面向切面编程AOP
本文的主要内容(AOP):
1.AOP面向切面编程的相关概念(思想、原理、相关术语)
2.AOP编程底层实现机制(动态代理机制:JDK代理、Cglib代理)
3.Spring的传统AOP编程的案例(计算方法的运行时间)
4.Spring结合AspectJ实现AOP编程(XML和注解)
5.JdbcTemplate编程(连接池的配置(传统连接池、jndi连接池)、外部属性文件的引入、实现DAO的CRUD操作(快捷使用模版类的方法dao类))
目标:
1.掌握AOP的概念、思想、应用
2.aop的编程(传统xml——要会,aspectj注解——掌握)
3.其他:外部属性文件引入、连接池、使用jdbctemplate操作数据库(jdbctemplateDAO)
4.动态代理(JDK代理、CGLIB代理)-了解-知道-会写--会用
1. AOP面向切面编程的相关概念
1.1. 什么是AOP ?
AOP (Aspect Oriented Programing) 称为:面向切面编程,它是一种编程思想。
AOP采取横向抽取机制,取代了传统纵向继承体系重复性代码的编写方式(例如性能监视、事务管理、安全检查、缓存、日志记录等)。
【扩展了解】AOP 是 OOP(面向对象编程(Object Oriented Programming,OOP,面向对象程序设计)是一种计算机编程架构),思想延续!
什么是OCP:即开闭原则。
参考网站:http://www.cnblogs.com/muzongyan/archive/2010/08/05/1793454.html
AOP 思想: 基于代理思想,对原来目标对象,创建代理对象,在不修改原对象代码情况下,通过代理对象,调用增强功能的代码,从而对原有业务方法进行增强!
切面:需要代理一些方法和增强代码 。
1.2. AOP的应用场景
场景一: 记录日志
场景二: 监控方法运行时间 (监控性能)
场景三: 权限控制
场景四: 缓存优化 (第一次调用查询数据库,将查询结果放入内存对象, 第二次调用, 直接从内存对象返回,不需要查询数据库)
场景五: 事务管理 (调用方法前开启事务, 调用方法后提交或者回滚、关闭事务 )
1.3. Spring AOP编程两种方式
l Spring AOP使用纯Java实现,不需要专门的编译过程和类加载器,在运行期通过代理方式向目标类植入增强代码。
l AsPectJ是一个基于Java语言的AOP框架,Spring2.0开始,Spring AOP引入对Aspect的支持。
简单的说,Spring内部支持两套AOP编程的方案:
l Spring 1.2 开始支持AOP编程(传统SpringAOP 编程),编程非常复杂 ---- 更好学习Spring 内置传统AOP代码
l Spring 2.0 之后支持第三方 AOP框架(AspectJ ),实现另一种 AOP编程 -- 推荐
1.4. AOP编程相关术语
AOP思想编程的机制
AOP的相关术语
Aspect(切面): 是通知和切入点的结合,通知和切入点共同定义了关于切面的全部内容---它的功能、在何时和何地完成其功能
joinpoint(连接点):所谓连接点是指那些被拦截到的点。在spring中,这些点指的是方法,因为spring只支持方法类型的连接点.
Pointcut(切入点):所谓切入点是指我们要对哪些joinpoint进行拦截的定义.
通知定义了切面的”什么”和”何时”,切入点就定义了”何地”.
Advice(通知):所谓通知是指拦截到joinpoint之后所要做的事情就是通知.通知分为前置通知,后置通知,异常通知,最终通知,环绕通知(切面要完成的功能)
Target(目标对象):代理的目标对象
Weaving(织入):是指把切面应用到目标对象来创建新的代理对象的过程.切面在指定的连接点织入到目标对象
Introduction(引入):在不修改类代码的前提下, Introduction可以在运行期为类动态地添加一些方法或Field.
通过案例解释AOP相关概念
Aspect切面(类):增强代码 Advice(writeLog方法)和 切入点 Pointcut(save,update,delete) 的结合。换句话说:对哪些方法进行怎样的代码增强。
2. AOP编程底层实现机制(了解)
AOP 就是要对目标进行代理对象的创建, Spring AOP是基于动态代理的,基于两种动态代理机制: JDK动态代理和CGLIB动态代理
面试题:动态代理和静态代理区别?
动态代理:在虚拟机内部,运行的时候,动态生成代理类(运行时生成,runtime生成) ,并不是真正存在的类, 一般格式:Proxy$$ (Proxy$$Customer)
静态代理:实际存在代理类 (例如:struts2 Action的代理类 ActionProxy,struts2的拦截器)
附录:什么是ActionProxy
参考:http://www.tuicool.com/articles/RNRRriz
2.1. JDK动态代理
JDK动态代理,针对目标对象的接口进行代理 ,动态生成接口的实现类 !(必须有接口)
【过程要点】:
1、必须对接口生成代理
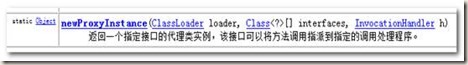
2、采用Proxy对象,通过newProxyInstance方法为目标创建代理对象。
(1)目标对象类加载器
(2)目标对象实现的接口
(3)代理后的处理程序InvocationHandler
使用 Proxy类提供 newProxyInstance 方法对目标对象接口进行代理
参数说明:
loader:定义代理类的类加载器
interfaces:代理类要实现的接口列表
h:指派方法调用的调用处理程序
3、实现InvocationHandler 接口中 invoke方法,在目标对象每个方法调用时,都会执行invoke
【示例】:需求:对目标对象中存在保存和查询的方法,在执行保存的方法的时候,记录日志
第一步:新建web工程:spring3_day02。创建包cn.itcast.spring.a_proxy包
第二步:编写业务接口,接口中定义save()和find()的方法。
//接口(表示代理的目标接口)
publicinterfaceICustomerService {
//保存
publicvoid save();
//查询
publicint find();
}
//实现类
publicclassCustomerServiceImpl implements ICustomerService{
publicvoid save() {
System.out.println("客户保存了。。。。。");
}
publicint find() {
System.out.println("客户查询数量了。。。。。");
return 100;
}
}
第四步:使用JDK代理完成
代理工厂:
有三种方案完成JDK动态代理:
方案一:在内部实现new InvocationHandler(),指定匿名类
//专门用来生成jdk的动态代理对象的-通用
publicclass JdkProxyFactory{
//成员变量
private Object target;
//注入target目标对象
public JdkProxyFactory(Object target) {
this.target = target;
}
public Object getProxyObject(){
//参数1:目标对象的类加载器
//参数2:目标对象实现的接口
//参数3:回调方法对象
/**方案一:在内部实现new InvocationHandler(),指定匿名类*/
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.getClass().getClassLoader(), target.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler(){
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable {
//如果是保存的方法,执行记录日志操作
if(method.getName().equals("save")){
writeLog();
}
//目标对象原来的方法执行
Object object = method.invoke(target, args);//调用目标对象的某个方法,并且返回目标对象
return object;
}
});
}
//记录日志
privatestaticvoid writeLog(){
System.out.println("增强代码:写日志了。。。");
}
}
//专门用来生成jdk的动态代理对象的-通用
publicclass JdkProxyFactory{
//成员变量
private Object target;
//注入target
public JdkProxyFactory(Object target) {
this.target = target;
}
public Object getProxyObject(){
//参数1:目标对象的类加载器
//参数2:目标对象实现的接口
//参数3:回调方法对象
/**方案二:传递内部类的对象,指定内部类*/
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.getClass().getClassLoader(), target.getClass().getInterfaces(),newMyInvocationHandler());
}
//自己制定内部类:类的内部可以多次使用类型
privateclassMyInvocationHandlerimplements InvocationHandler{
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable {
//如果是保存的方法,执行记录日志操作
if(method.getName().equals("save")){
writeLog();
}
//目标对象原来的方法执行
Object object = method.invoke(target, args);//调用目标对象的某个方法,并且返回目标对象方法的返回值
return object;
}
}
//记录日志
privatestaticvoid writeLog(){
System.out.println("增强代码:写日志了。。。");
}
}
方案三:直接使用调用类作为接口实现类,实现InvocationHandler接口
//专门用来生成jdk的动态代理对象的-通用
publicclass JdkProxyFactory implements InvocationHandler{
//成员变量
private Object target;
//注入target
publicJdkProxyFactory(Object target) {
this.target = target;
}
public Object getProxyObject(){
//参数1:目标对象的类加载器
//参数2:目标对象实现的接口
//参数3:回调方法对象
/**方案三:直接使用调用类作为接口实现类,实现InvocationHandler接口*/
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.getClass().getClassLoader(), target.getClass().getInterfaces(),this);
}
//记录日志
privatestaticvoid writeLog(){
System.out.println("增强代码:写日志了。。。");
}
//参数1:代理对象
//参数2:目标的方法对象
//参数3:目标的方法的参数
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable {
//如果是保存的方法,执行记录日志操作
if(method.getName().equals("save")){
writeLog();
}
//目标对象原来的方法执行
Object object = method.invoke(target, args);//调用目标对象的某个方法,并且返回目标对象
return object;
}
}
第五步:使用SpringTest.java进行测试
//目标:使用动态代理,对原来的方法进行功能增强,而无需更改原来的代码。
//JDK动态代理:基于接口的(对象的类型,必须实现接口!)
@Test
publicvoidtestJdkProxy(){
//target(目标对象)
ICustomerService target = new CustomerServiceImpl();
//实例化注入目标对象
JdkProxyFactory jdkProxyFactory = new JdkProxyFactory(target);
//获取Proxy Object代理对象:基于目标对象类型的接口的类型的子类型的对象
ICustomerService proxy=(ICustomerService)jdkProxyFactory.getProxyObject();
//调用目标对象的方法
proxy.save();
System.out.println("————————————————————————————————————————");
proxy.find();
}
第六步:在控制台查看输出结果
从结果上看出:在保存方法的前面,输入了日志增强。
最后,使用断点查看JDK代理,生成的代理对象
说明
Interface ICustomerService{
//目标接口
}
Class CustomerServiceImpl implements ICustomerService{
//目标类实现接口
}
JDK代理对接口代理
Class $Proxy2 implements ICustomerService{
ICustomerService customerService = new CustomerServiceImpl();
public void save() {
writeLog()
}
public int find() {
int returnValue = customerService.find();
return returnValue;
}
//记录日志
private static void writeLog(){
System.out.println("增强代码:写日志了。。。");
}
}
注意:
JDK动态代理的缺点: 只能面向接口代理,不能直接对目标类进行代理 ,如果没有接口,则不能使用JDK代理。
2.2. Cglib动态代理
Cglib的引入为了解决类的直接代理问题(生成代理子类),不需要接口也可以代理 !
什么是cglib ?
CGLIB(Code Generation Library)是一个开源项目!是一个强大的,高性能,高质量的Code生成类库,它可以在运行期扩展Java类与实现Java接口。
百度百科:参考网站http://baike.baidu.com/link?url=A19bwp5SinV_KZPV6TMorLe4oGpPVdAHgdRBJZC3HCuVqNm7JaDCnkOpvxdF4bnq-f9Wni4CBm5rZFiygUgHCa
该代理方式需要相应的jar包,但不需要导入。因为Spring core包已经包含cglib ,而且同时包含了cglib 依赖的asm的包(动态字节码的操作类库)
【示例】:需求:对目标对象中存在保存和查询的方法,在执行保存的方法的时候,记录日志
第一步:将spring的核心jar导入进来,因为spring的包,包含了cglib的包
将spring的core包引进来(他包含了cglib)
第二步:编写业务类,创建类ProductService.java,类不需要实现接口
//没有接口的类
publicclass ProductService {
publicvoid save() {
System.out.println("商品保存了。。。。。");
}
publicint find() {
System.out.println("商品查询数量了。。。。。");
return 99;
}
}
第三步:使用cglib代理,创建类CglibProxyFactory.java
//cglib动态代理工厂:用来生成cglib代理对象
publicclass CglibProxyFactory implementsMethodInterceptor{
//声明一个代理对象引用
private Object target;
//注入代理对象
public CglibProxyFactory(Object target) {
this.target = target;
}
//获取代理对象
public Object getProxyObject(){
//1.代理对象生成器(工厂思想)
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
//2.在增强器上设置两个属性
//设置要生成代理对象的目标对象:生成的目标对象类型的子类型
enhancer.setSuperclass(target.getClass());
//设置回调方法
enhancer.setCallback(this);
// Callback
//3.创建获取对象
return enhancer.create();
}
//回调方法(代理对象的方法)
//参数1:代理对象
//参数2:目标对象的方法对象
//参数3:目标对象的方法的参数的值
//参数4:代理对象的方法对象
public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args,
MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
//如果是保存的方法,执行记录日志操作
if(method.getName().equals("save")){
writeLog();
}
//目标对象原来的方法执行
Object object = method.invoke(target, args);//调用目标对象的某个方法,并且返回目标对象
return object;
}
//写日志的增强功能
//Advice通知、增强
//记录日志
privatestaticvoid writeLog(){
System.out.println("增强代码:写日志了。。。");
}
}
第四步:测试代码,使用SpringTest.java进行测试
//cglib动态代理:可以基于类(无需实现接口)生成代理对象
@Test
publicvoid testCglibProxy(){
//target目标:
ProductService target = new ProductService();
//weave织入,生成proxy代理对象
//代理工厂对象,注入目标
CglibProxyFactory cglibProxyFactory = new CglibProxyFactory(target);
//获取proxy:思考:对象的类型
//代理对象,其实是目标对象类型的子类型
ProductService proxy=(ProductService) cglibProxyFactory.getProxyObject();
//调用代理对象的方法
proxy.save();
System.out.println("————————————————————————————————————————");
proxy.find();
}
第五步:控制台输出结果
说明
Class ProductService{
//目标类
}
Cglib对类代理
Class ProductService$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$df9980d0 extends ProductService{
//CGLIB代理类是目标类的子类
ProductService productService= new ProductService();
public void save() {
writeLog()
productService.save();
}
public int find() {
int returnValue = productService.find();
return returnValue;
}
//记录日志
private static void writeLog(){
System.out.println("增强代码:写日志了。。。");
}
}
2.3. 代理知识小结
区别:
l Jdk代理:基于接口的代理,一定是基于接口,会生成目标对象的接口类型的子对象。
l Cglib代理:基于类的代理,不需要基于接口,会生成目标对象类型的子对象。
代理知识总结:
l spring在运行期,生成动态代理对象,不需要特殊的编译器.
l spring有两种代理方式:
1.若目标对象实现了若干接口,spring使用JDK的java.lang.reflect.Proxy类代理。
2.若目标对象没有实现任何接口,spring使用CGLIB库生成目标对象的子类。
l 使用该方式时需要注意:
1.对接口创建代理优于对类创建代理,因为会产生更加松耦合的系统,所以spring默认是使用JDK代理。
对类代理是让遗留系统或无法实现接口的第三方类库同样可以得到通知,这种方式应该是备用方案。
2.标记为final的方法不能够被通知。spring是为目标类产生子类。任何需要被通知的方法都被复写,将通知织入。final方法是不允许重写的。
3.spring只支持方法连接点:不提供属性接入点,spring的观点是属性拦截破坏了封装。
面向对象的概念是对象自己处理工作,其他对象只能通过方法调用的得到的结果。
提示:
l Spring AOP 优先对接口进行代理 (使用Jdk动态代理)
l 如果目标对象没有实现任何接口,才会对类进行代理(使用cglib动态代理)
3. 传统Spring AOP编程案例
传统SpringAOP 是指 1.2版本之后开始支持AOP编程 。
提示:
老的AOP的编程配置过于复杂,这里采用AspectJ的切入点语法来讲解。
1、确定目标对象(target—>bean)
2、编写Advice通知方法(增强代码)
3、配置切入点和切面
直接使用 CustomerService(需要接口)和ProductService(不需要接口)作为 target目标对象
提示:spring的所有功能,都是基于bean的,下面所说的“目标”,都是bean。
3.1. 传统SpringAOP的Advice编写(了解)
传统Spring AOP的通知(增强)种类:
l AOP联盟为通知Advice定义了org.aopalliance.aop.Interface.Advice
l Spring按照通知Advice在目标类方法的连接点位置,可以分为5类
(1)前置通知 org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice
* 在目标方法执行前实施增强
(2)后置通知 org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice
* 在目标方法执行后实施增强
(3)环绕通知 org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor
* 在目标方法执行前后实施增强
(4)异常抛出通知 org.springframework.aop.ThrowsAdvice
* 在方法抛出异常后实施增强
(5)引介通知 org.springframework.aop.IntroductionInterceptor
* 在目标类中添加一些新的方法和属性
简单的说:通知就是增强的方式方法
遵循aop联盟规范,传统Spring AOP编程的Advice有五种(前置通知、后置通知、环绕通知、异常通知、引介通知) ,
传统SpringAOP的Advice 必须实现对应的接口!
【需求】:开发一个记录方法运行时间的例子。将目标方法的运行时间,写入到log4j的日志中。
开发步骤:
第一步:导入jar包 (11个)
基本spring开发 6个 (4+2)(包含配置文件)
Spring测试集成 1个
Spring AOP编程 4个 (2对)
l com.springsource.org.aopalliance-1.0.0.jar: AOP联盟规范
l spring-aop-3.2.0.RELEASE.jar:springAOP 整合扩展
l com.springsource.org.aspectj.weaver-1.6.8.RELEASE.jar:aspectJ官方包
l spring-aspects-3.2.0.RELEASE.jar:spring对aspectJ集成
AOP联盟包:
路径:spring-framework-3.0.2.RELEASE-dependencies\org.aopalliance\com.springsource.org.aopalliance\1.0.0
Aspectj包:
路径:spring-framework-3.0.2.RELEASE-dependencies\org.aspectj\com.springsource.org.aspectj.weaver\1.6.8.RELEASE
共需要导入的jar包
第二步:编写传统aop的Advice通知类。
创建包:cn.itcast.spring.b_oldaop,创建类TimeLogInterceptor。
传统aop的通知,必须实现MethodInterceptor接口
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
//传统的aop的advice通知,增强类,必须实现org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor接口(注意和cglib代理接口区分开)
publicclassTimeLogInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
//log4j记录器
privatestatic Logger LOG=Logger.getLogger(TimeLogInterceptor.class);
//回调方法
//参数:目标方法回调函数的包装类,获取调用方法的相关属性、方法名、调用该方法的对象(即封装方法、目标对象,方法的参数)
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable {
//业务:记录目标的方法的运行时间
//方法调用之前记录时间
long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
//目标对象原来的方法的调用,返回目标对象方法的返回值。
Object object = methodInvocation.proceed();//类似于invoke
//方法调用之后记录时间
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
//计算运行时间
long runTime=endTime-beginTime;
//写日志:
* 1:记录日志到数据库(优势:便于查询;劣势:要占用数据库空间,日志一般都非常庞大)
* 2:记录日志到log4j(优势:文件存储,可以记录非常大的日志数据,而且还有日志级别的特点;劣势:不便于查询)
*/
LOG.info("方法名为:"+methodInvocation.getMethod().getName()+"的运行时间为:"+runTime+"毫秒");
return object;
}
}
第三步:核心配置文件中,创建applicationContext.xml文件:(确定目标和配置通知),仍然使用CustomerServiceImpl和ProductService进行测试。
<!-- 1.确定了要增强的target对象 -->
<!-- 对于spring来说,目标:就是bean对象 -->
<!-- 基于接口类 -->
<beanid="customerService"class="cn.itcast.spring.a_proxy.CustomerServiceImpl"/>
<!-- 基于一般类(没有实现接口的类) -->
<beanid="productService"class="cn.itcast.spring.a_proxy.ProductService"/>
<!-- 2.配置增强:原则bean能增强bean
Advice:通知,增强
-->
<beanid="timeLogAdvice"class="cn.itcast.spring.b_oldaop.TimeLogInterceptor"/>
第四步:导入log4j.properties,用来向D盘目录下的mylog.log文件中写入数据。日志操作,也是企业开发重要的一个环节。
### direct log messages to stdout ###
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.Target=System.out
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{ABSOLUTE}%5p%c{1}:%L-%m%n
### direct messages to file mylog.log ###
log4j.appender.file=org.apache.log4j.FileAppender
log4j.appender.file.File=D\:\\mylog.log
log4j.appender.file.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.file.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{ABSOLUTE}%5p%c{1}:%L-%m%n
### set log levels - for more verbose logging change 'info' to 'debug' ###
log4j.rootLogger=info,stdout,file
第五步:使用SpringTest进行测试
//springjunit集成测试
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:applicationContext.xml")
publicclass SpringTest {
//注入要测试bean
@Autowired
private ICustomerService customerService;
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
//测试
@Test
publicvoidtest(){
//基于接口
customerService.save();
customerService.find();
//基于类的
productService.save();
productService.find();
}
}
第六步:查看执行结果:
但是发现,此时并没有执行TimeLogInterceptor 类的invoke()方法,也就是说,并没有计算执行Service类的时间,那怎么办呢?我们往下看,需要在spring容器中配置spring的aop。
3.2. 配置切入点和切面
目的:让哪个类(切面)、哪个方法(切入点),进行怎样的增强(通知)。
第一步: 引用aop的名称空间
查看:spring-framework-3.2.0.RELEASE-dist\spring-framework-3.2.0.RELEASE\docs\spring-framework-reference\html中的xsd-config.html,搜素aop,发现:
需要我们引入aop的文件约束。如图
<beansxmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
配置aop提示
<beansxmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!-- 1.确定了要增强的target对象 -->
<!-- 对于spring来说,目标:就是bean对象 -->
<!-- 基于接口类 -->
<beanid="customerService"class="cn.itcast.spring.a_proxy.CustomerServiceImpl"/>
<!-- 基于一般类(没有实现接口的类) -->
<beanid="productService"class="cn.itcast.spring.a_proxy.ProductService"/>
<!-- 2.配置增强:原则bean能增强bean
Advice:通知,增强
-->
<beanid="timeLogAdvice"class="cn.itcast.spring.b_oldaop.TimeLogInterceptor"/>
<!-- 3.配置切入点和切面 :aop:config-->
<aop:config>
<!--
配置切入点:即你要拦截的哪些 连接点(方法)
* expression:表达式:匹配方法的,语法:使用aspectj的语法,相对简单
* 表达式:bean(bean的名字),你要对哪些bean中的所有方法增强
* bean(customerService):要对customerservice的bean中的所有方法进行增强
-->
<!--
<aop:pointcut expression="bean(customerService)" id="myPointcut"/>
* expression=bean(*Service):在spring容器中,所有以Service单词结尾的bean的都能被拦截
* id="myPointcut":为切入点定义唯一标识
-->
<!--
<aop:advisor advice-ref="timeLogAdvice" pointcut-ref="myPointcut"/>
* 配置切面:通知(增强的方法)关联切入点(目标对象调用的方法)
* 告诉:你要对哪些方法(pointcut),进行怎强的增强(advice)
-->
<aop:pointcut expression="bean(*Service)" id="myPointcut"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="timeLogAdvice" pointcut-ref="myPointcut"/>
</aop:config>
</beans>
第三步:使用SpringTest.java进行测试:
//springjunit集成测试
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:applicationContext.xml")
publicclass SpringTest {
//注入要测试bean
@Autowired
private ICustomerService customerService;
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
//测试
@Test
publicvoidtest(){
//基于接口
customerService.save();
customerService.find();
//基于类的
productService.save();
productService.find();
}
}
第四步:查看结果:
第五步:查看d盘的日志文件,mylog.log文件。
附录:切入点表达式的语法,可参考官方文档(重点掌握,要能看懂):
参考:spring-framework-3.2.0.RELEASE-dist\spring-framework-3.2.0.RELEASE\docs\spring-framework-reference\pdf\spring-framework-reference.pdf
切入点表达式的语法整理如下:
例如 bean(customerService) 增强spring容器中定义id属性/name属性为customerService的bean中所有方法
l execution(<访问修饰符>?<返回类型>空格<方法名>(<参数>)<异常>?)
例如:
execution(* cn.itcast.spring.a_jdkproxy.CustomerServiceImpl.*(..)) 增强bean对象所有方法
execution(* cn.itcast.spring..*.*(..)) 增强spring包和子包所有bean所有方法
提示:最灵活的
参考文档:Spring2.5-中文参考手册.chm
案例应用:
切入点的表达式
execution(void cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before.UserServiceImpl.saveUser(java.lang.String,java.lang.String))
* 表示:无返回类型,cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before包中的UserServiceImpl类,类中的saveUser方法,参数2个,都是String类型
表达式的写法
execution(modifiers-pattern? (非必填项)--<访问修饰符>?
ret-type-pattern (必填项)--<返回类型>
declaring-type-pattern? (非必填项)
name-pattern(param-pattern)(必填项)--<方法名>(<参数>)
throws-pattern?(非必填项)<异常>?
)
一共有5个参数
其中的?表示非必填项
文档中写的:
除了返回类型模式(上面代码片断中的ret-type-pattern),名字模式和参数模式以外, 所有的部分都是可选的。
返回类型模式决定了方法的返回类型必须依次匹配一个连接点。你会使用的最频繁的返回类型模式是*,它代表了匹配任意的返回类型。
一个全限定的类型名将只会匹配返回给定类型的方法。名字模式匹配的是方法名。 你可以使用*通配符作为所有或者部分命名模式。
参数模式稍微有点复杂:()匹配了一个不接受任何参数的方法, 而(..)匹配了一个接受任意数量参数的方法(零或者更多)。
模式(*)匹配了一个接受一个任何类型的参数的方法。 模式(*,String)匹配了一个接受两个参数的方法,第一个可以是任意类型, 第二个则必须是String类型。更多的信息请参阅AspectJ编程指南中 语言语义的部分。
1:modifiers-pattern? (非必填项):表示方法的修饰符
execution(public void cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before.UserServiceImpl.saveUser(java.lang.String,java.lang.String))
* 表示:共有方法,无返回类型,cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before包中的UserServiceImpl类,类中的saveUser方法,参数2个,都是String类型
execution(private void cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before.UserServiceImpl.saveUser(java.lang.String,java.lang.String))
* 表示:私有方法,无返回类型,cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before包中的UserServiceImpl类,类中的saveUser方法,参数2个,都是String类型
2:ret-type-pattern (必填项):表示方法的返回类型
execution(void cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before.UserServiceImpl.saveUser(java.lang.String,java.lang.String))
* 表示:无返回类型,cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before包中的UserServiceImpl类,类中的saveUser方法,参数2个,都是String类型
execution(java.lang.String cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before.UserServiceImpl.saveUser(java.lang.String,java.lang.String))
* 表示:返回类型String类型,cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before包中的UserServiceImpl类,类中的saveUser方法,参数2个,都是String类型
execution(* cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before.UserServiceImpl.saveUser(java.lang.String,java.lang.String))
* 表示:返回类型任意,cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before包中的UserServiceImpl类,类中的saveUser方法,参数2个,都是String类型
3:declaring-type-pattern? (非必填项):表示包,或者子包的,或者类的修饰符
execution(* cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before.UserServiceImpl.saveUser(java.lang.String,java.lang.String))
* 表示返回类型任意,cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before包中的UserServiceImpl类,类中的saveUser方法,参数2个,都是String类型
execution(* cn.itcast.e_xml.*.UserServiceImpl.saveUser(java.lang.String,java.lang.String))
* 表示返回类型任意,cn.itcast.e_xml包中的所有子包,包中UserServiceImpl类,类中的saveUser方法,参数2个,都是String类型
execution(* cn.itcast.e_xml.*.saveUser(java.lang.String,java.lang.String))
* 表示返回类型任意,cn.itcast.e_xml包中的所有类,类中的saveUser方法,参数2个,都是String类型
execution(* cn.itcast.e_xml..*.saveUser(java.lang.String,java.lang.String))
* 表示返回类型任意,cn.itcast.e_xml包中及其子包中的所有类,类中的saveUser方法,参数2个,都是String类型
execution(* *.saveUser(java.lang.String,java.lang.String))
* 表示返回类型任意,所有包中的所有类,类中的saveUser方法,参数2个,都是String类型
execution(* saveUser(java.lang.String,java.lang.String))
* 表示返回类型任意,所有包中的所有类,类中的saveUser方法,参数2个,都是String类型
4:name-pattern(param-pattern)(必填项):方法的名称(方法的参数)
(1)方法名称
execution(* cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before.UserServiceImpl.saveUser(java.lang.String,java.lang.String))
* 表示返回类型任意,cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before包中的UserServiceImpl类,类中的saveUser方法,参数2个,都是String类型
execution(* cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before.UserServiceImpl.save*(java.lang.String,java.lang.String))
* 表示返回类型任意,cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before包中的UserServiceImpl类,类中的以save开头的方法,参数2个,都是String类型
execution(* cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before.UserServiceImpl.*(java.lang.String,java.lang.String))
* 表示返回类型任意,cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before包中的UserServiceImpl类,类中的所有方法,参数2个,都是String类型
(2)方法的参数
execution(* cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before.UserServiceImpl.saveUser(java.lang.String,java.lang.String))
* 表示返回类型任意,cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before包中的UserServiceImpl类,类中的saveUser方法,参数2个,都是String类型
execution(* cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before.UserServiceImpl.saveUser(java.lang.String,java.lang.Integer))
* 表示返回类型任意,cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before包中的UserServiceImpl类,类中的saveUser方法,参数2个,参数1是String类型,参数二是Integer
execution(* cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before.UserServiceImpl.saveUser(java.lang.String,*))
* 表示返回类型任意,cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before包中的UserServiceImpl类,类中的saveUser方法,参数2个,参数1是String类型,参数二是任意类型
execution(* cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before.UserServiceImpl.saveUser(*))
* 表示返回类型任意,cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before包中的UserServiceImpl类,类中的saveUser方法,参数1个,参数是任意类型
execution(* cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before.UserServiceImpl.saveUser())
* 表示返回类型任意,cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before包中的UserServiceImpl类,类中的saveUser方法,没有参数
execution(* cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before.UserServiceImpl.saveUser(..))
* 表示返回类型任意,cn.itcast.e_xml.a_before包中的UserServiceImpl类,类中的saveUser方法,参数任意(可以是0个,也可以多个)
5:throws-pattern?(非必填项):方法上抛出的异常
项目开发中表达式(最多用)
1:execution(* cn.itcast.procject.service..*.*(..))
* 返回类型任意,cn.itcast.procject.service包及其子包中所有类,类中所有方法,参数任意
2:execution(* *..*.*(..))
* 返回类型任意,任意包中及其子包中所有类,类中所有方法,参数任意
3:execution(* *(..))
* 返回类型任意,任意包中及其子包中所有类,类中所有方法,参数任意
下面给出一些通用切入点表达式的例子。
任意公共方法的执行:
execution(public * *(..))
任何一个名字以“set”开始的方法的执行:
execution(* set*(..))
AccountService接口定义的任意方法的执行:
execution(* com.xyz.service.AccountService.*(..))
在service包中定义的任意方法的执行:
execution(* com.xyz.service.*.*(..))
在service包或其子包中定义的任意方法的执行:
execution(* com.xyz.service..*.*(..))
l within(包.类)
例如: within(cn.itcast.spring..*) 增强spring包和子包所有bean“所有方法 ”
范围最小,只针对某个类型。
this对某一个类-(对代理对象有效),target对代理对象无效(只对目标对象有效)
例如: this(cn.itcast.spring.a_jdkproxy.CustomerServiceImpl) 增强类型所有方法(对代理对象有效)
target(cn.itcast.spring.a_jdkproxy.CustomerServiceImpl)增强类型所有方法(对目标对象有效)
注意:我们一般都对目标对象进行拦截,很少对代理对象进行拦截
【AspectJ类型匹配的通配符】
*:匹配任何数量字符(一个);
..:匹配任何数量字符的重复(多个),如在类型模式中匹配任何数量子包;而在方法参数模式中匹配任何数量参数。
+:匹配指定类型的子类型;仅能作为后缀放在类型模式后边。
【测试】:在applicationContext.xml文件中,测试切入点表达式的写法:
<!-- 3.配置切入点和切面 :aop:config-->
<aop:config>
<!-- <aop:pointcut expression="bean(*Service)" id="myPointcut"/> -->
<!-- <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* cn.itcast.spring..*.*(..))" id="myPointcut"/> -->
<!-- <aop:pointcut expression="within(cn.itcast.spring1..*)" id="myPointcut"/> -->
<aop:pointcutexpression="target(cn.itcast.spring.a_proxy.CustomerServiceImpl)"id="myPointcut"/>
<aop:advisoradvice-ref="timeLogAdvice"pointcut-ref="myPointcut"/>
</aop:config>
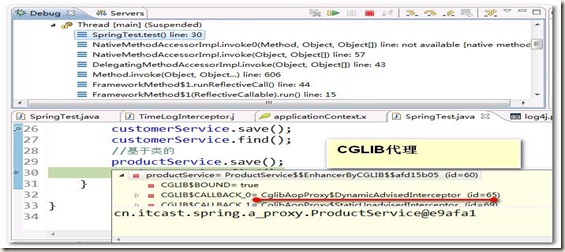
【补充】:事实上,当运行的时候,两个Service已经是代理对象了。如:使用Debug断点进行调试
(1)有接口的customerService类:(jdk动态代理)
(2)没有接口的productService:(cglib动态代理)
4. AspectJ 切面编程(xml方式)
百度百科文档:http://baike.baidu.com/link?url=2h5jS5pGRtcNexdPQBt1CSgPXpqFyyCu0WR-dJKh9mLxjdpLloT9XsY7pQIwGdOLQB1n7Shfoqr65JXiOtmDEK
早期传统Spring1.2 AOP编程 , 确定目标 --- 编写通知(通知需要实现一个接口)
---- 配置ProxyFactoryBean生成代理对象,配置非常复杂,
spring2.0 支持AspectJ 语法 ,简化AOP开发。
开发方法还是三步:
(1)确定目标对象(bean)
(2)编写通知,对目标对象增强(advice)
(3)配置切入点(pointcut)、切面(aspect)
4.1. AspectJ 提供Advice类型
普通的pojo即可。(不需要实现接口)
AspectJ提供不同的通知类型:
l AfterReturning 后置通知,相当于AfterReturningAdvice
l Around 环绕通知,相当于MethodInterceptor
l AfterThrowing抛出通知,相当于ThrowAdvice
l After 最终final通知,不管是否异常,该通知都会执行
l DeclareParents 引介通知,相当于IntroductionInterceptor (不要求掌握)
相比传统Spring AOP通知类型多了 After最终通知 (类似 finally )。
实现步骤:
第一步:确定目标对象,即确定bean对象
第二步:advice通知(编写)
第一步:确定目标对象,即确定bean对象:
在src下,创建applicationContext-aspectj.xml。
<!-- 1.确定了要增强的target对象 -->
<!-- 对于spring来说,目标对象:就是bean对象 -->
<!-- 基于接口类 -->
<beanid="customerService"class="cn.itcast.spring.a_proxy.CustomerServiceImpl"/>
<!-- 基于一般类 -->
<beanid="productService"class="cn.itcast.spring.a_proxy.ProductService"/>
第二步:编写Before 前置通知Advice增强:
创建包:cn.itcast.spring.c_aspectjaop
创建类:MyAspect.java
编写MyAspect.java
//aspectj的advice通知增强类,无需实现任何接口
publicclassMyAspect {
//前置通知
//普通的方法。方法名随便,但也不能太随便,一会要配置
publicvoid firstbefore(){
System.out.println("------------第一个个前置通知执行了。。。");
}
}
将前置通知配置到spring的容器中
<!-- 2.配置advice通知增强 -->
<beanid="myAspectAdvice"class="cn.itcast.spring.c_aspectjaop.MyAspect"/>
4.2. 配置切入点和切面(让切入点关联通知)
第三步:配置切面(包括切入点),让切入点关联通知
核心配置文件applicationContext-aspectj.xml中添加:
<!-- 2.配置advice通知增强 -->
<beanid="myAspectAdvice"class="cn.itcast.spring.c_aspectjaop.MyAspect"/>
<!-- 3:配置aop -->
<aop:config>
<!-- 切入点:拦截哪些bean的方法 -->
<aop:pointcutexpression="bean(*Service)"id="myPointcut"/>
<!--
切面:要对哪些方法进行怎样的增强
aop:aspect:aspejctj的方式!
ref:配置通知
-->
<aop:aspectref="myAspectAdvice">
<!-- 第一个前置通知 :在访问目标对象方法之前,先执行通知的方法
method:advice类中的方法名,
pointcut-ref="myPointcut":注入切入点
目的是让通知关联切入点
-->
<aop:beforemethod="firstbefore"pointcut-ref="myPointcut"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
使用SpringTest测试代码:
//springjunit集成测试
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:applicationContext-aspectj.xml")
publicclass SpringTest {
//注入要测试bean
@Autowired
private ICustomerService customerService;
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
//测试
@Test
publicvoid test(){
//基于接口
customerService.save();
customerService.find();
//基于类的
productService.save();
productService.find();
}
}
测试结果:
和传统的aop配置相比,更灵活,advice不需要实现接口,简单的pojo就可以了;一个通知可以增强多个连接点,一个连接点可以被多次增强。
【扩展优化】:
1.将切入点放入aspectj标签里面写,同时配置多个通知方法
<!-- 2.配置advice通知增强 -->
<beanid="myAspectAdvice"class="cn.itcast.spring.c_aspectjaop.MyAspect"/>
<!-- 3:配置aop -->
<aop:config>
<!--
切面:要对哪些方法进行怎样的增强
aop:aspect:aspejctj的方式!
ref:配置通知
-->
<aop:aspectref="myAspectAdvice">
<aop:pointcutexpression="bean(*Service)"id="myPointcut"/>
<!-- 第一个前置通知 :在访问目标对象方法之前,先执行通知的方法
method:advice类中的方法名,
pointcut-ref="myPointcut":注入切入点
目的是让通知关联切入点
-->
<aop:beforemethod="firstbefore"pointcut-ref="myPointcut"/>
<aop:beforemethod="firstbefore2"pointcut-ref="myPointcut"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
2.配置多个通知方法:
//aspectj的advice通知增强类,无需实现任何接口
publicclass MyAspect {
//前置通知
//普通的方法。方法名随便,但也不能太随便,一会要配置
publicvoid firstbefore(){
System.out.println("------------第一个前置通知执行了。。。");
}
publicvoid firstbefore2(){
System.out.println("------------第二个前置通知执行了222。。。");
}
}
3.执行结果:表示在执行目标对象方法之前执行
AspectJ切面编程,相比于传统的SpringAOP,定义的通知方法更多。
4.3. 分析各种通知应用
4.3.1. Before前置通知
案例应用: 实现权限控制 (即:权限不足的时候,抛出异常)、 记录方法调用信息日志
第一步:配置MyAspect类(切面),配置before方法(通知)
//aspectj的advice通知增强类,无需实现任何接口
publicclass MyAspect {
//前置通知的:方法运行之前增强
//应用: 权限控制 (权限不足,抛出异常)、 记录方法调用信息日志
//参数:org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint
//参数:连接点对象(方法的包装对象:方法,参数,目标对象)
publicvoid before(JoinPoint joinPoint){
//分析:抛出异常拦截的
//当前登录用户
String loginName = "Rose";
System.out.println("方法名称:"+joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
System.out.println("目标对象:"+joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName());
System.out.println("代理对象:"+joinPoint.getThis().getClass().getName());
//判断当前用户有没有执行方法权限
if(joinPoint.getSignature().getName().equals("find")){
if(!loginName.equals("admin")){
//只有超级管理员admin有权限,其他人不能执行某个方法,比如查询方法
thrownew RuntimeException("您没有权限执行方法:"+joinPoint.getSignature().getName()+",类型为:"+joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName());
}
}
}
}
通过JoinPoint 连接点对象,获取目标对象信息 !
这里注意:引包不要引错了,使用aspectj中的连接点(org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint):
第二步:Spring容器中配置,配置applicationContext-aspectJ.xml
<!-- 1.确定了要增强的target对象 -->
<!-- 对于spring来说,目标对象:就是bean对象 -->
<!-- 基于接口类 -->
<beanid="customerService"class="cn.itcast.spring.a_proxy.CustomerServiceImpl"/>
<!-- 基于一般类的 -->
<beanid="productService"class="cn.itcast.spring.a_proxy.ProductService"/>
<!-- 2.配置advice通知增强 -->
<beanid="myAspectAdvice"class="cn.itcast.spring.c_aspectjaop.MyAspect"/>
<!-- 3:配置aop -->
<aop:config>
<aop:aspectref="myAspectAdvice">
<aop:pointcutexpression="bean(*Service)"id="myPointcut"/>
<!-- 前置通知 -->
<aop:beforemethod="before"pointcut-ref="myPointcut" />
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
//springjunit集成测试
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:applicationContext-aspectj.xml")
publicclass SpringTest {
//注入要测试bean
@Autowired
private ICustomerService customerService;
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
//测试
@Test
publicvoidtest(){
//基于接口
customerService.save();
customerService.find();
//基于类的
productService.save();
productService.find();
}
}
提示:
Aspectj的文档
JoinPoint使用参考文档:\jar\aspectj-1.7.3\doc\runtime-api\index.html
提示:和传统aop的对比发现,aspectj更灵活,一个类中可以写N个增强方法,但传统的只能是一个类对应一个方法。
4.3.2. AfterReturing 后置通知
特点:在目标方法运行后,返回值后执行通知增强代码逻辑。
应用场景:与业务相关的,如网上营业厅查询余额后,自动下发短信功能。
分析: 后置通知可以获取到目标方法返回值,如果想对返回值进行操作,使用后置通知(但不能修改目标方法返回)
第一步:配置MyAspect类(切面),配置afterReturing方法(通知)
//aspectj的advice通知增强类,无需实现任何接口
publicclass MyAspect {
//应用场景:与业务相关的,如网上营业厅查询余额后,自动下发短信。
//后置通知:会在目标方法执行之后调用通知方法增强。
//参数1:连接点对象(方法的包装对象:方法,参数,目标对象)
//参数2:目标方法执行后的返回值,类型是object,“参数名”随便,但也不能太随便,一会要配置
publicvoidafterReturing(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object returnVal){
//下发短信:调用运行商的接口,短信猫。。。
System.out.println("-++++++++-后置通知-当前下发短信的方法"+"-尊敬的用户,您调用的方法返回余额为:"+returnVal);
//同时可以可以在下发后,记录日志:
System.out.println("----日志记录,操作的类型:"+joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getSimpleName()
+",操作的方法:"+joinPoint.getSignature().getName()
);
}
}
第二步:Spring容器中配置,配置applicationContext-aspectJ.xml
<!-- 1.确定了要增强的target对象 -->
<!-- 对于spring来说,目标对象:就是bean对象 -->
<!-- 基于接口类 -->
<beanid="customerService"class="cn.itcast.spring.a_proxy.CustomerServiceImpl"/>
<!-- 基于一般类的 -->
<beanid="productService"class="cn.itcast.spring.a_proxy.ProductService"/>
<!-- 2.配置advice通知增强 -->
<beanid="myAspectAdvice"class="cn.itcast.spring.c_aspectjaop.MyAspect"/>
<!-- 3:配置aop -->
<aop:config>
<aop:aspectref="myAspectAdvice">
<aop:pointcutexpression="bean(*Service)"id="myPointcut"/>
<!-- 后置通知
returning:配置方法中的参数名字,与通知方法的第二个参数的名字,名字必须对应。
在运行的时候,spring会自动将返回值传入该参数中。
-->
<aop:after-returningmethod="afterReturing"returning="returnVal"pointcut-ref="myPointcut"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
第三步:使用SpringTest.java进行测试:
//springjunit集成测试
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:applicationContext-aspectj.xml")
publicclass SpringTest {
//注入要测试bean
@Autowired
private ICustomerService customerService;
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
//测试
@Test
publicvoidtest(){
//基于接口
customerService.save();
customerService.find();
//基于类的
productService.save();
productService.find();
}
}
4.3.3. Around 环绕通知
特点:目标执行前后,都进行增强(控制目标方法执行)
应用场景:日志、缓存、权限、性能监控、事务管理
增强代码的方法要求:
接受的参数:ProceedingJoinPoint(可执行的连接点)
返回值:Object返回值(即目标对象方法的返回值)
抛出Throwable异常。
第一步:配置MyAspect类(切面),配置around方法(通知)
//aspectj的advice通知增强类,无需实现任何接口
publicclass MyAspect {
//应用场景:日志、缓存、权限、性能监控、事务管理
//环绕通知:在目标对象方法的执行前+后,可以增强
//参数:可以执行的连接点对象ProceedingJoinPoint(方法),特点是调用proceed()方法可以随时随地执行目标对象的方法(相当于目标对象的方法执行了)
//必须抛出一个Throwable
publicObjectaround(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable{
//目标:事务的控制:
//开启事务:
System.out.println("-----开启了事务。。。。。。。。。");
//执行了目标对象的方法
Object resultObject = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
//结束事务
System.out.println("-----提交了事务。。。。。。。。。");
return resultObject;//目标对象执行的结果
}
}
第二步:Spring容器中配置,配置applicationContext-aspectJ.xml
<!-- 1.确定了要增强的target对象 -->
<!-- 对于spring来说,目标对象:就是bean对象 -->
<!-- 基于接口类 -->
<beanid="customerService"class="cn.itcast.spring.a_proxy.CustomerServiceImpl"/>
<!-- 基于一般类的 -->
<beanid="productService"class="cn.itcast.spring.a_proxy.ProductService"/>
<!-- 2.配置advice通知增强 -->
<beanid="myAspectAdvice"class="cn.itcast.spring.c_aspectjaop.MyAspect"/>
<!-- 3:配置aop -->
<aop:config>
<aop:aspectref="myAspectAdvice">
<aop:pointcutexpression="bean(*Service)"id="myPointcut"/>
<!-- 环绕通知 -->
<aop:aroundmethod="around"pointcut-ref="myPointcut"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
第三步:使用SpringTest.java进行测试:
//springjunit集成测试
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:applicationContext-aspectj.xml")
publicclass SpringTest {
//注入要测试bean
@Autowired
private ICustomerService customerService;
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
//测试
@Test
publicvoidtest(){
//基于接口
customerService.save();
customerService.find();
//基于类的
productService.save();
productService.find();
}
}
4.3.4. AfterThrowing 抛出通知
作用:目标代码出现异常,通知执行。记录异常日志、通知管理员(短信、邮件)
应用场景:处理异常(一般不可预知),记录日志
第一步:配置MyAspect类(切面),配置aterThrowing方法(通知)
//aspectj的advice通知增强类,无需实现任何接口
publicclass MyAspect {
//作用:目标代码出现异常,通知执行。记录异常日志、通知管理员(短信、邮件)
//只有目标对象方法抛出异常,通知才会执行
//参数1:静态连接点(方法对象)
//参数2:目标方法抛出的异常,参数名随便,但也不能太随便
publicvoidaterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint,Throwable ex){
//一旦发生异常,发送邮件或者短信给管理员
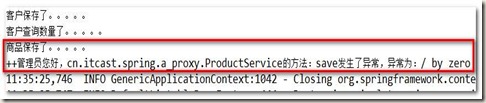
System.out.println("++管理员您好,"+joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName()+"的方法:"
+joinPoint.getSignature().getName()+"发生了异常,异常为:"+ex.getMessage());
}
}
第二步:Spring容器中配置,配置applicationContext-aspectJ.xml
<!-- 1.确定了要增强的target对象 -->
<!-- 对于spring来说,目标对象:就是bean对象 -->
<!-- 基于接口类 -->
<beanid="customerService"class="cn.itcast.spring.a_proxy.CustomerServiceImpl"/>
<!-- 基于一般类的 -->
<beanid="productService"class="cn.itcast.spring.a_proxy.ProductService"/>
<!-- 2.配置advice通知增强 -->
<beanid="myAspectAdvice"class="cn.itcast.spring.c_aspectjaop.MyAspect"/>
<!-- 3:配置aop -->
<aop:config>
<aop:aspectref="myAspectAdvice">
<aop:pointcutexpression="bean(*Service)"id="myPointcut"/>
<!-- 抛出通知
throwing:通知中的方法的第二个参数,异常类型的参数的名字,在运行的时候,spring会自动将异常传入该参数中。-->
<aop:after-throwingmethod="aterThrowing"throwing="ex"pointcut-ref="myPointcut"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
第三步:使用SpringTest.java进行测试:
//springjunit集成测试
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:applicationContext-aspectj.xml")
publicclass SpringTest {
//注入要测试bean
@Autowired
private ICustomerService customerService;
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
//测试
@Test
publicvoidtest(){
//基于接口
customerService.save();
customerService.find();
//基于类的
productService.save();
productService.find();
}
}
此时发现通知的方法并没有执行。
那我们在目标对象的方法中故意抛出异常,大家看看效果
测试:
在ProductService.java中save的方法中,制造异常:
//没有接口的类
publicclass ProductService {
publicvoid save() {
System.out.println("商品保存了。。。。。");
//故意制造异常
int d = 1/0;
}
publicint find() {
System.out.println("商品查询数量了。。。。。");
return 99;
}
}
查看测试结果:
4.3.5. After 最终通知
作用:不管目标方法是否发生异常,最终通知都会执行(类似于finally代码功能)
应用场景:释放资源 (关闭文件、 关闭数据库连接、 网络连接、 释放内存对象 )
【示例】
第一步:配置MyAspect类(切面),配置after方法(通知)
//aspectj的advice通知增强类,无需实现任何接口
publicclass MyAspect {
//应用场景:释放资源(关闭文件、 关闭数据库连接、 网络连接、 释放内存对象 )
//最终通知:不管是否有异常都会执行
publicvoidafter(JoinPoint joinPoint){
//释放数据库连接
System.out.println("数据库的connection被释放了。。。。。,执行的方法是:"+joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
}
}
第二步:Spring容器中配置,配置applicationContext-aspectJ.xml
<!-- 1.确定了要增强的target对象 -->
<!-- 对于spring来说,目标对象:就是bean对象 -->
<!-- 基于接口类 -->
<beanid="customerService"class="cn.itcast.spring.a_proxy.CustomerServiceImpl"/>
<!-- 基于一般类的 -->
<beanid="productService"class="cn.itcast.spring.a_proxy.ProductService"/>
<!-- 2.配置advice通知增强 -->
<beanid="myAspectAdvice"class="cn.itcast.spring.c_aspectjaop.MyAspect"/>
<!-- 3:配置aop -->
<aop:config>
<aop:aspectref="myAspectAdvice">
<aop:pointcutexpression="bean(*Service)"id="myPointcut"/>
<!-- 最终通知 -->
<aop:aftermethod="after"pointcut-ref="myPointcut"/>
<!-- 以上代码也可以写成:pointcut切入点表达式:只能给一个通知方法来用,相当于省略了<aop:pointcut expression="bean(*Service)" id="myPointcut"/>
<aop:after method="after" pointcut="bean(*Service)"/>-->
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
第三步:使用SpringTest.java进行测试:
//springjunit集成测试
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:applicationContext-aspectj.xml")
publicclass SpringTest {
//注入要测试bean
@Autowired
private ICustomerService customerService;
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
//测试
@Test
publicvoidtest(){
//基于接口
customerService.save();
customerService.find();
//基于类的
productService.save();
productService.find();
}
}
查看测试结果:
五种通知小结:
(1)只要掌握Around(环绕通知)通知类型,就可实现其他四种通知效果。
(2)因为你可以在环绕通知的方法中编写如下代码:
try {
//前置通知
Object result = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
//后置通知
}catch(Exception){
//抛出通知
}finally{
//最终通知
}
4.3.6. 各种Advice方法可接收的参数和返回值小结(参考)
方法格式:
public returnType method (param)
public 返回值类型 方法名 (参数类型参数名)
返回值类型:void和Object
方法名:任意名称(但是也不能太随意)
参数类型:
* 参数类型为JoinPoint接口类型,返回值类型为void
* 参数类型为ProceedingJoinPoint接口类型,返回值类型为Object
具体为:
| 通知类型 | 输入参数(可选) | 返回值类型 | 其他 |
| Before前置通知 | JoinPoint(静态连接点信息) | void | |
| AfterReturning后置通知 | JoinPoint,Object | void | |
| Around环绕通知 | ProceedingJoinPoint(可执行的连接点信息) | Object | throws Throwable |
| AfterThrowing抛出通知 | JoinPoint,Throwable | void | |
| After最终通知 | JoinPoint | void |
5. @Aspectj注解配置切面编程
5.1. 搭建环境
新建web项目 spring3_day02_annotation , 导入jar包(11个)
同时导入
applicationContext.xml,
log4j.properties到工程
5.2. 第一步:编写目标对象(bean)、spring容器、测试类
创建包:cn.itcast.spring.a_aspectj
(1):创建接口CustomerService.java
//接口
publicinterface CustomerService {
//保存
publicvoid save();
//查询
publicint find();
}
创建接口的实现类,CustomerServiceImpl
//实现类
/**
* @Service("customerService")
* 相当于spring容器中定义:
* <bean id="customerService" class="cn.itcast.spring.a_aspectj.CustomerServiceImpl">
*/
@Service("customerService")
publicclass CustomerServiceImpl implements CustomerService{
publicvoid save() {
System.out.println("客户保存了。。。。。");
}
publicint find() {
System.out.println("客户查询数量了。。。。。");
return 100;
}
}
创建类ProductService.java,不需要实现接口
//没有接口的类
/**
* @Service("productService")
* 相当于spring容器中定义:
* <bean id="productService" class="cn.itcast.spring.a_aspectj.ProductService">
*/
@Service("productService")
publicclass ProductService {
publicvoid save() {
System.out.println("商品保存了。。。。。");
}
publicint find() {
System.out.println("商品查询数量了。。。。。");
return 99;
}
}
(2):配置applicationContext.xml
引入几个命名空间:bean、aop、context
<beansxmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
使用bean注解的扫描(自动开启注解功能)
<!-- 1。确定目标 -->
<!-- 扫描bean组件 -->
<context:component-scanbase-package="cn.itcast.spring"/>
(3):测试代码SpringTest.java
//springjunit集成测试
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:applicationContext.xml")
publicclass SpringTest {
//注入要测试bean
@Autowired
private CustomerService customerService;
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
//测试
@Test
publicvoid test(){
//基于接口
customerService.save();
customerService.find();
//基于类的
productService.save();
productService.find();
}
}
测试结果:
5.3. 第二步:编写通知,配置切面
1) 编写通知类,在通知类添加@Aspect 注解,代表这是一个切面类,并将切面类交给spring管理(能被spring扫描到@Component)。
@Component(“myAspect”):将增强的类交给spring管理,才可以增强
@Aspect:将该类标识为切面类(这里面有方法进行增强),相当于<aop:aspect ref=”myAspect”>
//advice通知类增强类
@Component("myAspect")//相当于<bean id="myAspect" class="cn.itcast.spring.a_aspectj.MyAspect"/>
@Aspect//相当于<aop:aspect ref="myAspect">
publicclass MyAspect {
}
2) 在切面的类,通知方法上添加
@AspectJ提供不同的通知类型
@AfterReturning 后置通知,相当于AfterReturningAdvice
@Around 环绕通知,相当于MethodInterceptor
@AfterThrowing抛出通知,相当于ThrowAdvice
@After 最终final通知,不管是否异常,该通知都会执行
@DeclareParents 引介通知,相当于IntroductionInterceptor (不要求掌握)
复习回顾:如果是applicationContext.xml中配置通知类型:如下:
<bean id="myAspectAdvice" class="cn.itcast.spring.c_aspectjaop.MyAspect"/>
<aop:config>
<aop:aspectref="myAspectAdvice">
<aop:pointcutexpression="bean(*Service)"id="myPointcut"/>
<!-- 前置通知 -->
<aop:beforemethod="before"pointcut-ref="myPointcut" />
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
等同于:以下是简化的写法!可以省略<aop:pointcut>
<bean id="myAspectAdvice" class="cn.itcast.spring.c_aspectjaop.MyAspect"/>
<aop:config>
<aop:aspectref="myAspectAdvice">
<!-- 前置通知 -->
<aop:beforemethod="before" pointcut="bean(*Service)" />
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
3) 在spring容器中开启AspectJ 注解自动代理机制
使用<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
作用:能自动扫描带有@Aspect的bean,将其作为增强aop的配置,有点相当于:<aop:config>
<!-- 1。确定目标 -->
<!-- 扫描bean组件 -->
<context:component-scanbase-package="cn.itcast.spring"/>
<!-- 2:编写通知 -->
<!-- 3:配置aop的aspectj的自动代理:
自动扫描bean组件中,含有@Aspect的bean,将其作为aop管理,开启动态代理-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
5.3.1. 前置通知:
在切面的类MyAspect.java类中添加通知方法@Before(),
方案一:可以直接将切入点的表达式写到@Before()中
//前置通知
//相当于:<aop:before method="before" pointcut="bean(*Service)"/>
//@Before("bean(*Service)"):参数值:自动支持切入点表达式或切入点名字
@Before("bean(*Service)")
publicvoid before(JoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println("=======前置通知。。。。。");
}
方案二:可以使用自定义方法,使用@Pointcut 定义切入点
切入点方法的语法要求:
切点方法:private void 无参数、无方法体的方法,方法名为切入点的名称
一个通知方法@Before可以使用多个切入点表达式,中间使用“||”符合分隔,用来表示多个切入点
//自定义切入点
//方法名就是切入点的名字
//相当于<aop:pointcut expression="bean(*Service)" id="myPointcut"/>
@Pointcut("bean(*Service)")
privatevoidmyPointcut(){}
//自定义切入点
//方法名就是切入点的名字
//相当于<aop:pointcut expression="bean(*Service)" id="myPointcut2"/>
@Pointcut("bean(*Service)")
privatevoidmyPointcut2(){}
//前置通知
//相当于:<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="myPointcut"/>
//相当于:<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="myPointcut2"/>
@Before("myPointcut()||myPointcut2()")
publicvoid before(JoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println("=======前置通知。。。。。");
}
使用SpringTest进行测试:
//springjunit集成测试
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:applicationContext.xml")
publicclass SpringTest {
//注入要测试bean
@Autowired
private CustomerService customerService;
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
//测试
@Test
publicvoid test(){
//基于接口
customerService.save();
customerService.find();
//基于类的
productService.save();
productService.find();
}
}
测试结果:
5.3.2. 后置通知
//后置通知
//target:拦截某一个类型的bean(唯一),表示只对CustomerServiceImpl类中的方法做后置通知的查找
@AfterReturning(value="target(cn.itcast.spring.a_aspectj.CustomerServiceImpl)",returning="returnVal")
publicvoid afterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object returnVal){
System.out.println("=======后置通知。。。。。");
}
使用SpringTest进行测试:
//springjunit集成测试
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:applicationContext.xml")
publicclass SpringTest {
//注入要测试bean
@Autowired
private CustomerService customerService;
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
//测试
@Test
publicvoid test(){
//基于接口
customerService.save();
customerService.find();
//基于类的
productService.save();
productService.find();
}
}
查看测试结果:
5.3.3. 环绕通知
//环绕通知:
// @Around("execution(* cn.itcast.spring.a_aspectj.*.*(..))")//要增强返回类型任意,所有的cn.itcast.spring.a_aspectj包中的类,类中所有的方法,参数任意
// @Around("execution(* cn.itcast.spring..*.*(..))")//要增强返回类型任意,cn.itcast.spring包,及其子包中所有类,类中所有的方法,参数任意
// @Around("execution(* cn.itcast..*.save(..))")//要增强cn.itcast包及其子包中所有的类,类中以save结尾的方法,参数任意
//要增强cn.itcast.spring.a_aspectj包中的ICustomerService类的子类型的所有方法,参数任意
@Around("execution(* cn.itcast.spring.a_aspectj.ICustomerService+.*(..))")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable{
System.out.println("---环绕通知-----前");
Object object = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("---环绕通知-----后");
return object;
}
使用SpringTest进行测试:
//springjunit集成测试
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:applicationContext.xml")
publicclass SpringTest {
//注入要测试bean
@Autowired
private CustomerService customerService;
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
//测试
@Test
publicvoid test(){
//基于接口
customerService.save();
customerService.find();
//基于类的
productService.save();
productService.find();
}
}
测试结果:
5.3.4. 抛出通知
//抛出通知
//切入点表达式:增强所有cn包以及子包下面的所有类型的bean的所有方法
@AfterThrowing(value="within(cn..*)",throwing="ex")
publicvoid afterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint ,Throwable ex){
System.out.println("---抛出通知。。。。。。"+"抛出的异常信息:"+ex.getMessage());
}
使用SpringTest进行测试:
//springjunit集成测试
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:applicationContext.xml")
publicclass SpringTest {
//注入要测试bean
@Autowired
private CustomerService customerService;
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
//测试
@Test
publicvoid test(){
//基于接口
customerService.save();
customerService.find();
//基于类的
productService.save();
productService.find();
}
}
发现没有执行抛出通知,原因是目标对象没有异常,在ProductService添加异常。
@Service("productService")
publicclass ProductService {
publicvoid save() {
System.out.println("商品保存了。。。。。");
intd = 1/0;
}
publicint find() {
System.out.println("商品查询数量了。。。。。");
return 99;
}
}
测试结果:
5.3.5. 最终通知
在切面的类MyAspect.java类中添加通知方法
//最终通知
//拦截所有以ice结尾的bean
@After("bean(*ice)")
publicvoid after(JoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println("+++++++++最终通知。。。。。。。");
}
使用SpringTest进行测试:
//springjunit集成测试
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:applicationContext.xml")
publicclass SpringTest {
//注入要测试bean
@Autowired
private CustomerService customerService;
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
//测试
@Test
publicvoid test(){
//基于接口
customerService.save();
customerService.find();
//基于类的
productService.save();
productService.find();
}
}
测试不管是否抛出异常,都会执行最终通知。
@Service("productService")
publicclass ProductService {
publicvoid save() {
System.out.println("商品保存了。。。。。");
intd = 1/0;
}
publicint find() {
System.out.println("商品查询数量了。。。。。");
return 99;
}
}
测试结果:
【扩展补充】: 我们的aop代理是使用的Spring的内部代理机制,默认是如果有接口就优先对接口代理(jdk动态代理)。
问题:如果目标对象有接口,能否只对实现类代理,而不对接口进行代理呢?
当然可以了
【测试】
第一步:在CustomerServiceImpl的子类中添加一个新的方法update(),而接口中不要定义update()的方法:
@Service("customerService")
publicclass CustomerServiceImpl implements CustomerService{
publicvoid save() {
System.out.println("客户保存了。。。。。");
}
publicint find() {
System.out.println("客户查询数量了。。。。。");
return 100;
}
//子类扩展方法
publicvoid update(){
System.out.println("客户更新了。。。新增方法。。。");
}
}
第二步:在测试类中调用子类的扩展方法:
//springjunit集成测试
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:applicationContext.xml")
publicclass SpringTest {
//注入要测试bean
@Autowired
privateCustomerServicecustomerService;
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
//测试
@Test
publicvoid test(){
//基于接口
customerService.save();
customerService.find();
//基于类的
productService.save();
productService.find();
//扩展方法执行:customerService是一个动态代理对象,原因,该对象是接口的子类型的对象
((CustomerServiceImpl)customerService).update();
}
}
结果发现异常:
为什么会抛出异常呢?原因是代理的目标对象是接口,无法转换为子类。
设置 proxy-target-class = true
方案一:注解方式:
<!-- 配置aop的aspectj的自动代理:
自动扫描bean组件中,含有@Aspect的bean,将其作为aop管理,开启动态代理
proxy-target-class:设置是否使用cglib代理,默认是false,表示使用的是jdk接口代理
proxy-target-class="true":表示cglib代理
-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxyproxy-target-class="true"/>
方案二:配置文件XML的方式
<!-- 3:配置aop -->
<aop:configproxy-target-class="true">
</aop:config>
6. Spring JdbcTemplate的使用
Spring JdbcTemplate 是一个模板工具类,简化Jdbc编程(类似 Apache DbUtils )
为了方便Dao中注入JdbcTemplate,Spring为每一个持久化技术都提供了支持类。
Spring对不同持久化技术的支持,Spring为各种支持的持久化技术,都提供了简单操作的模板和回调:
| ORM持久化技术 | 模板类 |
| JDBC | org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate |
| Hibernate3.0 | org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTemplate |
| IBatis(MyBatis) | org.springframework.orm.ibatis.SqlMapClientTemplate |
| JPA | org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTemplate |
我们的课程主要讲解2个模板:
JdbcTemplate 简化 jdbc编程
HibernateTemplate 极大的简化 Hibernate编程(后续的课程)
6.1. JdbcTemplate 快速入门
第一步: 基础工程搭建:
新建web项目 spring3_day2_jdbctemplate
第二步:导入jar包
l Spring核心包6个
l 测试包1个
l JDBC模版开发包2个
(1)spring-jdbc-3.2.0.RELEASE.jar
(2)spring-tx-3.2.0.RELEASE.jar
l 数据库驱动1个(mysql)
总共需要的jar包
导入配置文件:在src中导入log4j.properties和applicationContiext.xml
第三步: 建立mysql数据库,创建itcastspring
附加知识:解决数据库乱码问题:
参考文档:http://www.cnblogs.com/ndxsdhy/archive/2011/11/19/2255111.html
第四步:使用JDBCTemplate编写程序(建表) ,基本步骤如下:
2)构建JDBCTemplate
使用mysql数据库,创建包cn.itcast.spring.test,创建测试类JdbcTemplateTest.java进行测试:
publicclassJdbcTemplateTest{
@Test
publicvoid test(){
//目标:使用jdbctemplate执行一段sql
//1.构建数据源
//spring内置了一个数据源
DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql:///itcastspring");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("root");
//2.创建jdbctemplate实例
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);
//等同于
// jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(dataSource)
//3.执行sql,创建表test001
jdbcTemplate.execute("create table test001(id int,name varchar(20))");
}
}
6.2. 通过XML配置创建JdbcTemplate对象(多种数据源)
下面将使用几种数据源的方式进行配置。
6.2.1. Spring内置数据源
目标:将数据源和jdbcTemplate都交给Spring来管理:
在applicationContext.xml中配置dataSource连接池和jdbcTemplate模版对象。编写applicationContext.xml文件
<!--
类似于:DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql:///itcastspring");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("root");
-->
<!-- 配置内置的数据源bean -->
<beanid="dataSource"class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<propertyname="driverClassName"value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<propertyname="url"value="jdbc:mysql:///itcastspring"/>
<propertyname="username"value="root"/>
<propertyname="password"value="root"/>
</bean>
<!-- jdbctemplate对象 -->
<beanid="jdbcTemplate"class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<!-- 注入数据源 -->
<propertyname="dataSource"ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
数据源:DriverManagerDataSource是spring内置的连接池,不建议生产环境使用,可以在测试环境使用
编写测试,使用SpringTest.java进行测试
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:applicationContext.xml")
publicclass SpringTest {
//注入要测试bean
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Test
publicvoidtestCreatetable(){
jdbcTemplate.execute("create table test002(id int,name varchar(20))");
}
}
6.2.2. Apache DBCP连接池配置
Apache commons-dbcp 需要导入dbcp包和 pool包 ,可以从spring3_day1_课前资料\spring-framework-3.0.2.RELEASE-dependencies包中找到。
l com.springsource.org.apache.commons.dbcp-1.2.2.osgi.jar
l com.springsource.org.apache.commons.pool-1.5.3.jar
找到org.apache.commons路径
配置applicationContext.xml文件
<!-- 配置apache的dbcp连接池 -->
<beanid="dataSource"class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource">
<propertyname="driverClassName"value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<propertyname="url"value="jdbc:mysql:///itcastspring"/>
<propertyname="username"value="root"/>
<propertyname="password"value="root"/>
</bean>
<!-- jdbctemplate对象 -->
<beanid="jdbcTemplate"class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<!-- 注入数据源 -->
<propertyname="dataSource"ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
测试类:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:applicationContext.xml")
publicclass SpringTest {
//注入要测试bean
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Test
publicvoid testCreatetable(){
jdbcTemplate.execute("create table test003(id int,name varchar(20))");
}
}
6.2.3. C3P0 连接池配置
导入C3P0的jar,可以从spring3_day1_课前资料\spring-framework-3.0.2.RELEASE-dependencies包中找到。
路径在com.mchange.c3p0中
l com.springsource.com.mchange.v2.c3p0-0.9.1.2.jar
配置applicationContext.xml文件
<!-- c3p0连接池 -->
<beanid="dataSource"class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<propertyname="driverClass"value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<propertyname="jdbcUrl"value="jdbc:mysql:///itcastspring"/>
<propertyname="user"value="root"/>
<propertyname="password"value="root"/>
</bean>
<!-- jdbctemplate对象 -->
<beanid="jdbcTemplate"class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<!-- 注入数据源 -->
<propertyname="dataSource"ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:applicationContext.xml")
publicclass SpringTest {
//注入要测试bean
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Test
publicvoidtestCreatetable(){
jdbcTemplate.execute("create table test004(id int,name varchar(20))");
}
}
6.2.4. Tomcat JNDI连接池配置和访问(了解)
目标:连接池基于tomcat容器来配置和访问
优点:一个tomcat中的多个应用程序可以公用一个连接池。
JNDI是 Java 命名与目录接口(Java Naming and Directory Interface),是个规范。
JNDI方式作用:由web容器创建一个对象,为对象绑定一个名称,程序通过名称访问这个对象。
所有的java服务器(tomcat),都必须遵循JNDI。
JNDI的数据源连接池方式,好处是将数据源的维护交给了tomcat,多个应用共享同一个连接池。
配置步骤:
第一步:配置DataSource数据源,交给应用服务器(Tomcat)创建
可以配置server.xml 、context.xml 、工程/META-INF/context.xml (只对当前工程生效)
| 配置的位置: l tomcat/ conf/ server.xml 针对整个tomcat下所有虚拟主机的所有工程有效。 l tomcat/ conf/ context.xml 针对整个tomcat下所有虚拟主机的所有工程有效。 l tomcat/ conf/Catalina/虚拟主机的名称/context.xml(路径和文件可能需要手动建立) 针对tomcat下某个虚拟主机的所有工程有效。 l 项目工程/WebRoot/ META-INF/ context.xml(文件需要手动建立) 只针对tomcat下面的某一个虚拟主机的某一个工程有效。(当前工程有效) |
如果不存在这个目录,则需要手动建立。
什么是虚拟主机:
参照百度百科:http://baike.baidu.com/link?url=xhptvpzGoiU7NK9P0TfAvOXA4AUb-Aw56vqiNF3ywxblOBn_eWPEkJ7F4HqbPkIvN3YVe2e2OKuUfyv1p9bbiK
在WebRoot/META-INF中新建context.xml文件:
提示:该文件可以从D:\tomcat\apache-tomcat-7.0.52\conf\ context.xml拷贝过来
一定注意:在context.xml中<Context>中的C必须大写
先把jdbc驱动包,放入tomcat的lib目录,
了解:tomcat构建连接池底层使用了apache自己的dbcp。
第二步:配置context.xml;以下针对mysql数据库
(1)启动tomcat
访问:http://localhost:8080
(3)选择JDBC DataSources
(4)选择MySQL DBCP Example
(5)根据文档复制到我们的配置文件中:
(6)根据案例,配置WebRoot/META-INF/context.xml文件
<?xmlversion="1.0"encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Context>
<!--
配置jndi方式的连接池
* name:jndi(tomcat大箱子)里面,该连接池对象的名字,名字规范:类型/自定义的名字
* type:使用连接池的类型,默认使用的dbcp的连接,如果你使用别的连接池,连接池的类型
-->
<Resourcename="jdbc/itcastspring"auth="Container"type="javax.sql.DataSource"
maxActive="100"maxIdle="30"maxWait="10000"
username="root"password="root"driverClassName="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"
url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/itcastspring"/>
</Context>
当我们的项目启动的时候,tomcat会自动读取该配置文件,构建连接池。
(7)如何使用获取jndi的连接池呢?
在spring的容器中配置:applicationContext.xml文件
<!-- jndi方式的连接池
Class:spring提供好的一个类,专门用来获取jndi连接池的,JndiObjectFactoryBean:从web容器,获取jndi的对象
-->
<beanid="dataSource"class="org.springframework.jndi.JndiObjectFactoryBean">
<!--
name:配置jndi名字(大箱子)
value:两部分组成
java:/comp/env:jndi容器的名字(固定写法)
jdbc/itcastspring:连接池对象的名字 ,对应context.xml文件中的name属性
-->
<propertyname="jndiName"value="java:/comp/env/jdbc/itcastspring"></property>
</bean>
<!-- jdbctemplate对象 -->
<beanid="jdbcTemplate"class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<!-- 注入数据源 -->
<propertyname="dataSource"ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
(8)spring配置获取数据源,可参考:
地址:http://localhost:8080/docs/jndi-datasource-examples-howto.html#MySQL_DBCP_Example
用来解释为什么spring容器中配置的value的值是:java:/comp/env/jdbc/itcastspring
第三步:必须编写Servlet程序,通过启动tomcat,通过web调用,才能得到数据源,加载JDBCTemplate测试
创建包cn.itcast.spring.web.servlet
(1)创建Servlet类:JndiDsServlet
publicclassJndiDsServletextends HttpServlet {
publicvoid doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
//从spring容器中获取jdbctemplate
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate=(JdbcTemplate)applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate");
jdbcTemplate.execute("create table test005(id int,name varchar(20))");
}
publicvoid doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request, response);
}
}
(2)web.xml文件的配置:
<servlet>
<servlet-name>JndiDsServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>cn.itcast.spring.web.servlet.JndiDsServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>JndiDsServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/jndiDsServlet</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
第四步:启动tomcat进行测试
访问:http://localhost:8080/spring3_day02_jdbctemplate/jndiDsServlet
6.3. 外部属性文件的配置
模拟需求:
现在数据源的相关参数配置,是测试环境下的。
现在,要将工程搭建在正式的服务器上,因为测试环境和正式环境的数据库肯定不是一个,所以肯定首先要更改数据源相关的配置。
缺点:必须手动修改applicationContext.xml文件,容易造成误操作。
解决方案:不修改。可以将数据源相关配置参数,外置。
目的:可以将xml配置中可能要经常修改内容,抽取到一个properties文件
应用:使用properties文件配置参数,如数据库连接参数等。
第一步: src新建db.properties
将经常需要修改变量抽取出来
jdbc.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql:///itcastspring
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=root
第二步: 配置applicationContext.xml文件,在applicationContext.xml 通过
<context:property-placeholder> 引入外部属性文件
通过${key} 引用属性的值
<!-- 引入外部属性配置文件-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/>
<!-- 配置内置的数据源bean,使用db.properties -->
<beanid="dataSource"class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<propertyname="driverClassName"value="${jdbc.driverClass}"/>
<propertyname="url"value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<propertyname="username"value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<propertyname="password"value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
第三步:使用SpringTest.java进行测试
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:applicationContext.xml")
publicclass SpringTest {
//注入要测试bean
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Test
publicvoidtestCreatetable(){
jdbcTemplate.execute("create table test006(id int,name varchar(20))");
}
}
6.4. 基于JdbcTemplate实现DAO(CURD)
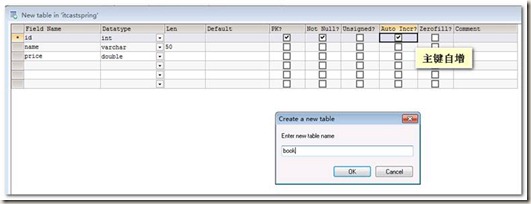
第一步:创建一个表book:
第二步:创建cn.itcast.spring.domain包,创建Book类,类中的属性用来对应book表的字段
//实体类
publicclass Book {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Double price;
public Integer getId() {
returnid;
}
publicvoid setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
returnname;
}
publicvoid setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Double getPrice() {
returnprice;
}
publicvoid setPrice(Double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public String toString() {
return"Book [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", price=" + price + "]";
}
}
第三步:编写Dao类
为了方便Dao中注入JdbcTemplate,Spring为每一个持久化技术都提供了支持类,如图
如果想编写DAO实现CURD,只需要继承Spring提供 JdbcDAOSupport支持类 !
源代码分析JdbcDaoSupport:不难发现,需要注入数据源
而且只要注入datasource,就有了jdbcTemplate,相当于也注入了jdbcTemplate
编写的Dao类继承JdbcDaoSupport
//图书操作的dao层
//JdbcDaoSupport简化JdbcTemplate的代码开发。
publicclass BookDao extends JdbcDaoSupport {
//注入jdbctempate
// private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
// public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
// this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
// }
//保存图书
publicvoid save(Book book){
String sql="insert into book values(null,?,?)";
//调用jdbctemplate
// jdbcTemplate.update(sql, book.getName(),book.getPrice());
super.getJdbcTemplate().update(sql, book.getName(),book.getPrice());
}
}
配置spring核心配置文件,注入jdbcTemplate到BookDao:
<!-- jdbctemplate对象 -->
<beanid="jdbcTemplate"class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<!-- 注入数据源 -->
<propertyname="dataSource"ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- 配置dao,注入jdbctemplate -->
<beanid="bookDao"class="cn.itcast.spring.dao.BookDao">
<!-- 方案一:在BookDao中提供jdbcTempate属性,通过set方法注入 jdbcTemplate-->
<!-- <property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"/> -->
<!-- 方案二:BookDao类继承JdbcDaoSupport,直接注入数据源,就拥有了jdbctempate对象 -->
<propertyname="dataSource"ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
6.4.1. 实现增加、删除、修改功能
通过jdbcTemplate提供 update一个方法就可以
参看api文档:spring-framework-3.2.0.RELEASE/docs/javadoc-api/index.html
创建cn.itcast.spring.dao包,创建BookDao类
编写BookDao类:
//图书操作的dao层
//JdbcDaoSupport简化JdbcTemplate的代码开发。
publicclass BookDao extends JdbcDaoSupport {
//注入jdbctempate
// private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
// public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
// this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
// }
//保存图书
publicvoid save(Book book){
String sql="insert into book values(null,?,?)";
//调用jdbctemplate
// jdbcTemplate.update(sql, book.getName(),book.getPrice());
super.getJdbcTemplate().update(sql, book.getName(),book.getPrice());
}
publicvoid update(Book book){
String sql="update book set name =? ,price =? where id =?";
super.getJdbcTemplate().update(sql, book.getName(),book.getPrice(),book.getId());
}
//删除
publicvoid delete(Book book){
super.getJdbcTemplate().update("delete from book where id =?", book.getId());
}
}
6.4.2. 简单返回值的查询
查询单个对象
查询数量
编写BookDao类:
//根据id查询一个
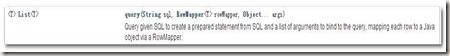
public Book findById(Integer id){
returnsuper.getJdbcTemplate().queryForObject("select * from book where id =?", ParameterizedBeanPropertyRowMapper.newInstance(Book.class),id);
}
//查询图书的数量
publicint findCount(Book book){
// return super.getJdbcTemplate().queryForInt("select count(*) from book");
returnsuper.getJdbcTemplate().queryForInt("select count(*) from book where name like ?","%"+book.getName()+"%");
}
6.4.3. 复杂对象返回的查询
查询集合
手动装配对象和自动装配对象
//查询所有
public List<Book> findAll(){
//dbutil:beanlisthan
returnsuper.getJdbcTemplate().query("select * from book", ParameterizedBeanPropertyRowMapper.newInstance(Book.class));
// RowMapper<T>
}
//复杂条件查询列表
public List<Book> findByCondition(Book book){
//ParameterizedBeanPropertyRowMapper自动装备对象(行对象)
// return super.getJdbcTemplate().query("select * from book where name =? and price =?", ParameterizedBeanPropertyRowMapper.newInstance(Book.class), book.getName(),book.getPrice());
returnsuper.getJdbcTemplate().query("select * from book where name =? and price =?", new BookRowMapper(), book.getName(),book.getPrice());
}
//自定义的手动装配的类
class BookRowMapper implements RowMapper<Book>{
//参数1:自动将查询出来的结果集传进来
//返回是:封装好的数据对象
public Book mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
Book book = new Book();
//取当前指针的结果集
book.setId(rs.getInt(1));
book.setName(rs.getString(2));
book.setPrice(rs.getDouble(3));
return book;
}
}
【这里注意】:
1:如果表中列非常多,而且列名和属性名一样 ,使用反射代码简化
使用ParameterizedBeanPropertyRowMapper 自动匹配
//查询所有
public List<Book> findAll(){
//dbutil:beanlisthan
returnsuper.getJdbcTemplate().query("select * from book", ParameterizedBeanPropertyRowMapper.newInstance(Book.class));
//RowMapper<T>--接口
}
2:如果表中列很少,字段列名称和属性名不一样,可以使用自定义RowMapper的方式装配bean:
使用new BookRowMapper() 手动装配
//复杂条件查询列表
public List<Book> findByCondition(Book book){
//ParameterizedBeanPropertyRowMapper自动装备对象(行对象)
// return super.getJdbcTemplate().query("select * from book where name =? and price =?", ParameterizedBeanPropertyRowMapper.newInstance(Book.class), book.getName(),book.getPrice());
returnsuper.getJdbcTemplate().query("select * from book where name =? and price =?", new BookRowMapper(), book.getName(),book.getPrice());
}
//自定义的手动装配的类
classBookRowMapper implements RowMapper<Book>{
//参数1:自动将查询出来的结果集传进来
//返回是:封装好的数据对象
publicBook mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
Book book = new Book();
//取当前指针的结果集
book.setId(rs.getInt(1));
book.setName(rs.getString(2));
book.setPrice(rs.getDouble(3));
return book;
}
}
创建包cn.itcast.spring.test
创建SpringTest.java进行测试:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:applicationContext.xml")
publicclass SpringTest {
//测试dao
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
/**保存测试*/
@Test
publicvoid testSave(){
Book book = new Book();
book.setName("如来神掌");
book.setPrice(1998d);
bookDao.save(book);
}
/**更新测试*/
@Test
publicvoid testUpdate(){
Book book = new Book();
book.setId(1);
book.setName("降龙十八掌");
book.setPrice(298d);
bookDao.update(book);
}
/**保存更新*/
@Test
publicvoid testDelete(){
Book book = new Book();
book.setId(2);
bookDao.delete(book);
}
/**使用主键ID查询测试*/
@Test
publicvoid testFindById(){
Integer id = 3;
Book book = bookDao.findById(id);
System.out.println(book);
}
/**使用名称的模糊查询数量测试*/
@Test
publicvoid testCountByName(){
String name = "神掌";
Book book = new Book();
book.setName(name);
int count = bookDao.findCount(book);
System.out.println(count);
}
/**查询测试*/
@Test
publicvoid testFindAll(){
List<Book> list = bookDao.findAll();
System.out.println(list);
}
/**查询条件查询测试*/
@Test
publicvoidtestFindCondition(){
Book book = new Book();
book.setName("如来神掌");
book.setPrice(1998d);
List<Book> list = bookDao.findByCondition(book);
System.out.println(list);
}
}
知识点:
1、 AOP的思想(如何实现),AOP在哪些地方使用?
2、 aop的原理(动态代理:jdk,cglib)
3、 传统Spring AOP编程 (必须写一遍 )
4、 AspectJ AOP 编程 (XML或者注解 重点掌握一套 )
问题:advice(通知增强)、 advisor(传统aop切面配置标签) 、aspect(aspectj的aop切面配置的标签) 、aspectj(可以进行aop的第三方的开源框架) 区别 ?
Advice 通知 ,增强代码
Advisor 传统SpringAOP切面,只包含一个切入点和一个通知
Aspect AspectJ定义切面 ,可以包含多个切入点和多个通知
AspectJ 第三方AOP框架
5、 数据源配置、JNDI配置
6、 外部属性文件 (context:placehoder)
7、 JdbcTemplate 实现 CURD –要都用一遍