第十六章 下载数据
1.打印第一列的值并且追到到列表中
filename='D:\\weather.csv' with open(filename) as f: reader=csv.reader(f) header_row=next(reader) highs=[] for row in reader: high=int(row[1]) highs.append(high) print(highs)
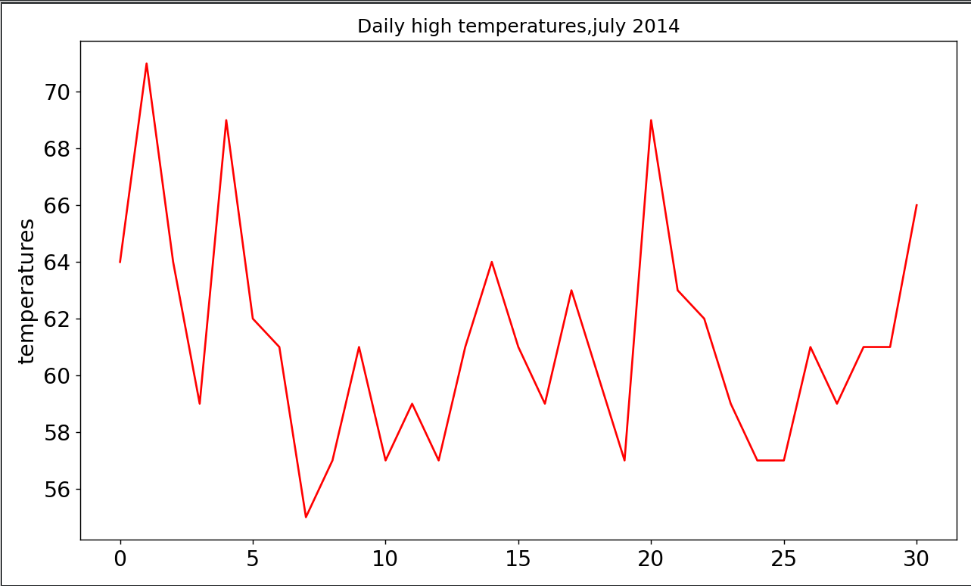
2.绘制高温折线图
import csv import matplotlib.pyplot as plt filename='D:\\weather.csv' with open(filename) as f: reader=csv.reader(f) header_row=next(reader) highs=[] for row in reader: high=int(row[1]) highs.append(high) print(highs) #用数据绘制图形 fig=plt.figure(dpi=128,figsize=(10,6)) #设置颜色 plt.plot(highs,c='red') #设置图形格式 plt.title("Daily high temperatures,july 2014",fontsize=14) plt.xlabel('',fontsize=16) plt.ylabel('temperatures',fontsize=16) plt.tick_params(axis='both',which='major',labelsize=16) plt.show()
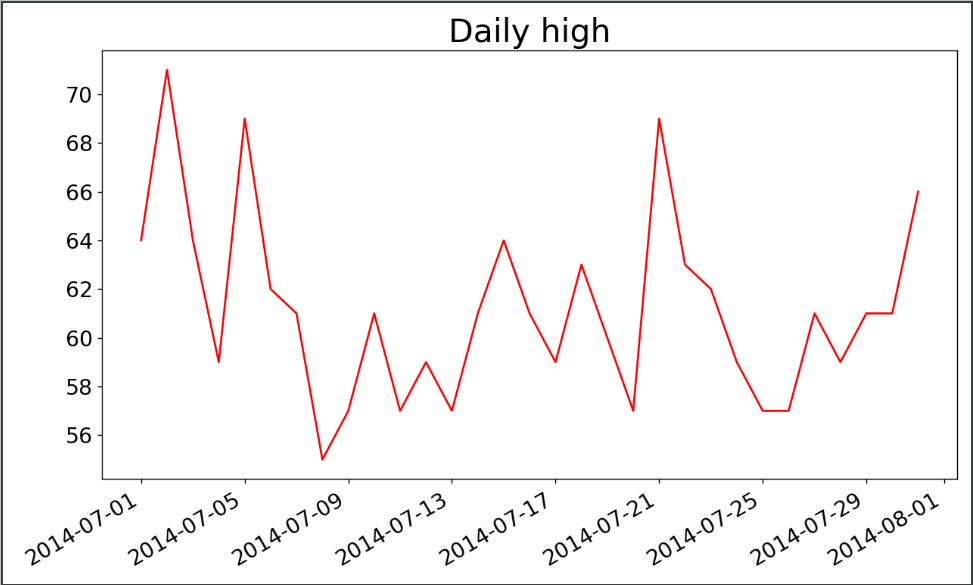
3.加上日期
import csv from datetime import datetime import matplotlib.pyplot as plt filename='D:\\weather.csv' with open(filename) as f: reader=csv.reader(f) header_row=next(reader) dates,highs=[],[] for row in reader: current_Date=datetime.strptime(row[0],"%Y/%m/%d") dates.append(current_Date) high=int(row[1]) highs.append(high) #绘制图形 fig=plt.figure(dpi=128,figsize=(10,6)) plt.plot(dates,highs,c='red') #设置数据绘制图形,设置图形的格式 plt.title("Daily high",fontsize=24) plt.xlabel('',fontsize=16) #绘制斜标签 fig.autofmt_xdate() plt.ylabel('',fontsize=16) plt.tick_params(axis='both',which='major',labelsize=16) plt.show()
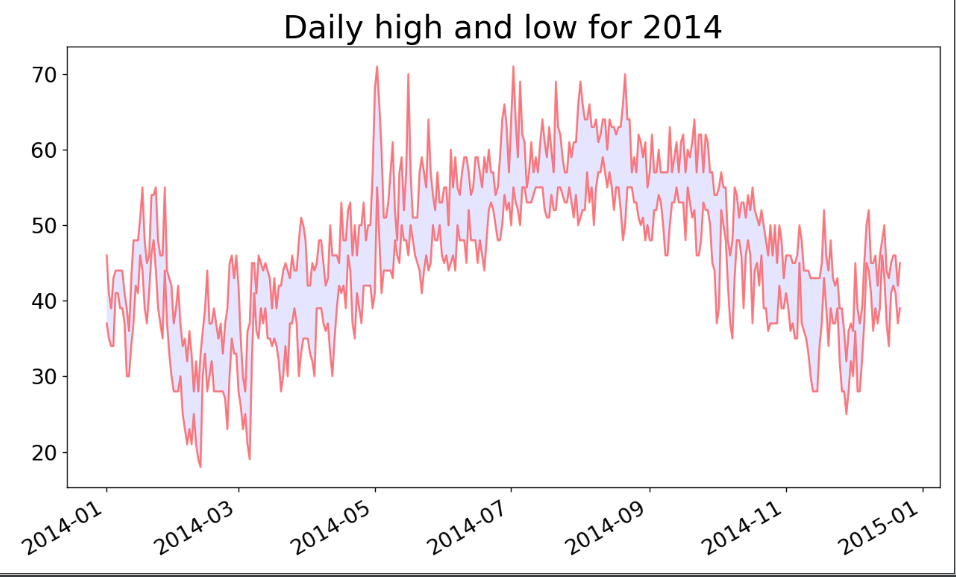
4.添加最低气温
import csv from datetime import datetime import matplotlib.pyplot as plt filename='D:\\weatherTime.csv' with open(filename) as f: reader=csv.reader(f) header_row=next(reader) dates,highs,lows=[],[],[] for row in reader: try: current_Date=datetime.strptime(row[0],"%Y-%m-%d") high=int(row[1]) low=int(row[3]) except ValueError: print("sorry,data not to get") else: dates.append(current_Date) highs.append(high) lows.append(low) #绘制图形,alpha 是颜色的透明度 fig=plt.figure(dpi=128,figsize=(10,6)) plt.plot(dates,highs,c='red',alpha=0.5) plt.plot(dates,lows,c='red',alpha=0.5) plt.fill_between(dates,highs,lows,facecolor='blue',alpha=0.1) #设置数据绘制图形,设置图形的格式 plt.title("Daily high and low for 2014",fontsize=24) plt.xlabel('',fontsize=16) #绘制斜标签 fig.autofmt_xdate() plt.ylabel('',fontsize=16) plt.tick_params(axis='both',which='major',labelsize=16) plt.show()
5 获取json 数据
import json filename='E:\population_data.json' with open(filename) as f: data=json.load(f) for pop_dict in data: if pop_dict['Year'] =='2010': coutry_name=pop_dict['Country Name'] population=int(float(pop_dict['Value'])) print(coutry_name+": "+str(population))
3.获取国别码
import pygal.maps.world def getCountryName(coutry_name): for code,name in pygal.maps.world.COUNTRIES.items(): if name == coutry_name: return code return None if __name__ == '__main__': print(getCountryName("Andorra"))import json
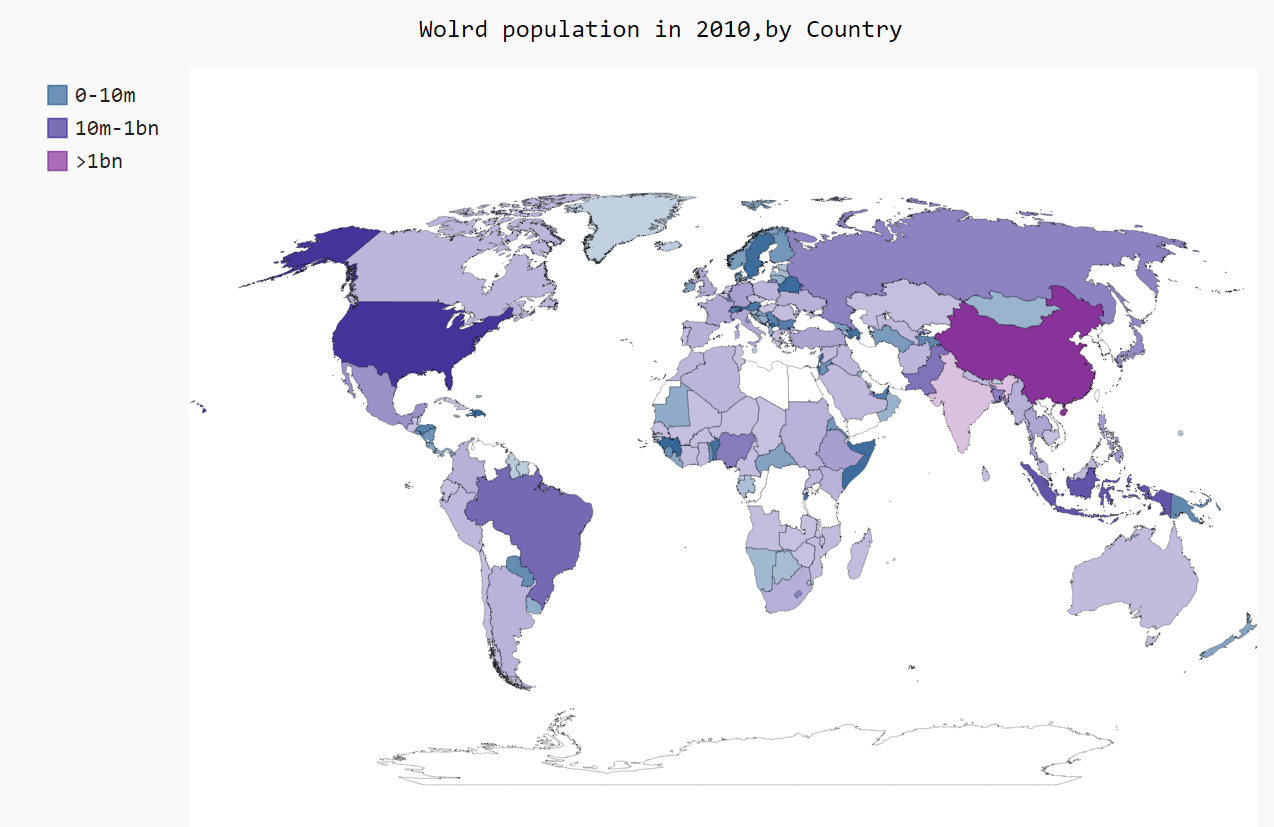
绘制人口地图
import json import pygal from pygal.style import RotateStyle from GetCountryName import getCountryName filename = 'E:\population_data.json' with open(filename) as f: pop_data = json.load(f) cc_populations = {} for pop_dict in pop_data: if pop_dict['Year'] == '2010': country = pop_dict['Country Name'] population = int(float(pop_dict['Value'])) code=getCountryName(country) if code: cc_populations[code]=population #将人口数量的所有国家分成3个组 cc1,cc2,cc3={},{},{} for cc,pop in cc_populations.items(): if pop<10000000: cc1[cc]=pop elif pop<1000000000: cc2[cc]=pop else: cc3[cc]=pop wm_style=RotateStyle('#336699') wm = pygal.maps.world.World(style=wm_style) wm.title='Wolrd population in 2010,by Country' wm.add('0-10m',cc1) wm.add('10m-1bn',cc2) wm.add('>1bn',cc3) wm.render_to_file('world_population.svg')