49. 把字符串转换为整数
很多细节需要注意。(空格,符号,溢出等)
Go: 8. String to Integer (atoi)
50. 树种两个结点的最低公共祖先
A. 若是二叉搜索树,直接与根结点对比。 若都大于根节点,则在友子树;若都小于根节点,则在左子树;若根节点介于两数之间,则根节点即为答案。
B. 普通树,若是孩子节点有指向父节点的指针,则问题变为求两个链表的第一个公共结点。 如:37题。
C. 普通树:思路1,若一个结点的子树同时包含两个结点,而它的任一孩子结点的子树却不能同时包含,则该节点即为答案。需要重复遍历,时间复杂度较高。
思路2:先序优先遍历,分别记录从根节点到两个结点的路径。然后转换为求第一个公共结点问题。
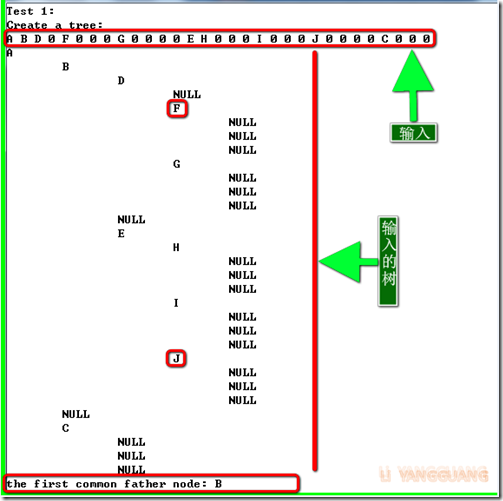
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <list> using namespace std; typedef struct Node { char v; // In this code, default positive Integer. Node *child[3]; Node(char x) : v(x){ child[0] = NULL; child[1] = NULL;child[2] = NULL; } } Tree; typedef list<Node*> PATH; /********************************************************/ /***** Basic functions for tree ***********/ Tree* createTree() // input a preOrder sequence, 0 denote empty node. { Node *pRoot = NULL; char r; cin >> r; if(r != '0') // equal to if(!r) return; { pRoot = new Node(r); for(int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) pRoot->child[i] = createTree(); } return pRoot; } void printTree(Tree *root, int level = 1){ if(root == NULL) { cout << "NULL"; return; }; string s; for(int i = 0; i < level; ++i) s += "\t"; printf("%c", root->v); for(int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) { cout << endl << s; printTree(root->child[i], level+1); } } void releaseTree(Tree *root){ if(root == NULL) return; for(int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) releaseTree(root->child[i]); delete[] root; root = NULL; } /******************************************************************/ /**** 获取第一个公共父节点 ******/ bool getPath(Tree *root, Node *node, PATH& path) { if(root == NULL) return false; path.push_back(root); if(root == node) return true; bool found = false; for(int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) { found = getPath(root->child[i], node, path); if(found) break; } if(!found) path.pop_back(); return found; } Node* getLastCommonNode(const PATH &path1, const PATH &path2) // get the last common node of two lists { Node *father = NULL; for(auto it1 = path1.begin(), it2 = path2.begin(); it1 != path1.end() && it2 != path2.end(); ++it1, ++it2) { if(*it1 == *it2) father = *it1; else break; } return father; } Node* getFirstCommonFather(Tree *root, Node *node1, Node *node2) { if(root == NULL || node1 == NULL || node2 == NULL) return NULL; PATH path1, path2; if(getPath(root, node1, path1) && getPath(root, node2, path2)) return getLastCommonNode(path1, path2); return NULL; } /************************************************************************/ int main(){ int TestTime = 3, k = 1; while(k <= TestTime) { cout << "Test " << k++ << ":" << endl; cout << "Create a tree: " << endl; Node *pRoot = createTree(); printTree(pRoot); cout << endl; Node *node1 = pRoot->child[0]->child[0]->child[1]; Node *node2 = pRoot->child[0]->child[2]->child[0]; Node *father; father = getFirstCommonFather(pRoot, node1, node2); cout << "the first common father node: " << father->v << endl; releaseTree(pRoot); } return 0; }