python 函数使用
在Python中,定义一个函数要使用def语句,依次写出函数名、括号、括号中的参数和冒号:,然后,在缩进块中编写函数体,函数的返回值用return语句返回。
以自定义一个除法div()函数为例:
def div(a,b):
if not isinstance(a,(int,float)): # 判断一下a是否是数字
return None
if not isinstance(b,(int,float)): # 判断一下b是否是数字
return None
if b == 0:
return None
return a/b
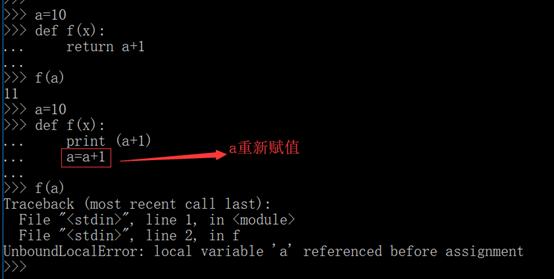
1.函数中全局变量与局部变量
UnboundLocalError:局部变量a在赋值前被引用
1.如果使用了赋值操作,此变量为局部变量在使用前必须初始化。
2.函数中使用全局变量,申明为global

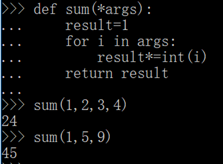
2.可变参数 (*args, **kw)
注意:*args 是元组,**kw 是字典
def sum(*args):
result=1
for i in args:
result*=int(i)
return result

3.可变参数求函数(缺省参数)相加的值
该函数为 sum(1,2,3,4,b=5,c=6,d=7)
#encoding=utf-8
def sum(a,*arg,**args):
sum=0
sum=sum+a
for i in arg:
sum=sum+int(i)
for i in args.values():
sum=sum+int(i)
return sum
4.1exec函数说明
当我们需要动态的创造python代码,然后将其作为语句或作为表达式去执行。exec语句用来执行存储在字符串或文本中有效的python语句
exce语句执行python语句不会返回结果
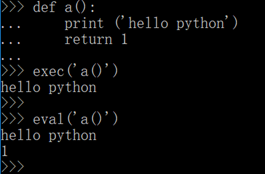
def a():
print 'hello python'
exec('a()')
执行结果:hello python
def a():
return 'test'
exec('a()')
>>> exec("print ('hello python')")
hello python
4.2.eval函数说明
eval语句用来执行存储在字符串或文本中有效的python表达式,并返回计算结果
和exec函数区别:
a:eval函数有返回值,而exec函数没有返回值
b:eval函数可以打印,而print exec函数会报语法错误
def a():
print 'hello python'
return 1
exec('a()')
eval('a()')