第一:什么是AOP?
AOP是面切面编程,是OOP的补充和增强,在程序开发中主要用来解决一些系统层面上的问题。比如,日志事物,权限等待。利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行分离,比如我们在做控制层的时候有时候会碰到需要一些验证等,而使用AOP可以将这些部分与业务逻辑分开,使我们的代码更加专注于业务逻辑的处理,这样不仅降低了逻辑部分之间的耦合性,还增强了代码的可重用性,同时也提高了开发的效率。
第二:AOP的原理是什么?
在我们学习AOP之前都碰到过这样一个问题,那就是我们设计一个项目的时候,往往这个项目的不同部分都是需要验证的,虽然我们可以把相同的代码复制到需要验证的地方,但是这样不仅增加了类之间的耦合性,还使得业务逻辑代码和验证代码混合在一起,不利于代码的维护和管理,而且还增加了大量的重复性代码。而AOP就可以很好的帮助我们解决这个问题,所谓的面向切面编程就是我们利用spring的IOC管理来告诉我们的业务逻辑代码需要插入一个验证信息了,这个时候就是利用AOP直接插入就可以了,而不需要我们在去关心需要什么样的代码这样的问题了。
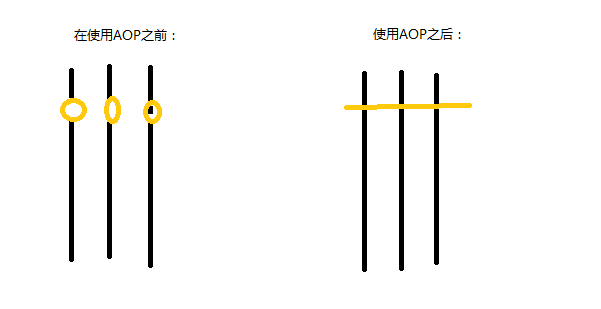
当我们没有使用AOP的时候,我们就需要在每个需要验证的地方添加代码,而如果使用了AOP,我们只需要写一份代码,然后让IOC管理实现我们在需要的地方插入就可以了。
AOP是基于23种设计模式之一的代理模式来实现的,因为在学习AOP之前,我们需要来学习一下代理模式。
第三:代理模式
代理模式可以分为静态代理模式和动态代理模式;其中动态代理又可以分为jdk动态代理和cglib动态代理
先来学习静态代理:下面给出一个静态代理的小案例
静态代理需要有接口以及该接口的实现类
静态代理中需要用到的包:这里除了spring的IOC需要用到的包外还多了一个aop的包,需要注意
代码如下:
接口代码:
1 public interface SomeService { 2 String doSome(); 3 void say(); 4 }
接口的实现类代码:
1 public class SomeServiceImpl implements SomeService{ 2 @Override 3 public String doSome() { 4 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 5 System.out.println("dosome"); 6 return "halou.."; 7 } 8 @Override 9 public void say() { 10 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 11 System.out.println("say...."); 12 } 13 }
代理的实现方式之一:静态代理类需要自己写代理类
1 public class ProxyFactory implements SomeService{ 2 3 private SomeService target; 4 5 public ProxyFactory(SomeService target) { 6 super(); 7 this.target = target; 8 } 9 10 @Override 11 public String doSome() { 12 System.out.println("---代理1--"); 13 // 执行目标对象的方法 14 String doSome = target.doSome(); 15 System.out.println("---代理2--"); 16 return doSome.toUpperCase(); 17 } 18 19 }
测试类的代码:
1 public class Test { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 // 实例化目标对象 5 SomeService target = new SomeServiceImpl(); 6 // 获取代理类 7 SomeService proxy = new ProxyFactory(target ); 8 // 通过代理对象调用方法 9 System.out.println(proxy.doSome()); 10 11 } 12 13 }
测试结果如下:

动态代理之jdk代理模式:
接口代码:
1 public interface SomeService { 2 String doSome(); 3 }
实现类代码:
1 public class SomeServiceImpl implements SomeService { 2 @Override 3 public String doSome() { 4 System.out.println("dosome...."); 5 return "hello.."; 6 } 7 }
测试类以及代理类代码:
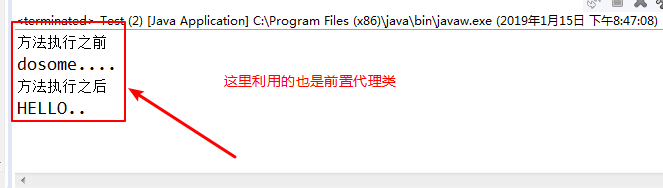
1 import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; 2 import java.lang.reflect.Method; 3 import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; 4 import com.sxt.service.SomeService; 5 import com.sxt.serviceimpl.SomeServiceImpl; 6 7 /** 8 * @author ASUS 这是通过jdk动态代理的方式来测试 9 * 10 */ 11 public class Test { 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 //实例化目标对象 14 SomeService service=new SomeServiceImpl(); 15 //通过jdk动态代理的方式获取代理对象 16 SomeService proxy=(SomeService) Proxy.newProxyInstance(service.getClass().getClassLoader(),//设置类加载器 17 service.getClass().getInterfaces(),//获取目标对象的所有实现的接口 18 new InvocationHandler() { 19 /** 20 * proxy 代理对象 21 * method 需要执行目标对象的方法 22 * args 目标对象的参数 23 */ 24 @Override 25 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { 26 System.out.println("方法执行之前"); 27 String invoke =(String)method.invoke(service, args); 28 System.out.println("方法执行之后"); 29 return invoke.toUpperCase(); 30 } 31 }); 32 System.out.println(proxy.doSome()); 33 } 34 }
运行结果如吓:
动态代理之cglib代理:在cglib代理中需要接口,只需要有对应的目标类就可以了。
目标类代码:
1 package com.sxt.serviceimpl; 2 /** 3 * @author ASUS 4 * cglib的目标类 5 * 6 */ 7 public class SomeServiceImpl { 8 public String doSome() { 9 System.out.println("dosome...."); 10 return "hello.."; 11 } 12 }
测试类代码:
1 import com.sxt.cglib.CglibProxy; 2 import com.sxt.serviceimpl.SomeServiceImpl; 3 4 /** 5 * @author ASUS 这是通过cglib动态代理的方式来测试 6 * 7 */ 8 public class Test { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 //实例化目标对象 11 SomeServiceImpl service=new SomeServiceImpl(); 12 //获取代理类 13 SomeServiceImpl proxy=new CglibProxy(service).createProxy(); 14 System.out.println(proxy.doSome()); 15 } 16 }
cglib代理类代码:
1 import java.lang.reflect.Method; 2 import com.sxt.serviceimpl.SomeServiceImpl; 3 import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer; 4 import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor; 5 import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy; 6 7 /** 8 * @author ASUS 9 * cglib代理类 10 * 11 */ 12 public class CglibProxy implements MethodInterceptor{ 13 //目标对象 14 private SomeServiceImpl service; 15 public CglibProxy(SomeServiceImpl service) { 16 super(); 17 this.service = service; 18 } 19 /** 20 * 创建代理对象 21 * @return 22 */ 23 public SomeServiceImpl createProxy() { 24 //获取Enhancer对象 25 Enhancer e=new Enhancer(); 26 // 设置父类对象,设置目标对象的类型 27 e.setSuperclass(SomeServiceImpl.class); 28 //设置callback对象,就是this 29 e.setCallback(this); 30 return (SomeServiceImpl)e.create(); 31 } 32 @Override 33 public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable { 34 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 35 System.out.println("执行之前"); 36 String invoke =(String) method.invoke(service, args); 37 System.out.println("执行之后"); 38 return invoke.toUpperCase(); 39 } 40 }
注意:在cglib代理中虽然不需要接口,但是要用到一个jar包

我们已经了解了代理模式的原理,现在我们来学习AOP的几种实现方式:
方式一:前置通知,顾名思义就是在目标类的方法执行执行,该前置类的方法会被执行
代码如下:
接口代码:
package com.sxt.service; /** * @author ASUS * 静态代理的公共接口 * */ public interface SomeService { String doSome(); void say(); }
接口的实现类代码:
1 import com.sxt.service.SomeService; 2 /** 3 * @author ASUS 4 * 前置代理接口的实现类 5 * 6 */ 7 public class SomeServiceImpl implements SomeService { 8 @Override 9 public String doSome() { 10 System.out.println("dosome...."); 11 return "hello.."; 12 } 13 @Override 14 public void say() { 15 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 16 System.out.println("ssssss"); 17 } 18 }
前置代理类代码:
1 import java.lang.reflect.Method; 2 import org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice; 3 /** 4 * @author ASUS 5 * 6 */ 7 public class MyMethodBeforeAdvice implements MethodBeforeAdvice{ 8 @Override 9 public void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable { 10 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 11 System.out.println("前置通知》》》"); 12 } 13 }
测试类代码:
1 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 2 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 3 import com.sxt.service.SomeService; 4 5 /** 6 * @author ASUS 测试类 7 * 8 */ 9 public class Test { 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 // 获取ApplicationContext对象 加载配置文件 反射+xml解析 12 ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml"); 13 // 从容器中获取代理对象 14 SomeService service = ac.getBean("proxyFactoryBean", SomeService.class); 15 16 String res = service.doSome(); 17 System.out.println(res); 18 System.out.println("-----------------"); 19 service.say(); 20 } 21 }
配置文件代码:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" 5 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> 6 <!-- 注册目标对象 --> 7 <bean class="com.sxt.serviceimpl.SomeServiceImpl" id="someServiceImpl"/> 8 <!-- 注册前置通知 --> 9 <bean class="com.sxt.aspect.MyMethodBeforeAdvice" id="myMethodBeforeAdvice"/> 10 <!-- AOP 配置代理类 --> 11 <bean class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean" id="proxyFactoryBean"> 12 <!-- 配置代理类 --> 13 <property name="target" ref="someServiceImpl"/> 14 <!-- 配置代理类实现的接口 --> 15 <property name="interfaces" value="com.sxt.service.SomeService"/> 16 <!-- 配置通知 --> 17 <property name="interceptorNames"> 18 <list> 19 <!-- 配置前置通知 --> 20 <value>myMethodBeforeAdvice</value> 21 </list> 22 </property> 23 </bean> 24 </beans>
测试结果如下:

需要用到的jar包如下:

AOP实现之后置通知:也就是在目标类的方法执行之后才会执行的
接口代码:
1 package com.sxt.service; 2 /** 3 * @author ASUS 4 * 静态代理的公共接口 5 * 6 */ 7 public interface SomeService { 8 String doSome(); 9 void say(); 10 }
实现类代码:
1 import com.sxt.service.SomeService; 2 /** 3 * @author ASUS 4 * 后置代理接口的实现类 5 * 6 */ 7 public class SomeServiceImpl implements SomeService { 8 @Override 9 public String doSome() { 10 System.out.println("dosome...."); 11 return "hello.."; 12 } 13 @Override 14 public void say() { 15 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 16 System.out.println("ssssss"); 17 } 18 }
后置代理类的代码:
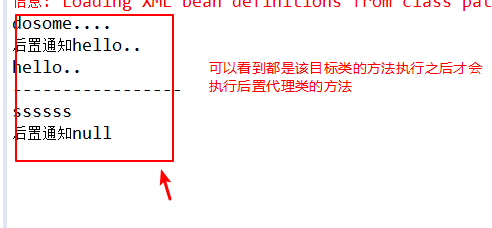
1 package com.sxt.aspect; 2 3 import java.lang.reflect.Method; 4 import org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice; 5 /** 6 * @author ASUS 7 * 8 */ 9 public class MyAfterReturningAdvice implements AfterReturningAdvice{ 10 @Override 11 public void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable { 12 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 13 System.out.println("后置通知"+returnValue); 14 //returnValue=((String)returnValue).toUpperCase(); 15 } 16 }
测试类代码:
1 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 2 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 3 import com.sxt.service.SomeService; 4 /** 5 * @author ASUS 测试类 6 * 7 */ 8 public class Test { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 // 获取ApplicationContext对象 加载配置文件 反射+xml解析 11 ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml"); 12 // 从容器中获取代理对象 13 SomeService service = ac.getBean("proxyFactoryBean", SomeService.class); 14 String res = service.doSome(); 15 System.out.println(res); 16 System.out.println("-----------------"); 17 service.say(); 18 } 19 }
配置文件代码:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" 5 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> 6 7 <!-- 注册目标对象 --> 8 <bean class="com.sxt.serviceimpl.SomeServiceImpl" id="someServiceImpl"/> 9 <!-- 注册前置通知 --> 10 <!-- <bean class="com.sxt.aspect.MyMethodBeforeAdvice" id="myMethodBeforeAdvice"/> --> 11 <!-- 注册后置通知 --> 12 <bean class="com.sxt.aspect.MyAfterReturningAdvice" id="myAfterReturningAdvice"/> 13 <!-- AOP 配置代理类 --> 14 <bean class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean" id="proxyFactoryBean"> 15 <!-- 配置代理类 --> 16 <property name="target" ref="someServiceImpl"/> 17 <!-- 配置代理类实现的接口 --> 18 <property name="interfaces" value="com.sxt.service.SomeService"/> 19 <!-- 配置通知 --> 20 <property name="interceptorNames"> 21 <list> 22 <!-- 配置前置通知 --> 23 <!-- <value>myMethodBeforeAdvice</value> --> 24 <!-- 配置后置通知 --> 25 <value>myAfterReturningAdvice</value> 26 </list> 27 </property> 28 </bean> 29 </beans>
测试结果如下:
AOP实现之环绕代理通知:就是在整个目标类方法执行的前后都会执行该环绕代理类的方法
接口代码:
1 public interface SomeService { 2 String doSome(); 3 void say(); 4 }
实现类代码:
1 public class SomeServiceImpl implements SomeService { 2 @Override 3 public String doSome() { 4 System.out.println("dosome...."); 5 return "hello.."; 6 } 7 @Override 8 public void say() { 9 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 10 System.out.println("ssssss"); 11 } 12 }
环绕代理通知代码:

测试类代码:
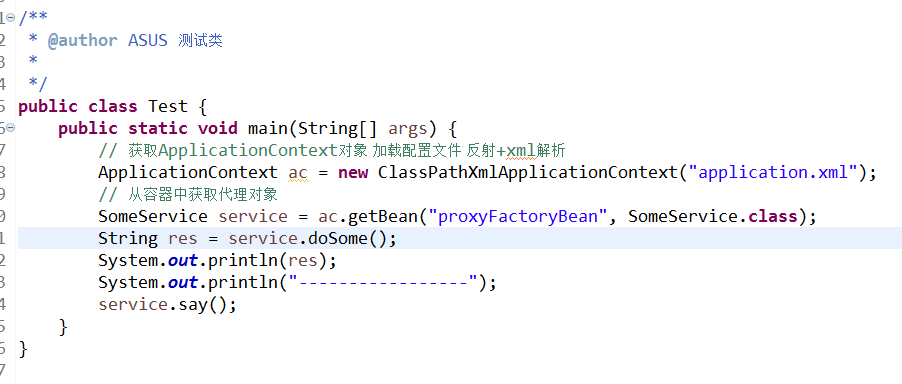
配置文件代码:

测试结果如下:
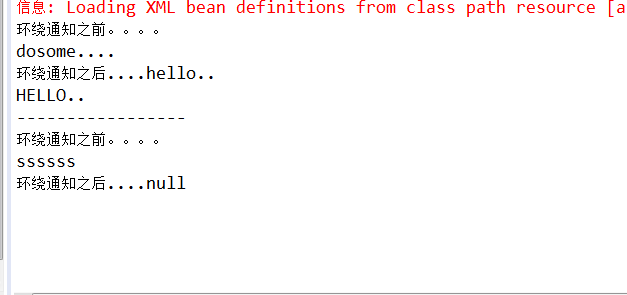
异常代理:
异常代理类代码:
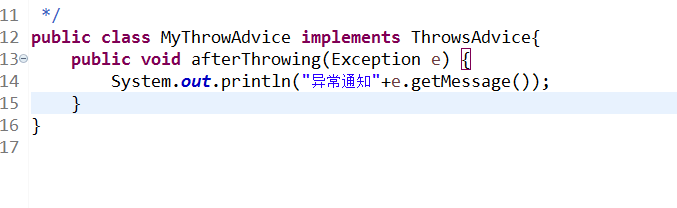
接口代码:

实现类代码:
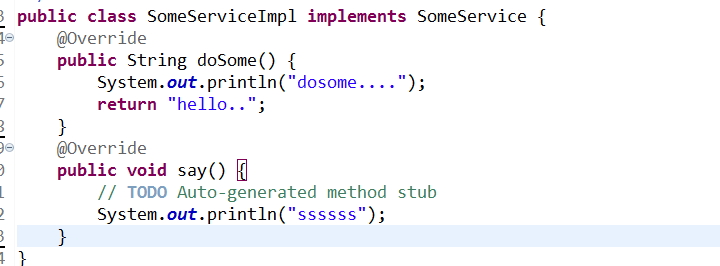
测试类代码:

配置文件代码参考上面的。这里需要自己随便创造一个异常。
由于在配置文件中配置代理类太麻烦了,下面我们来介绍使用注解的方式实现代理
利用注解的方式需要用到的jar包与上面的配置文件的方式不一样;这里需要用到一个aspectj-tools的jar包
这里一共要用到6个注解《比上面多了一个最终代理类》
注解一:@Aspect这个是用在代理类的前面的,与配置文件相结合
注解二:@Before这个是前置代理类的注解,用在前置代理方法的前面
注解三:@AfterReturning后置代理类的注解
注解四:@Around环绕注解
注解五:@AfterThrowing异常代理类注解
注解六:@After最终代理类注解
这里还要在注解的后面指明代理类方法切入的位置,前面的代理实现只能指明切入的类,不能指明具体的方法,而使用注解的方式则可以指明切入的具体的方法
因此,这个最为常用
代理类代码:
1 import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; 2 import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After; 3 import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning; 4 import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing; 5 import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around; 6 import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; 7 import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before; 8 /** 9 * @author ASUS 10 * @ASPECT表示该类就是一个切面 11 * 12 */ 13 @Aspect 14 public class MyAspect { 15 /** 16 * execution切入点表达式:定位该通知的切入点 17 * execution(* com.dpb.service.*.doSome(..)) 18 */ 19 @Before("execution(* com.sxt.serviceimpl..*(..))") 20 public void before() { 21 System.out.println("前置通知"); 22 } 23 /** 24 * 后置通知 25 */ 26 @AfterReturning(value="execution(* com.sxt.service.*.doSome(..))",returning="msg") 27 public void afterReturn(Object msg) { 28 System.out.println("后置通知"+msg); 29 } 30 /** 31 * 环绕通知 32 * @param pjp 33 * @return 34 * @throws Throwable 35 */ 36 @Around(value="execution(* com.sxt.service.*.doSome(..))") 37 public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable { 38 System.out.println("环绕通知之前"); 39 String proceed =(String) pjp.proceed(); 40 System.out.println("环绕通知之后"+proceed); 41 return proceed.toUpperCase(); 42 } 43 /** 44 * 异常通知 45 * @param e 46 */ 47 @AfterThrowing(value="execution(* com.sxt.service.*.doSome(..)",throwing="e") 48 public void throwing(Exception e) { 49 System.out.println("异常通知"+e.getMessage()); 50 } 51 /** 52 * 最终通知 53 */ 54 @After("execution(* com.sxt.service.*.doSome(..))") 55 public void after() { 56 System.out.println("最终通知---"); 57 } 58 }
配置文件代码:在配置文件中需要指明目标对象,代理类对象以及开启aspectj注解
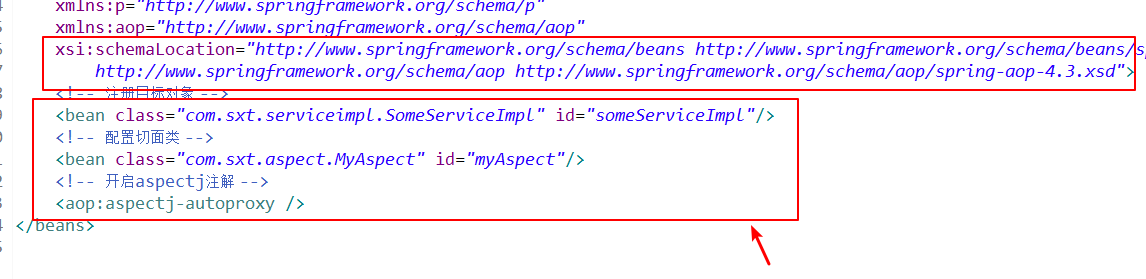
接口,实现类,测试类代码参照上面的代理通知类代码
在这里我们还介绍一种使用配置文件的实现方式
就是将前面分散的代理方式的代码的配置文件合在一起就可以了。

