如下

相关系数代码如下

#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <cmath> using namespace std; // 计算平均值 double mean(vector<double> v) { double sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) { sum += v[i]; } return sum / v.size(); } // 计算协方差 double covariance(vector<double> x, vector<double> y) { double x_mean = mean(x); double y_mean = mean(y); double sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < x.size(); i++) { sum += (x[i] - x_mean) * (y[i] - y_mean); } return sum / x.size(); } // 计算相关系数 double correlation(vector<double> x, vector<double> y) { double cov = covariance(x, y); double x_std = sqrt(covariance(x, x)); double y_std = sqrt(covariance(y, y)); double res = 0; if(x_std != 0 && y_std !=0) res = cov / (x_std * y_std); return res; } int main() { vector<double> x1 = { 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 }; vector<double> y1 = { 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 }; cout << "x1: "; for (int i = 0; i < x1.size(); i++) { cout << x1[i] << " "; } cout << endl; cout << "y1: "; for (int i = 0; i < y1.size(); i++) { cout << y1[i] << " "; } cout << endl; cout << "x1-y1相关系数: " << correlation(x1, y1) << "\r\n" << endl; vector<double> x2 = { 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 }; vector<double> y2 = { 20, 30, 40, 50, 60 }; cout << "x2: "; for (int i = 0; i < x2.size(); i++) { cout << x2[i] << " "; } cout << endl; cout << "y2: "; for (int i = 0; i < y2.size(); i++) { cout << y2[i] << " "; } cout << endl; cout << "x2-y2相关系数: " << correlation(x2, y2) << "\r\n" << endl; vector<double> x3 = { 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 }; vector<double> y3 = { 2, 3, 5, 6, 7 }; cout << "x3: "; for (int i = 0; i < x1.size(); i++) { cout << x3[i] << " "; } cout << endl; cout << "y3: "; for (int i = 0; i < y3.size(); i++) { cout << y3[i] << " "; } cout << endl; cout << "x3-y3相关系数: " << correlation(x3, y3) << "\r\n" << endl; vector<double> x4 = { 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 }; vector<double> y4 = { 6, 2, 5, 3, 4 }; cout << "x4: "; for (int i = 0; i < x4.size(); i++) { cout << x4[i] << " "; } cout << endl; cout << "y4: "; for (int i = 0; i < y4.size(); i++) { cout << y4[i] << " "; } cout << endl; cout << "x4-y4相关系数: " << correlation(x4, y4) << "\r\n" << endl; vector<double> x5 = { 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 }; vector<double> y5 = { 7, 6, 5, 4, 3 }; cout << "x5: "; for (int i = 0; i < x5.size(); i++) { cout << x5[i] << " "; } cout << endl; cout << "y5: "; for (int i = 0; i < y5.size(); i++) { cout << y5[i] << " "; } cout << endl; cout << "x5-y5相关系数: " << correlation(x5, y5) << "\r\n" << endl; return 0; }
运行结果

相关系数越接近+1则两个向量同方向接近,相关系数越接近-1则两个向量反方向接近。该系数的应用举例 ---图像配准
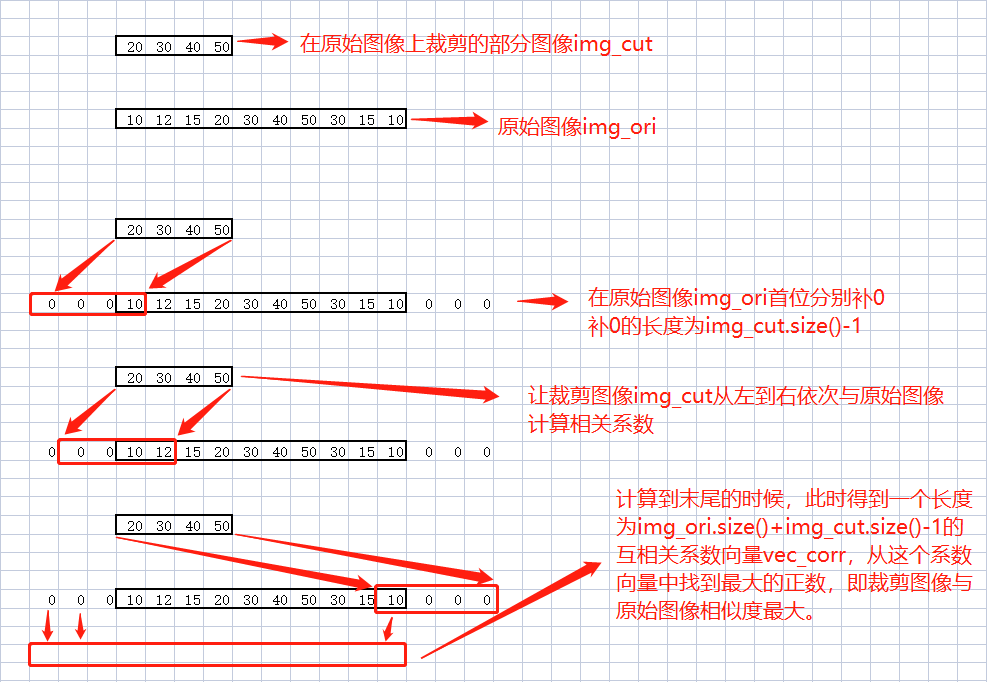
归一化一维互相关系数C++代码如下

#include <iostream> #include <iomanip> #include <vector> #include <cmath> using namespace std; // 计算平均值 double mean(vector<double> v) { double sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) { sum += v[i]; } return sum / v.size(); } // 计算协方差 double covariance(vector<double> x, vector<double> y) { double x_mean = mean(x); double y_mean = mean(y); double sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < x.size(); i++) { sum += (x[i] - x_mean) * (y[i] - y_mean); } return sum / x.size(); } // 计算相关系数 double correlation(vector<double> x, vector<double> y) { double cov = covariance(x, y); double x_std = sqrt(covariance(x, x)); double y_std = sqrt(covariance(y, y)); return cov / (x_std * y_std); } vector<double> correlation1(vector<double> x, vector<double> y) { int N1 = x.size(); int N2 = y.size(); int N = N1 + N2 - 1; vector<double> z(N); for (int i = 0; i < N1 - 1; i++) { y.insert(y.begin(), 0);//在头部补0 y.push_back(0);//在尾部补0 } for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { vector<double> cut(y.begin() + i, y.begin() + i + N1);//在y向量上从左到右依次截取N1个长度的元素放到cut中 z[i] = correlation(x,cut);//计算相关系数并存入z向量中 } return z; } int main() { vector<double> x = { 20, 30, 40, 50}; vector<double> y = { 10,12,15,20,30,40,50,30,15,10}; vector<double> z = correlation1(x, y); for (int i = 0; i < z.size(); i++) { cout << fixed << setprecision(4) << z[i] << " ";//四舍五入保留4位小数点 } cout << endl; return 0; }
运行结果如下
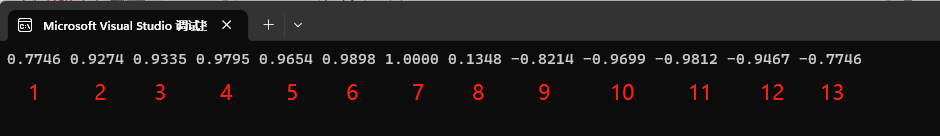
比较到7次(M)的时候相关系数为1,说明此时原始图像上的片段与裁剪图像完全相似。那裁剪图像在原始图像上相似的位置为M - img_cut.size() 即7 - 4 = 3
可以用matlab验证此C++代码
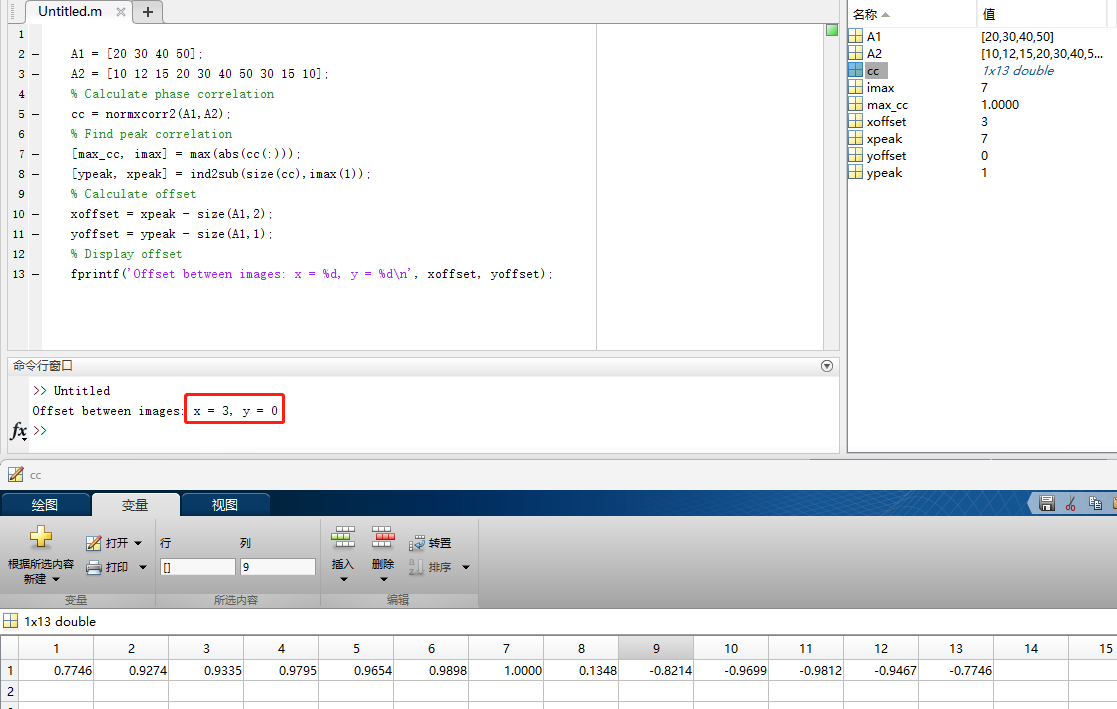
matlab里面的normxcorr2是归一化二维互相关算法函数,计算二维互相关系数其实就是把二维展开成一维再进行相关系数计算。原理如下图
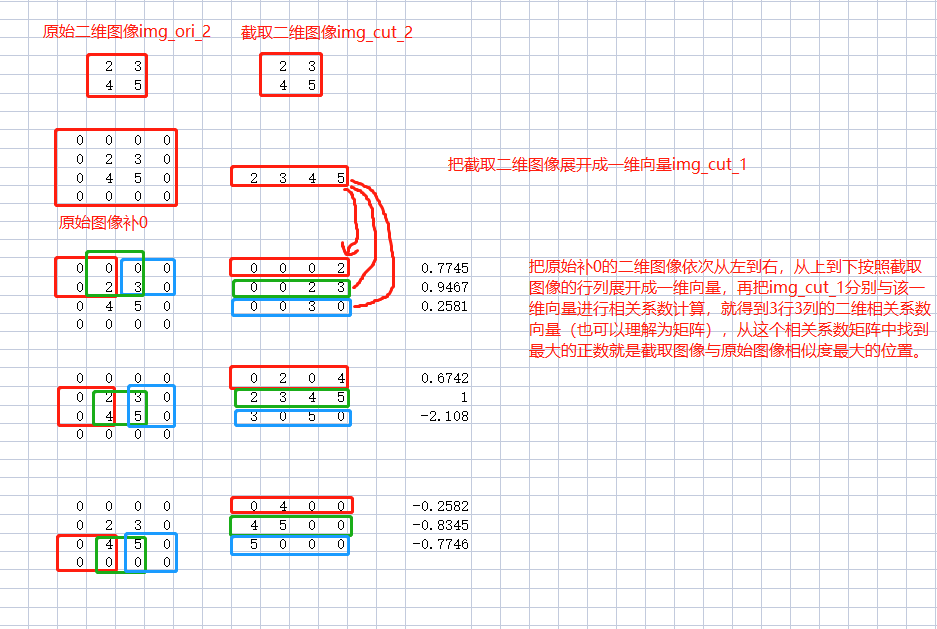
归一化二维相关系数C++代码如下

#include <iostream> #include <iomanip> #include <vector> #include <cmath> using namespace std; // 计算平均值 double mean(vector<double> v) { double sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) { sum += v[i]; } return sum / v.size(); } // 计算协方差 double covariance(vector<double> x, vector<double> y) { double x_mean = mean(x); double y_mean = mean(y); double sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < x.size(); i++) { sum += (x[i] - x_mean) * (y[i] - y_mean); } return sum / x.size(); } // 计算相关系数 double correlation(vector<double> x, vector<double> y) { double cov = covariance(x, y); double x_std = sqrt(covariance(x, x)); double y_std = sqrt(covariance(y, y)); return cov / (x_std * y_std); } // 计算两个一维向量的归一化互相关系数 vector<double> correlation1(vector<double> x, vector<double> y) { int N1 = x.size(); int N2 = y.size(); int N = N1 + N2 - 1; vector<double> z(N); for (int i = 0; i < N1 - 1; i++) { y.insert(y.begin(), 0);//在头部补0 y.push_back(0);//在尾部补0 } for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { vector<double> cut(y.begin() + i, y.begin() + i + N1);//在y向量上从左到右依次截取N1个长度的元素放到cut中 z[i] = correlation(x,cut);//计算相关系数并存入z向量中 } return z; } //二维向量转成一维向量 vector<double> vector2to1(vector<vector<double>> a) { int n = a.size(); // a的行数 int m = a[0].size(); // a的列数 vector<double> b; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) for(int j = 0; j < m; j++) b.push_back(a[i][j]); return b; } //截取二维向量指定的区域 vector<vector<double>> vector_sub(vector<vector<double>> a, int start_row, int start_col, int end_row, int end_col) { vector<vector<double>> sub_x; for (int i = start_row; i < end_row; i++) { vector<double> row; for (int j = start_col; j < end_col; j++) { row.push_back(a[i][j]); } sub_x.push_back(row); } return sub_x; } // 计算两个矩阵的归一化互相关系数 vector<vector<double>> correlation2(vector<vector<double>> x, vector<vector<double>> y) { int N1 = x.size(); // x的行数 int N2 = x[0].size(); // x的列数 int M1 = y.size(); // y的行数 int M2 = y[0].size(); // y的列数 int N = N1 + M1 - 1; // z的行数 int M = N2 + M2 - 1; // z的列数 vector<vector<double>> z(N, vector<double>(M, 0)); // 初始化z //补0的行 for (int i = 0; i < N1 - 1; i++) { y.insert(y.begin(), vector<double>(M2, 0));//在y开始插入1行10元素 y.push_back(vector<double>(M2, 0));//在y尾部追加1行0元素 } //补0的列 for (int i = 0; i < N2 - 1; i++) { for (int i = 0; i < y.size(); i++) { y[i].insert(y[i].begin(), 0);//在头部补0 y[i].push_back(0);//在尾部补0 } } vector<double> x1 = vector2to1(x); vector<double> y1; for(int n = 0; n < N; n++) for (int m = 0; m < M; m++) { y1 = vector2to1(vector_sub(y, n, m, n + N1,m + N2)); z[n][m] = correlation(x1,y1); } return z; } int main() { vector<vector<double>> x = { {2, 3}, {4, 5} }; vector<vector<double>> y = { {2, 3}, {4, 5} }; vector<vector<double>> z =correlation2(x,y); for (int i = 0; i < z.size(); i++) { for (int j = 0; j < z[0].size(); j++) cout << fixed << setprecision(4) << z[i][j] << " ";//四舍五入保留4位小数点 cout << endl; } return 0; }
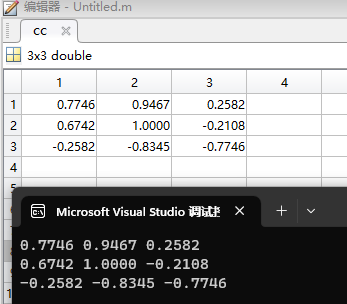
归一化二维相关系数Matlab代码如下

A1 = [2 3;4 5]; A2 = [2 3;4 5]; % Calculate phase correlation cc = normxcorr2(A1,A2); % Find peak correlation [max_cc, imax] = max(abs(cc(:))); [ypeak, xpeak] = ind2sub(size(cc),imax(1)); % Calculate offset xoffset = xpeak - size(A1,2); yoffset = ypeak - size(A1,1); % Display offset fprintf('Offset between images: x = %d, y = %d\n', xoffset, yoffset);
对比结果如下图
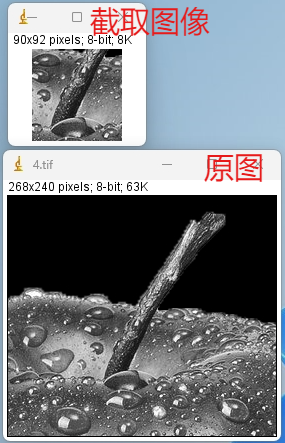
我们用两张图像做个演示
Matlab代码如下

t0 = cputime; gray1 = imread('C:\Users\MingYi-LZQ\Desktop\3.tif'); gray2 = imread('C:\Users\MingYi-LZQ\Desktop\4.tif'); % Compute the normalized cross-correlation between the two images corr = normxcorr2(gray1, gray2); % Find the location of the peak correlation [max_corr, max_index] = max(abs(corr(:))); [y_peak, x_peak] = ind2sub(size(corr), max_index(1)); % Compute the offset between the two images offset = [y_peak - size(gray1, 1), x_peak - size(gray1, 2)]; % Apply the offset to the second image registered = imtranslate(gray2, -offset); % Display the registered image imshow(registered); %耗时时间 t1 = cputime-t0;
C++代码如下

#include <iostream> #include <iomanip> #include <vector> #include <cmath> #include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> using namespace std; using namespace cv; // 计算平均值 double mean(vector<double> v) { double sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) { sum += v[i]; } return sum / v.size(); } // 计算协方差 double covariance(vector<double> x, vector<double> y) { double x_mean = mean(x); double y_mean = mean(y); double sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < x.size(); i++) { sum += (x[i] - x_mean) * (y[i] - y_mean); } return sum / x.size(); } // 计算相关系数 double correlation(vector<double> x, vector<double> y) { double cov = covariance(x, y); double x_std = sqrt(covariance(x, x)); double y_std = sqrt(covariance(y, y)); double res = 0; if(x_std != 0 && y_std !=0) res = cov / (x_std * y_std); return res; } // 计算两个一维向量的归一化互相关系数 vector<double> correlation1(vector<double> x, vector<double> y) { int N1 = x.size(); int N2 = y.size(); int N = N1 + N2 - 1; vector<double> z(N); for (int i = 0; i < N1 - 1; i++) { y.insert(y.begin(), 0);//在头部补0 y.push_back(0);//在尾部补0 } for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { vector<double> cut(y.begin() + i, y.begin() + i + N1);//在y向量上从左到右依次截取N1个长度的元素放到cut中 z[i] = correlation(x,cut);//计算相关系数并存入z向量中 } return z; } //二维向量转成一维向量 vector<double> vector2to1(vector<vector<double>> a) { int n = a.size(); // a的行数 int m = a[0].size(); // a的列数 vector<double> b; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) for(int j = 0; j < m; j++) b.push_back(a[i][j]); return b; } //截取二维向量指定的区域 vector<vector<double>> vector_sub(vector<vector<double>> a, int start_row, int start_col, int end_row, int end_col) { vector<vector<double>> sub_x; for (int i = start_row; i < end_row; i++) { vector<double> row; for (int j = start_col; j < end_col; j++) { row.push_back(a[i][j]); } sub_x.push_back(row); } return sub_x; } // 计算两个矩阵的归一化互相关系数 vector<vector<double>> correlation2(vector<vector<double>> x, vector<vector<double>> y) { int N1 = x.size(); // x的行数 int N2 = x[0].size(); // x的列数 int M1 = y.size(); // y的行数 int M2 = y[0].size(); // y的列数 int N = N1 + M1 - 1; // z的行数 int M = N2 + M2 - 1; // z的列数 vector<vector<double>> z(N, vector<double>(M, 0)); // 初始化z //补0的行 for (int i = 0; i < N1 - 1; i++) { y.insert(y.begin(), vector<double>(M2, 0));//在y开始插入1行10元素 y.push_back(vector<double>(M2, 0));//在y尾部追加1行0元素 } //补0的列 for (int i = 0; i < N2 - 1; i++) { for (int i = 0; i < y.size(); i++) { y[i].insert(y[i].begin(), 0);//在头部补0 y[i].push_back(0);//在尾部补0 } } vector<double> x1 = vector2to1(x); vector<double> y1; for(int n = 0; n < N; n++) for (int m = 0; m < M; m++) { y1 = vector2to1(vector_sub(y, n, m, n + N1,m + N2)); z[n][m] = correlation(x1,y1); } return z; } int main() { vector<vector<double>> img1; Mat image1 = imread("C:/Users/MingYi-LZQ/Desktop/3.tif", IMREAD_UNCHANGED); if (image1.empty()) { cout << "Could not open or find the image" << endl; return -1; } img1.resize(image1.rows, vector<double>(image1.cols)); for (int i = 0; i < image1.rows; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < image1.cols; j++) { img1[i][j] = (double)image1.at<uchar>(i, j); } } vector<vector<double>> img2; Mat image2 = imread("C:/Users/MingYi-LZQ/Desktop/4.tif", IMREAD_UNCHANGED); if (image2.empty()) { cout << "Could not open or find the image" << endl; return -1; } img2.resize(image2.rows, vector<double>(image2.cols)); for (int i = 0; i < image2.rows; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < image2.cols; j++) { img2[i][j] = (double)image2.at<uchar>(i, j); } } vector<vector<double>> z = correlation2(img1, img2); double max_corr = 0; int x_peak = 0; int y_peak = 0; vector<vector<double>> offset; for (int i = 0; i < z.size(); i++) { for (int j = 0; j < z[0].size(); j++) { if (z[i][j] > max_corr) { max_corr = z[i][j];//找到最大的相关系数 x_peak = j + 1;//最大相关系数对应的x坐标 y_peak = i + 1;//最大相关系数对应的y坐标 } } } //计算出实际x y的偏移量 vector<double> temp; temp.push_back(x_peak - img1.size()); temp.push_back(y_peak - img1[0].size()); offset.push_back(temp); return 0; }
对比结果
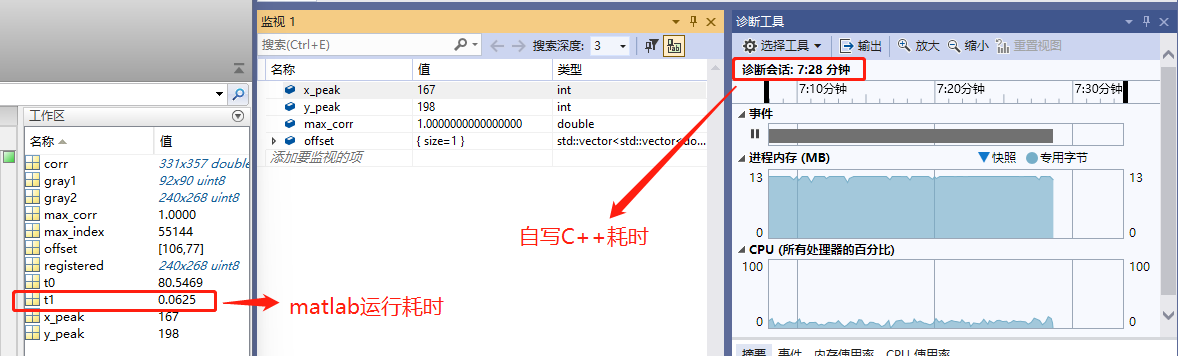
速度虽然差很多,但是原理都是一样的。下一节探讨如何提高C++运行速度。
本文参考文章如下:






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
2021-06-28 C# 读写16位tif图片灰度数据