Golang 基础语法介绍及对比(二)
传值与传参
Golong
func main() { a := 3 fmt.Println("a = ", a) // 应该输出 "a= 3" a1 := add1(a) //调用add1(x) fmt.Println("a+1 = ", a1) // 应该输出"a+1 = 4" fmt.Println("a = ", a) // 应该输出"a = 3" } func add(a *int) int { *a = *a+1 // 我们改变了a的值 return *a //返回一个新值 } func add1(a int) int { a = a+1 // 我们改变了a的值 return a //返回一个新值 }
C#
static void Main(string[] args) { int a = 3; var r= add1(a); Console.WriteLine(r); Console.WriteLine(a); Console.ReadKey(); } static int add(ref int a ) { a = a + 1; return a; } static int add1(int a) { a = a + 1; return a; }
Javascript
Javascript可以用变量作用域这块来比较,函数内部作用域以及全局作用域
var a=3; function main() { var r=add(a); alert("r:"+r+"\r\n"+"a:"+a); } function add(a){ a= a+1; return a; }
var a=3; function main() { var r=add(a); alert("r:"+r+"\r\n"+"a:"+a); } function add(x){ a= x+1; return a; }
这里还有一个有不同的地方就是C#与Golang在Class、Struct
在C#中Class就是引用类型,C#中的Struct也是值类型的,Golang中的Struct就类似C#中的Struct,下面来看下这几种输出结果
C# Class
所以这里给不给ref都是一样的结果,都会变成引用类型
static void Main(string[] args) { var test = new TestObject { name = "黎又铭", age = 23 }; var t= Con(test); // var t1 = Con(ref test); Console.WriteLine(t.name); Console.WriteLine(test.name); Console.ReadKey(); } static TestObject Con(TestObject testObject) { testObject.name = "张三"; return testObject; } static TestObject Con(ref TestObject testObject) { testObject.name = "张三"; return testObject; }
C# Struct
用Struct来输入就发现其实用ref 与不用输出的结果就不一样了
public struct TestObjectB { public string name { get; set; } public int age { get; set; } } static TestObjectB Con(TestObjectB testObject) { testObject.name = "张三"; return testObject; } static TestObjectB Con(ref TestObjectB testObject) { testObject.name = "张三"; return testObject; } static void Main(string[] args) { var test = new TestObjectB { name = "黎又铭", age = 23 }; var t= Con(test); // var t1 = Con(ref test); Console.WriteLine(t.name); Console.WriteLine(test.name); Console.ReadKey(); }
Golang Struct
这里我们来看看Golang中的写法,在使用TestZZ得到的结果是不同的
func main() { test:=TestObject{"黎又铭",22 } t:= TestZZ1(test) // t:= TestZZ(&test) f.Println(t.name) f.Println(test.name) } func TestZZ(test *TestObject) *TestObject { test.name="zhangsan" return test } func TestZZ1(test TestObject) TestObject{ test.name="zhangsan" return test }
函数申明
Golang
func testMethod(arg1 int) int { 方法体 } //解析: 方法关键字 方法名称(参数1 参数1类型) 返回值 { 方法体 } Golang 返回参数可以是多个
C#
public int testMethod(int arg1) { } //解析: 访问关键字 返回值 方法名称(参数1类型 参数1) { 方法体 } C#返回参数只能是一个,如果是多个需要用对象类定义
Javascript
function testMethod(arg1){ 方法体 } //解析: 可以返回任意类型,弱类型语言,当然也可以返回 function ,{} ,[]
变量声明
Golong
var a int32 =1 var a int32 默认就是0 申明的变量都是需要使用的,不然会出现编译错误 var a bool fmt.Print(a) -- false var a int32 fmt.Print(a) 0 Golang中提供了多变量申明以及简洁方式声明省略掉了 var以及类型 如: a:=1 或 多个 a,b:=1,3
C#
int a; int a=1; var a=1; var bol=true; int b=3,b1=1; 申明的变量是可以不用的,如果使用就需要对局部变量赋值
Javascript
var a=1; var a=1,b=2; var a; javascript也是可以申明多个变量的
变参
Golang
Golang中用了 ...int 这样的形式 func main() { sum:= Sum(1,2,3,4) fmt.Println(sum) //10 } func Sum(arg1 ...int) int { sum:=0 for _,x := range arg1 { sum+=x } return sum }
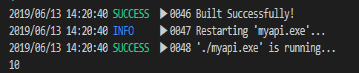
C#
这里参数需要使用关键字 params 如下 static int Sum(params int[] a) { int sum = 0; foreach(var item in a) { sum += item; } return sum; } static void Main(string[] args) { var r= Sum(1, 2, 3, 4); Console.WriteLine(r); //10 Console.ReadKey(); }
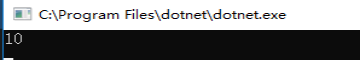
Javascript
Javascript变参可以用arguments与 apply和call 来理解,但是这里最趋近于apply,因为call还是要给个数,而apply给的是数组 function Sum() { var sum=0; for(var i=0;i<arguments.length;i++) { sum+=arguments[i]; } return sum; } alert(Sum.apply(this,[1,2,3,4]));

面向对象
Golang
type TestObject struct{ name string age int } func main() { test:=TestObject{name:"黎又铭",age:23 } f.Println("姓名", test.name) } golang在这里也可以这样写: person:=TestObject{"黎又铭",12 } 不用写名称,类似构造函数,但是需要注意顺序问题

type TestObject struct{ name string age int } type TestObjectB struct{ name string age int } func (test TestObject) print() { f.Println(test.name) } func (testb TestObjectB) print() { f.Println( testb.name) } func main() { test:=TestObject{"黎又铭",22 } testb:=TestObjectB{"徐洁敏",12 } test.print() testb.print() }

分别在 TestOjbect 或 TestObjectB 下添加的方法 print,而
func (test TestObject) print()
(test TestObject) 这种语法指定了调用者,C#中就像是在类中添加方法一样
C#
public class TestObject{ public string name { get; set; } public int age { get; set; } } static void Main(string[] args) { var test = new TestObject { name = "黎又铭", age = 23 }; Console.WriteLine("姓名:" + test.name); Console.ReadKey(); }

public class TestObject{ public string name { get; set; } public int age { get; set; } } public class TestObjectB { public string name { get; set; } public int age { get; set; } } public static class Extensions { public static string print(this TestObject test) { return test.name; } public static string print(this TestObjectB testb) { return testb.name; } } static void Main(string[] args) { var test = new TestObject { name = "黎又铭", age = 23 }; var testb = new TestObjectB { name = "徐洁敏", age = 21 }; var t = test.print(); var tb = testb.print(); Console.WriteLine(t); Console.WriteLine(tb); Console.ReadKey(); } 修正:可能用扩展来表达不合理,这里就是在类中添加方法,表示这个类中的方法,这里我们用了扩展不合理
Javascript
function testObject(n,a) { this.name=n; this.age=a; } var test=new testObject("黎又铭",23); alert(test.name);

function testObject(n,a) { this.name=n; this.age=a; } function testObjectB(n,a) { this.name=n; this.age=a; } testObject.prototype.print=function(){ alert(this.name); } testObjectB.prototype.print=function(){ alert(this.name); } var test=new testObject("黎又铭",31); test.print(); var testb=new testObjectB("徐洁敏",31); testb.print(); 在Javascript 用原型链方法来对于Golang中的
C# 函数作为参数传递(委托)
delegate void TestMethod(int x); public static void mytest(int a) { Console.WriteLine(a); } public static void mytest1(int a) { Console.WriteLine("ddd"+a); } static void Main(string[] args) { TestMethod testMethod= new TestMethod(mytest); testMethod += new TestMethod(mytest1); testMethod?.Invoke(1); }
Golang 函数作为值、类型
type testMethod func(int) int func testprint(a int) int{ f.Println(a) return a*a; } func testprint1(a int) int{ f.Println(a) return a+a; } func test(t testMethod) int{ x:= t(4) return x } func main() { x:= test(testprint) x1:= test(testprint1) f.Println(x) f.Println(x1) }
如果您觉得阅读本文对您有帮助,请点一下“推荐”按钮,您的“推荐”将是我最大的写作动力!
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,来源网址:http://www.cnblogs.com/liyouming欢迎各位转载,但是未经作者本人同意,转载文章之后必须在文章页面明显位置给出作者和原文连接。



