AOP的具体实践-简化结果返回的处理
原因:
以前学习Spring的时候着重学习过AOP概念,但是一直也没有用上,唯一碰到过的就是Spring内置的事务管理。现在碰到过一些结果后面的操作适合用到,所以这里就拿出来用一下,并且复习一下落下的知识。
概念:
基本概念这个博主解释的比较清楚,如果有不懂的可以去看一下。https://blog.csdn.net/csh624366188/article/details/7651702
在我的认识里,如果某些方法重复性特别高,可以抽象出来形成一个切面,则可以使用AOP来简化代码,即在方法的某些部分动态的添加某些方法,起到简化代码的作用。
具体需求:
项目的Service层通过webService获取到数据,需要对获取到的数据进行判断处理,对其异常信息作出记录和抛出异常。同时还需要在进入和结束方法的时候进行日志记录。
知识点:
配置方法:
在这里使用的是注解的方式来配置的AOP,首先,要保证项目中除了Spring基本包以外还包含aopalliance-1.0.jar,aspectjrt-1.8.7.jar,aspectjweaver-1.8.7.jar,cglib-nodep-3.2.4.jar这四个jar包,这里将其打包放到百度云,如果有需要的可以去下载。链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1rDqLY1lnWdiahVkLcZd_bw 密码:0uea
Spring配置添加如下, 添加<aop:aspectj-autoproxy />需要添加Spring的头部内容
注意aop不能添加到static方法上面。
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy /> // 扫描AOP
<!-- 这里配置后就不用再使用bean标签配置bean了 -->
<context:annotation-config></context:annotation-config>
<!-- 去哪个包扫描生成bean -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.dazhong.jnfy.alipay.action" />
首选建立切面类:其中的afterReturning就是主要的切面方法,用于对返回值进行判断并且进行对应的操作,这样可以不用再每个方法中都写一次。
@Pointcut("execution(* com.dazhong.jnfy.alipay.service.impl.*.*(..))"):表示AOP会代理那些方法,这里则表示com.dazhong.jnfy.alipay.service.impl包下面所有方法都会执行
@After("picter()"):后置通知
@Before("picter()"):前置通知
package com.dazhong.jnfy.alipay.aop;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.json.JSONObject;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import com.dazhong.jnfy.alipay.exception.ConnectionException;
import com.dazhong.jnfy.alipay.exception.ResultErrorException;
import com.dazhong.utils.LogUtil;
@Component
@Aspect
public class ServiceAop {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.dazhong.jnfy.alipay.service.impl.*.*(..))")
public void picter() {
}
/**
* @Description: 对返回值进行处理
* @param point
* @param rvt
* @throws ResultErrorException
*/
@AfterReturning(returning = "rvt", pointcut = "execution(* com.dazhong.jnfy.alipay.service.impl.*.*(..))")
public void afterReturning(JoinPoint point, Object rvt) throws Exception { // Object rvt则是方法返回值,这里变量名称要和注解retruning值相同
String[] strs = point.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName().split("\\.");
String fullname = strs[strs.length - 1] + "." + point.getSignature().getName();
JSONObject root = (JSONObject) rvt;
if (rvt == null) {
throw new ConnectionException("WebService连接失败" + fullname);
} else if (!root.has("resultCode") || !root.get("resultCode").toString().equals("0")) {
// 返回数据异常
throw new ResultErrorException("WebService 返回结果异常:" + root.toString());
}
}
@Before("picter()")
public void before(JoinPoint point) {
String[] strs = point.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName().split("\\.");
String fullname = strs[strs.length - 1] + "." + point.getSignature().getName();
LogUtil.info("进入方法:" + fullname);
}
@After("picter()")
public void after(JoinPoint point) {
String[] strs = point.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName().split("\\.");
String fullname = strs[strs.length - 1] + "." + point.getSignature().getName();
LogUtil.info("方法结束:" + fullname);
}
}
获取参数/方法名:
如果需要获取目标方法的参数/名字,则需要在切面的方法中添加变量 JoinPoint point,通过这个对象来进行获取。
String allname = point.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName(); // 获取整个路径 包名+类名
System.out.println(allname);
String[] split = allname.split("\\.");
System.out.println("目标方法:" + split[split.length - 1] + "." + point.getSignature().getName()); // point.getSignature().getName() 获取方法名
System.out.println("@Before:参数为:" + Arrays.toString(point.getArgs())); // 获取目标方法的参数 point.getArgs()
结果: 红框内容就是AOP自动添加的。
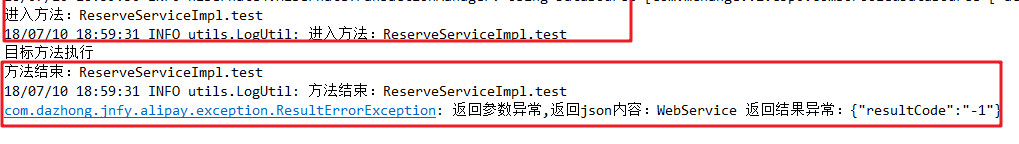
剩余代码:
目标方法:
public JSONObject test() throws Exception{
System.out.println("目标方法执行");
JSONObject js = new JSONObject();
js.put("resultCode", "-1");
return js;
}
测试方法:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext appCtx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
ReserveServiceImpl b = (ReserveServiceImpl) appCtx.getBean("reserveServiceImpl");
JSONObject js = new JSONObject();
js.put("s", "111");
try {
//JSONObject allDept = b.getDocterByTimeAndDept("YYKS002", "20180711");
b.test();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}


