Java Spring Boot VS .NetCore (七) 配置文件
Java Spring Boot VS .NetCore (一)来一个简单的 Hello World
Java Spring Boot VS .NetCore (二)实现一个过滤器Filter
Java Spring Boot VS .NetCore (三)Ioc容器处理
Java Spring Boot VS .NetCore (四)数据库操作 Spring Data JPA vs EFCore
Java Spring Boot VS .NetCore (五)MyBatis vs EFCore
Java Spring Boot VS .NetCore (六) UI thymeleaf vs cshtml
Java Spring Boot VS .NetCore (七) 配置文件
Java Spring Boot VS .NetCore (八) Java 注解 vs .NetCore Attribute
Java Spring Boot VS .NetCore (九) Spring Security vs .NetCore Security
Java Spring Boot VS .NetCore (十) Java Interceptor vs .NetCore Interceptor
Java Spring Boot VS .NetCore (十一)自定义标签 Java Tag Freemarker VS .NetCore Tag TagHelper
Spring Boot 配置文件
主要说下 properties & yml
下面来看下
application.properties的文件格式
Spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.0.233:3306/test1?useSSL=false Spring.datasource.username=uoso Spring.datasource.password=uosotech_123 Spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
yml配置格式
spring1: url1: dbc:mysql://192.168.0.102:3306/test1?useSSL=false
那么在代码中我们怎么来使用这些配置文件呢?
这里要介绍的就是注解 @Component 、 @Value 的使用了
默认只要编写名称为application.*.yml 都是能够被直接使用的,只需要把 配置文件映射到类的属性里面,代码如下
@Component public class PropertiesConfig { @Value("${Spring.datasource.url}") private String database; public String getDatabase() { return database; } public void setDatabase(String database) { this.database = database; } }
如果世界使用的application.yml 能够自动被填充的配置资源里面,写法给上面样就能拿到配置
我这里自定义一个yml 如:test.yml
这里需要添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
重新构建后,我新建一个class ,这里需要说明的就是 @ProtertySource 指定yml的路径 需要注意是的 classpath 这个指向的地址,是打包后的目录,调试的时候肯定找不到对应路径目录的文件需要自己配置下,否则就放在下图的目录结构
@Component @PropertySource(value = "classpath:/test.yml") @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring1") public class YMLConfig { public String getUrl1() { return url1; } public void setUrl1(String url1) { this.url1 = url1; } @Value("${url1}") private String url1;
使用通过注解 @Autowired \ @Resource 都可以
//测试yml配置 @Autowired private YMLConfig ymlConfig; @Test public void testYmlConfig() { System.out.print(ymlConfig.getUrl1()); }
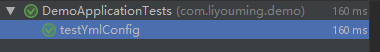

得到了我们想要的结果,下面在来说下.NetCore中的配置使用情况
.NetCore 配置文件
.NetCore提供了json 、xml 的方式来实现配置,这里我以json 来举个例子看下使用方式
默认也有一个appsettings.json 的文件,在不使用自定义配置的情况下,系统会加载这个配置文件 ,那么如果要把配置文件映射到class里面需要怎么处理呢?
下来创建一个配置类
public class AuthorityConfig { public string Authority { get; set; } public bool RequireHttpsMetadata { get; set; } }
在appsetting里面我们根据目录结构添加即可
"AuthorityConfig": { "Authority": "http://localhost:20001", "RequireHttpsMetadata": false }
那么怎么把这两个Bind起来呢? 前面可以看到Java是通过@Value注解
.NetCore则是通过 在Startup 启动类中添加服务 里面有 IConfiguration 接口,根据这个接口来操作即可
services.AddOptions(); services.Configure<AuthorityConfig>(Configuration.GetSection("AuthorityConfig"));
根据节点位置配置关联的类,需要使用的时候通过构造函数注入即可
如果需要添加自定义的配置,我们使用启动类的构建来创建相关路径下的相关文件绑定到配置中Configuration 最后通过 Configuration 来绑定 Class之间的关系
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration, IHostingEnvironment env) { var configurationbuilder = new ConfigurationBuilder() .SetBasePath(env.ContentRootPath) .AddJsonFile($"appsettings.json", optional: true, reloadOnChange: true) .AddXmlFile($"appsettings.xml", optional: true, reloadOnChange: true) .AddEnvironmentVariables(); Configuration = configurationbuilder.Build(); // Configuration = configuration; }
总结
其实 Spring Boot中也有其他的方式加载自定义的文件 ,这里的 ConfugurationBuilder 跟 Spring Boot中的 PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer 类似,Java还提供了2中创建方式
1、YamlPropertiesFactoryBean yaml = new YamlPropertiesFactoryBean();
2、YamlPropertySourceLoader loader = new YamlPropertySourceLoader();
MutablePropertySources sources = new MutablePropertySources();
可以看到第二种里面多了MutablePropertySources,英文上就是加载多个资源文件的,事实就是这个意思,加载多个资源文件,而第一种没抛出异常
下面来解析下第一种:看源码
public class YamlPropertiesFactoryBean extends YamlProcessor implements FactoryBean<Properties>, InitializingBean { private boolean singleton = true; @Nullable private Properties properties; public YamlPropertiesFactoryBean() { } public void setSingleton(boolean singleton) { this.singleton = singleton; } public boolean isSingleton() { return this.singleton; } public void afterPropertiesSet() { if (this.isSingleton()) { this.properties = this.createProperties(); } }
没有异常,而且是单例
看下第二种的源码,抛出了IO异常,在找不到文件目录文件的情况下会抛出异常
public class YamlPropertySourceLoader implements PropertySourceLoader { public YamlPropertySourceLoader() { } public String[] getFileExtensions() { return new String[]{"yml", "yaml"}; } public List<PropertySource<?>> load(String name, Resource resource) throws IOException { if (!ClassUtils.isPresent("org.yaml.snakeyaml.Yaml", (ClassLoader)null)) { throw new IllegalStateException("Attempted to load " + name + " but snakeyaml was not found on the classpath"); } else { List<Map<String, Object>> loaded = (new OriginTrackedYamlLoader(resource)).load(); if (loaded.isEmpty()) { return Collections.emptyList(); } else { List<PropertySource<?>> propertySources = new ArrayList(loaded.size()); for(int i = 0; i < loaded.size(); ++i) { String documentNumber = loaded.size() != 1 ? " (document #" + i + ")" : ""; propertySources.add(new OriginTrackedMapPropertySource(name + documentNumber, (Map)loaded.get(i))); } return propertySources; } } } }
配置这一块就说道这里~~~
下一章来介绍下自定的注解,同时也会结合.NetCore自定义属性标签来比较来时比较说明。
如果您觉得阅读本文对您有帮助,请点一下“推荐”按钮,您的“推荐”将是我最大的写作动力!
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,来源网址:http://www.cnblogs.com/liyouming欢迎各位转载,但是未经作者本人同意,转载文章之后必须在文章页面明显位置给出作者和原文连接。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号