ConcurrentHashMap代码解析
ConcurrentHashMap (JDK 1.7)的继承关系如下:

1. ConcurrentHashMap是线程安全的hash map。ConcurrentHashMap的数据结构是一个Segment<K, V>数组:
1 2 3 4 | /** * The segments, each of which is a specialized hash table. */final Segment<K,V>[] segments; |
Segment数组segments的每一个元素都包含一个HashEntry<K, V>数组table,这个table类似于HashMap中的table。因此ConcurrentHashMap的存储结构其实是两层,通过两次hash来定位元素所在的链表,图示结构如下:
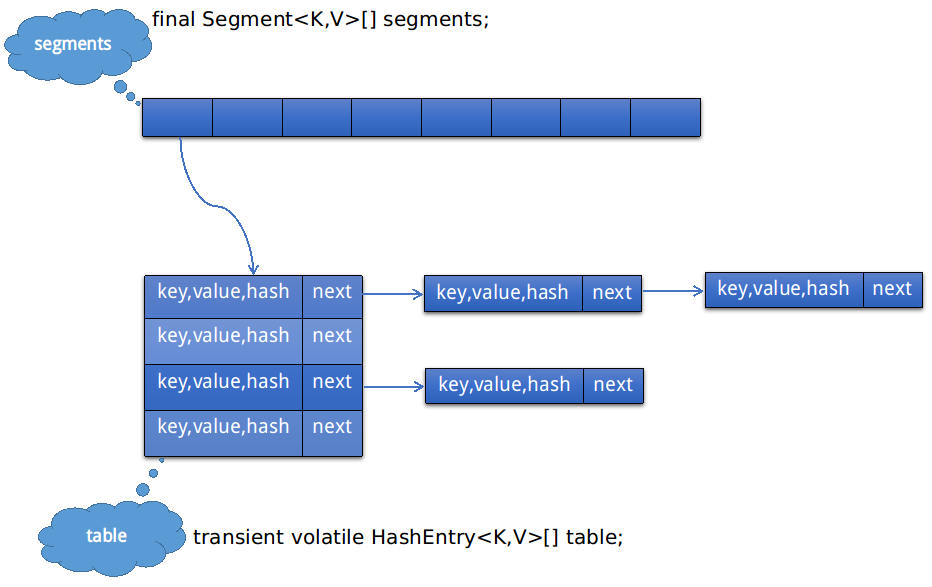
其中,HashEntry的定义如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | /** * ConcurrentHashMap list entry. Note that this is never exported * out as a user-visible Map.Entry. */static final class HashEntry<K,V> { final int hash; final K key; volatile V value; volatile HashEntry<K,V> next;} |
因此,Segment数组的意义就是将一个大的table分割成多个小的table来进行加锁(即,锁分离技术),而每一个Segment元素存储的是HashEntry数组+链表,和HashMap的数据存储结构一样。
2. Segment是静态static final类,
1 | static final class Segment<K,V> extends ReentrantLock implements Serializable {} |
他有自己的成员变量和方法:
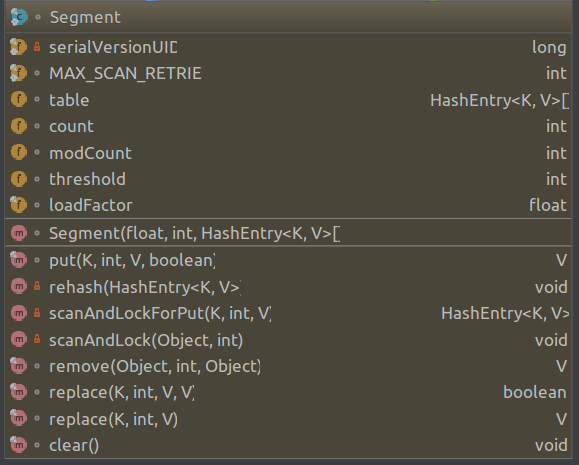
成员变量:
table: 表示每个segment的数组
count: 表示元素个数
modCount: 表示table被修改的次数
threshold: 表示table需要扩容的阈值
loadFactor: 表示table的负载因子,超过负载因子之后table会扩容
方法:
Segment继承了ReentrantLock类,所以他自带锁功能,在其方法中可以体现出来。
a. put()方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 | final V put(K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) { HashEntry<K,V> node = tryLock() ? null : scanAndLockForPut(key, hash, value); V oldValue; try { HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table; int index = (tab.length - 1) & hash;<br> // HashEntry<K,V> first = entryAt(tab, index); for (HashEntry<K,V> e = first;;) { if (e != null) { K k; if ((k = e.key) == key || (e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) { oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent) { e.value = value; ++modCount; } break; } e = e.next; } else { if (node != null) node.setNext(first); else node = new HashEntry<K,V>(hash, key, value, first); int c = count + 1; if (c > threshold && tab.length < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) rehash(node); else setEntryAt(tab, index, node); ++modCount; count = c; oldValue = null; break; } } } finally { unlock(); } return oldValue;} |
b. rehash()方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 | /** * Doubles size of table and repacks entries, also adding the * given node to new table */@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")private void rehash(HashEntry<K,V> node) { /* * Reclassify nodes in each list to new table. Because we * are using power-of-two expansion, the elements from * each bin must either stay at same index, or move with a * power of two offset. We eliminate unnecessary node * creation by catching cases where old nodes can be * reused because their next fields won't change. * Statistically, at the default threshold, only about * one-sixth of them need cloning when a table * doubles. The nodes they replace will be garbage * collectable as soon as they are no longer referenced by * any reader thread that may be in the midst of * concurrently traversing table. Entry accesses use plain * array indexing because they are followed by volatile * table write. */ HashEntry<K,V>[] oldTable = table; int oldCapacity = oldTable.length; int newCapacity = oldCapacity << 1; threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor); HashEntry<K,V>[] newTable = (HashEntry<K,V>[]) new HashEntry[newCapacity]; int sizeMask = newCapacity - 1; for (int i = 0; i < oldCapacity ; i++) { HashEntry<K,V> e = oldTable[i]; if (e != null) { HashEntry<K,V> next = e.next; int idx = e.hash & sizeMask; if (next == null) // Single node on list newTable[idx] = e; else { // Reuse consecutive sequence at same slot HashEntry<K,V> lastRun = e; int lastIdx = idx; for (HashEntry<K,V> last = next; last != null; last = last.next) { int k = last.hash & sizeMask; if (k != lastIdx) { lastIdx = k; lastRun = last; } } newTable[lastIdx] = lastRun; // Clone remaining nodes for (HashEntry<K,V> p = e; p != lastRun; p = p.next) { V v = p.value; int h = p.hash; int k = h & sizeMask; HashEntry<K,V> n = newTable[k]; newTable[k] = new HashEntry<K,V>(h, p.key, v, n); } } } } int nodeIndex = node.hash & sizeMask; // add the new node node.setNext(newTable[nodeIndex]); newTable[nodeIndex] = node; table = newTable;} |
这些都是Segment类自己的方法,不是ConcurrentHashMap()的方法。
3. ConcurrentHashMap同样会有的自己的put() / get() / remove()等方法,是在Segment类的方法上实现的。
ConcurrentHashMap默认构造函数为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | /** * Creates a new, empty map with a default initial capacity (16), * load factor (0.75) and concurrencyLevel (16). */public ConcurrentHashMap() { this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR, DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL);} |
this有3个参数:
a. DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY,表示table的默认大小
1 2 3 4 5 | /** * The default initial capacity for this table, * used when not otherwise specified in a constructor. */static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16; |
b. DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR,表示table的负载因子
1 2 3 4 5 | /** * The default load factor for this table, used when not * otherwise specified in a constructor. */static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; |
c. DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL,表示table默认的并发度,也就是segments数组的大小!!
1 2 3 4 5 | /** * The default concurrency level for this table, used when not * otherwise specified in a constructor. */static final int DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL = 16; |
this调用了:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 | /** * Creates a new, empty map with the specified initial * capacity, load factor and concurrency level. * * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity. The implementation * performs internal sizing to accommodate this many elements. * @param loadFactor the load factor threshold, used to control resizing. * Resizing may be performed when the average number of elements per * bin exceeds this threshold. * @param concurrencyLevel the estimated number of concurrently * updating threads. The implementation performs internal sizing * to try to accommodate this many threads. * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is * negative or the load factor or concurrencyLevel are * nonpositive. */@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) { if (!(loadFactor > 0) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); if (concurrencyLevel > MAX_SEGMENTS) concurrencyLevel = MAX_SEGMENTS; // Find power-of-two sizes best matching arguments、 // 寻找大于等于concurrencyLevel的一个整数ssize,这个整数是2的倍数,默认值应该是16 int sshift = 0; int ssize = 1; while (ssize < concurrencyLevel) { ++sshift; ssize <<= 1; } this.segmentShift = 32 - sshift; this.segmentMask = ssize - 1; // initialCapacity的默认是是table数组的大小(默认为16) if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; // c默认值是16 / 16 = 1 int c = initialCapacity / ssize; if (c * ssize < initialCapacity) ++c; // MIN_SEGMENT_TABLE_CAPACITY表示每个segment中table的最小容量(默认为2) int cap = MIN_SEGMENT_TABLE_CAPACITY; while (cap < c) cap <<= 1; // create segments and segments[0] Segment<K,V> s0 = new Segment<K,V>(loadFactor, (int)(cap * loadFactor), (HashEntry<K,V>[])new HashEntry[cap]); Segment<K,V>[] ss = (Segment<K,V>[])new Segment[ssize]; UNSAFE.putOrderedObject(ss, SBASE, s0); // ordered write of segments[0] this.segments = ss;} |
ConcurrentHashMap的put()方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | /** * Maps the specified key to the specified value in this table. * Neither the key nor the value can be null. * * <p> The value can be retrieved by calling the <tt>get</tt> method * with a key that is equal to the original key. * * @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated * @param value value to be associated with the specified key * @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or * <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt> * @throws NullPointerException if the specified key or value is null */@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public V put(K key, V value) { Segment<K,V> s; if (value == null) throw new NullPointerException(); // 此处的hash()方法是属于ConcurrentHashMap类,Segment的put()方法使用的hash方式是(table.length - 1) & hash,这个hash值是调用的ConcurrentHashMap的hash()方法产生的 int hash = hash(key); // j表示segment的索引 int j = (hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask; if ((s = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObject // nonvolatile; recheck (segments, (j << SSHIFT) + SBASE)) == null) // in ensureSegment // 获取第j个segment s = ensureSegment(j); // 这里的put()方法是Segment的方法 return s.put(key, hash, value, false);} |
get()方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | /** * Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, * or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key. * * <p>More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key * {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code key.equals(k)}, * then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise it returns * {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.) * * @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null */public V get(Object key) { Segment<K,V> s; // manually integrate access methods to reduce overhead HashEntry<K,V>[] tab; int h = hash(key); long u = (((h >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask) << SSHIFT) + SBASE; if ((s = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(segments, u)) != null && (tab = s.table) != null) { for (HashEntry<K,V> e = (HashEntry<K,V>) UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile (tab, ((long)(((tab.length - 1) & h)) << TSHIFT) + TBASE); e != null; e = e.next) { K k; if ((k = e.key) == key || (e.hash == h && key.equals(k))) return e.value; } } return null;} |
remove()方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | /** * Removes the key (and its corresponding value) from this map. * This method does nothing if the key is not in the map. * * @param key the key that needs to be removed * @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or * <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt> * @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null */public V remove(Object key) { int hash = hash(key); Segment<K,V> s = segmentForHash(hash); return s == null ? null : s.remove(key, hash, null);} |
segmentForHash()方法,通过hash值获取相应segment
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | /** * Get the segment for the given hash */@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")private Segment<K,V> segmentForHash(int h) { long u = (((h >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask) << SSHIFT) + SBASE; return (Segment<K,V>) UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(segments, u);} |






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 字符编码:从基础到乱码解决
2015-04-12 Git学习笔记五--分支管理
2015-04-12 Git库搭建好之后,当要提交一个新的文件,需要做的是3个步骤