k-均值算法‘手写识别系统’和‘改进约会网站的配对效果’(Python) 出处:机器学习实战
Python 代码:
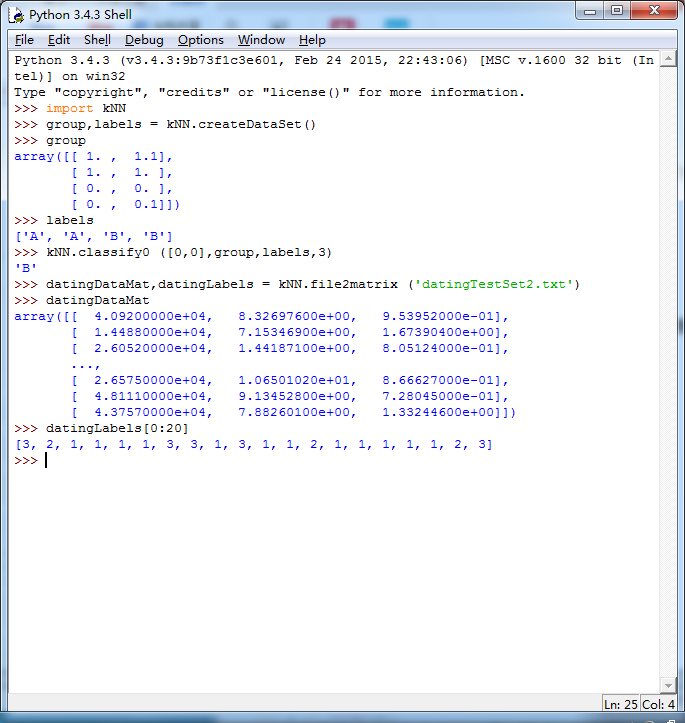
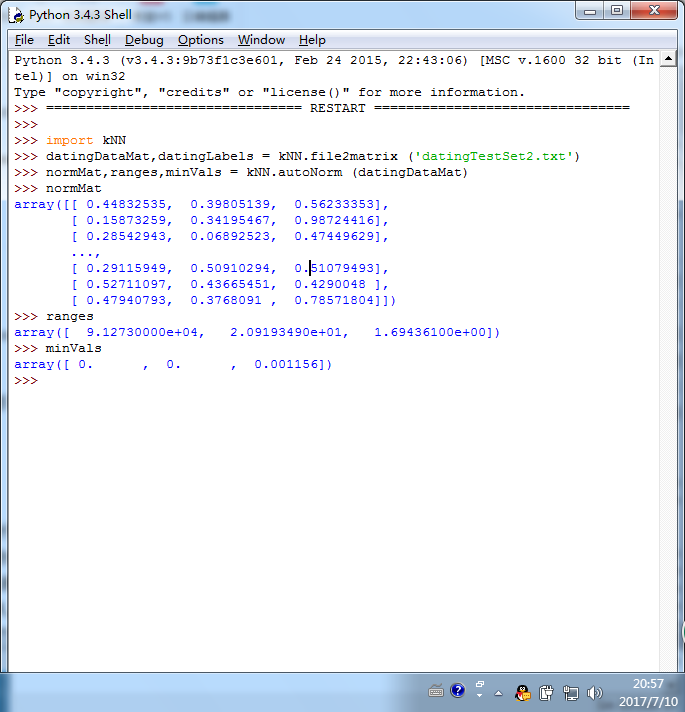
1 #准备:使用Python导入数据 2 3 from os import listdir #从os模块中导入函数listdir,可以列出给定目录的文件名 4 from numpy import * 5 import operator #运算符module 6 7 def createDataSet(): 8 group = array([[1.0,1.1],[1.0,1.0],[0,0],[0,0.1]]) #数据集 9 labels = ['A','A','B','B'] #标签 10 return group,labels 11 12 13 #从文本文件中解析数据 14 #k-近邻算法 15 16 def classify0(inX,dataSet,labels,k): 17 #inX:用于分类的输入变量,dataSet:输入的训练样本集,labels:标签向量,k:表示用于选择最近邻居的数目 18 #其中标签向量的元素数目和矩阵dataSet的行数相同 19 dataSetSize = dataSet.shape[0] 20 21 #距离计算:欧式距离公式,计算两个向量点A与B之间的距离 22 # ((A0 - B0) ** 2+(A1 - B1) ** 2) ** 0.5 23 diffMat = tile(inX,(dataSetSize,1)) - dataSet 24 sqDiffMat = diffMat ** 2 25 sqDistances = sqDiffMat.sum(axis=1) 26 distances = sqDistances ** 0.5 27 28 #按照距离递增次序排序 29 sortedDistIndicies = distances.argsort() 30 31 classCount = {} 32 33 #选择距离最小的k个点 34 for i in range(k): 35 voteIlabel = labels[sortedDistIndicies[i]] 36 classCount[voteIlabel] = classCount.get(voteIlabel,0) + 1 #get()函数返回指定键的值,如果值不在字典中返回默认值 37 38 #itemgetter函数用于获取对象哪些维的数据,参数为序号。然后进行排序,按从大到小排序,最后返回发生频率最高的元素标签 39 sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.items(),key = operator.itemgetter(1),reverse = True) 40 return sortedClassCount[0][0] 41 42 #准备数据:从文本文件中解析数据 43 #datingTestSet.txt 44 #数据特征:每年飞行里程数,玩视频游戏所耗时间百分比,每周的冰淇淋公升数 45 #标签向量:largeDoses、smallDoses、didntLike 46 #创建file2matrix函数,输入为文件名字符串,输出为训练样本矩阵和标签向量 47 48 def file2matrix(filename): 49 50 #得到文件行数 51 fr = open(filename) 52 arrayOLines = fr.readlines() 53 #获得长度 54 numberOfLines = len(arrayOLines) 55 56 #创建返回的Numpy矩阵,用零填充 57 returnMat = zeros((numberOfLines,3)) #zeros()函数创建矩阵,参数为(行数,列数) 58 classLabelVector = [] 59 index = 0 60 61 #解析文件数据到列表 62 for line in arrayOLines: 63 line = line.strip() #strip()函数截取所有的回车字符 64 listFromLine = line.split('\t') #tab字符将上一步得到的整行数据分割成一个元素列表 65 returnMat[index,:] = listFromLine[0:3] #选取前3个元素存储到特征矩阵中 66 classLabelVector.append(int(listFromLine[-1])) #索引值-1表示列表中的最后一列元素 67 index += 1 68 return returnMat,classLabelVector 69 70 71 #分析数据:使用Matplotlib创建散点图 72 73 import matplotlib 74 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 75 #datingDataMat,datingLabels = kNN.file2matrix ('datingTestSet2.txt') 76 #fig = plt.figure() 77 #ax = fig.add_subplot(111) 111的意思是将画布分割成1行1列,第1块 78 #ax.scatter(datingDataMat[:,0],datingDataMat[:,2],15.0 * array(datingLabels),15.0 * array(datingLabels)) 79 #plt.show() 80 81 82 #归一化特征值 83 84 def autoNorm(dataSet): 85 minVals = dataSet.min(0) #得到给定数据集当前列特征最小值 86 maxVals = dataSet.max(0) 87 ranges = maxVals - minVals 88 normDataSet = zeros(shape(dataSet)) 89 m = dataSet.shape[0] 90 91 #使用tile()函数将变量内容复制成输入矩阵同样大小的矩阵 92 normDataSet = dataSet - tile(minVals,(m,1)) 93 94 #特征值相除 95 normDataSet = normDataSet/tile(ranges,(m,1)) 96 return normDataSet,ranges,minVals 97 98 #分类器针对约会网站的测试代码 99 100 def datingClassTest(): 101 hoRatio = 0.01 #hold out 10% 102 datingDataMat,datingLabels = file2matrix('datingTestSet2.txt') #load data setfrom file 103 normMat, ranges, minVals = autoNorm(datingDataMat) 104 m = normMat.shape[0] 105 numTestVecs = int(m*hoRatio) 106 errorCount = 0.0 107 for i in range(numTestVecs): 108 classifierResult = classify0(normMat[i,:],normMat[numTestVecs:m,:],datingLabels[numTestVecs:m],3) 109 print ("the classifier came back with: %d, the real answer is: %d" % (classifierResult, datingLabels[i])) 110 if (classifierResult != datingLabels[i]): errorCount += 1.0 111 print ("the total error rate is: %f" % (errorCount/float(numTestVecs))) 112 print (errorCount) 113 114 115 116 #约会网站预测函数:输入信息,进行预测 117 def classifyPerson(): 118 resultList = ['not at all','in small doses','in large doses'] 119 120 percentTats = float(input('percentage of time spent playing video games?')) 121 ffMiles = float(input('frequent flier miles eraned per year?')) 122 iceCream = float(input('liters of ice cream consumed per year?')) 123 124 datingDataMat,datingLabels = file2matrix('datingTestSet2.txt') 125 normMat,ranges,minVals = autoNorm(datingDataMat) 126 inArr = array([ffMiles,percentTats,iceCream]) 127 classifierResult = classify0((inArr-minVals)/ranges,normMat,datingLabels,3) 128 print('You will probable like this person:',resultList[classifierResult - 1]) 129 130 131 132 133 134 #手写识别系统 135 #准备数据:将图像转换为测试向量(图像格式化处理为一个向量) 136 #将32*32的图像矩阵转换为1*1024的向量 137 138 #创建1*1024的Numpy数组,打开给定的文件,循环读出文件的前32行,并将每行的头32个字符值存储在NUmpy数组中,最后返回数组 139 def img2vector(filename): 140 returnVect = zeros((1,1024)) 141 fr = open(filename) 142 for i in range(32): 143 lineStr = fr.readline() 144 for j in range(32): 145 returnVect[0,32 * i + j] = int(lineStr[j]) 146 return returnVect 147 #testVector[0,0:31] 为第一行数据 148 149 #测试算法:使用k-近邻算法识别手写数字 150 151 def handwritingClassTest(): 152 153 #获取文件目录 154 hwLabels = [] 155 trainingFileList = listdir('digits/trainingDigits') 156 157 m = len(trainingFileList) 158 trainingMat = zeros((m,1024)) #该矩阵每行数据存储一个图像 159 for i in range(m): 160 #从文件名解析分类数据 161 fileNameStr = trainingFileList[i] 162 fileStr = fileNameStr.split('.')[0] 163 classNumStr = int(fileStr.split('_')[0]) 164 165 hwLabels.append(classNumStr) 166 trainingMat[i,:] = img2vector('digits/trainingDigits/%s' % fileNameStr) 167 testFileList = listdir('digits/testDigits') 168 errorCount = 0.0 169 mTest = len(testFileList) 170 for i in range(mTest): 171 fileNameStr = testFileList[i] 172 fileStr = fileNameStr.split('.')[0] 173 classNumStr = int(fileStr.split('_')[0]) 174 vectorUnderTest = img2vector('digits/testDigits/%s' % fileNameStr) 175 classifierResult = classify0(vectorUnderTest,trainingMat,hwLabels,3) 176 print('the classifier came back with: %d, the real answer is: %d' % (classifierResult,classNumStr)) 177 if (classifierResult != classNumStr): 178 errorCount += 1.0 179 print('\nthe total number of errors is: %d' % errorCount) 180 print('\nthe total error rate is: %f' % (errorCount/float(mTest))) 181
运行效果

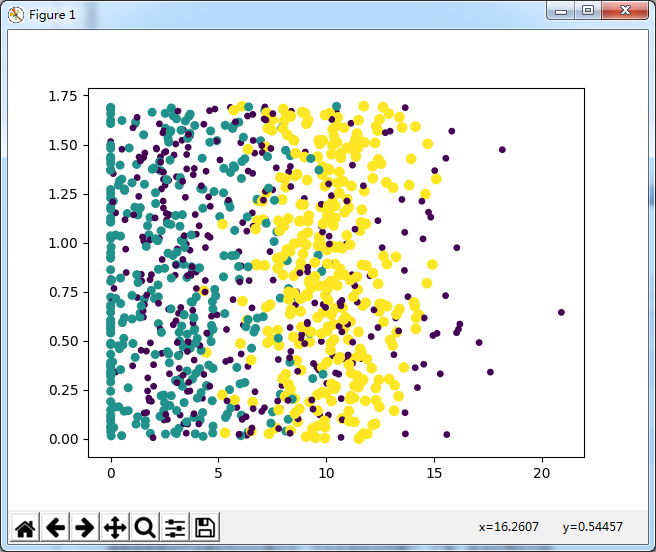
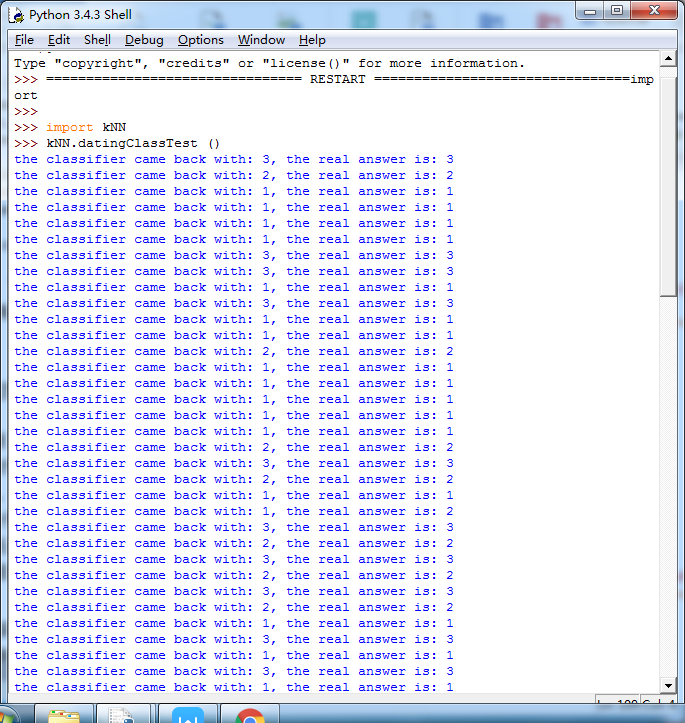
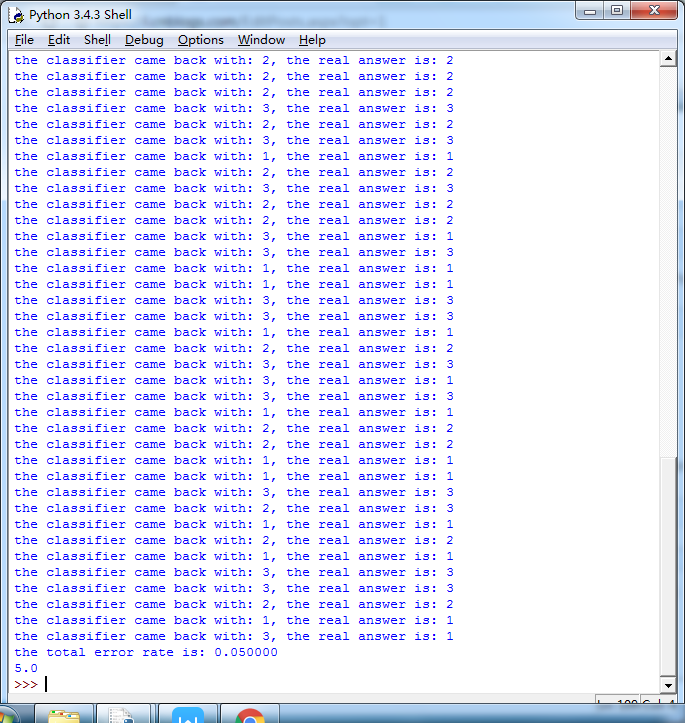
约会配对的效率还不错,达到了5%。
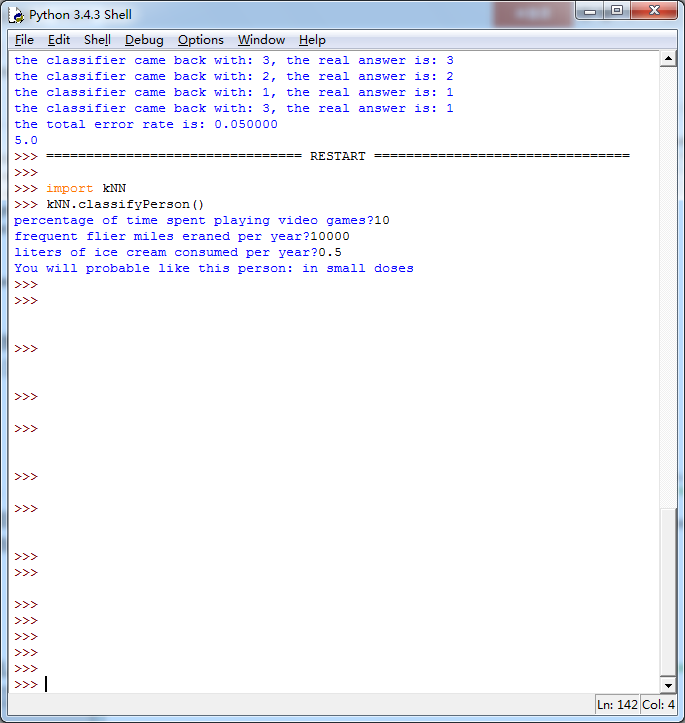
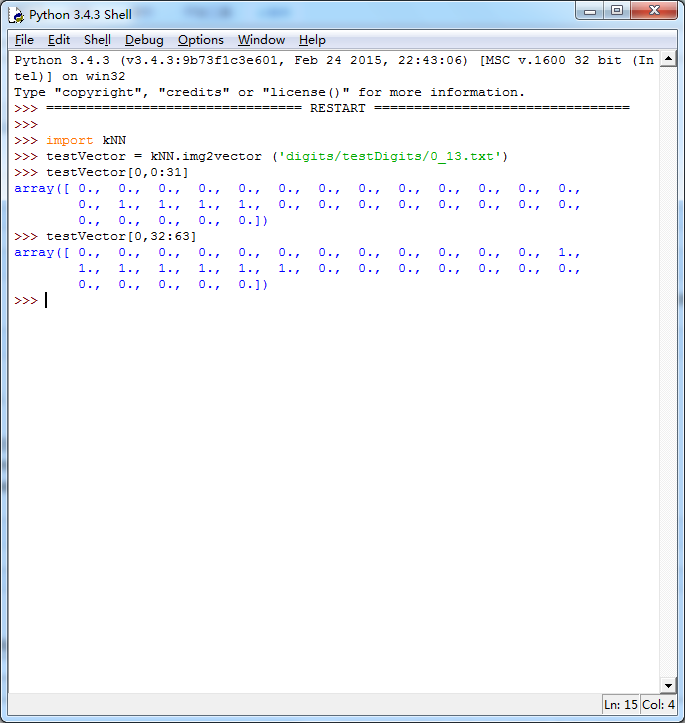
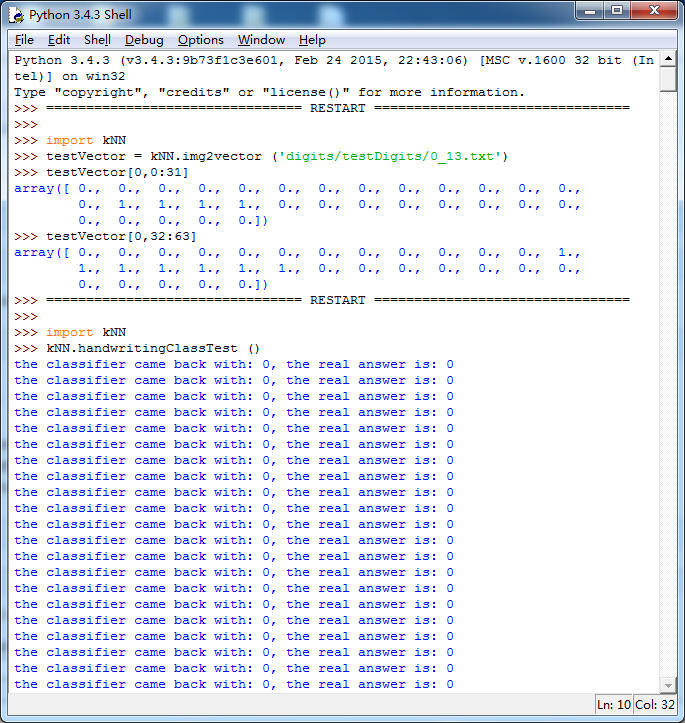
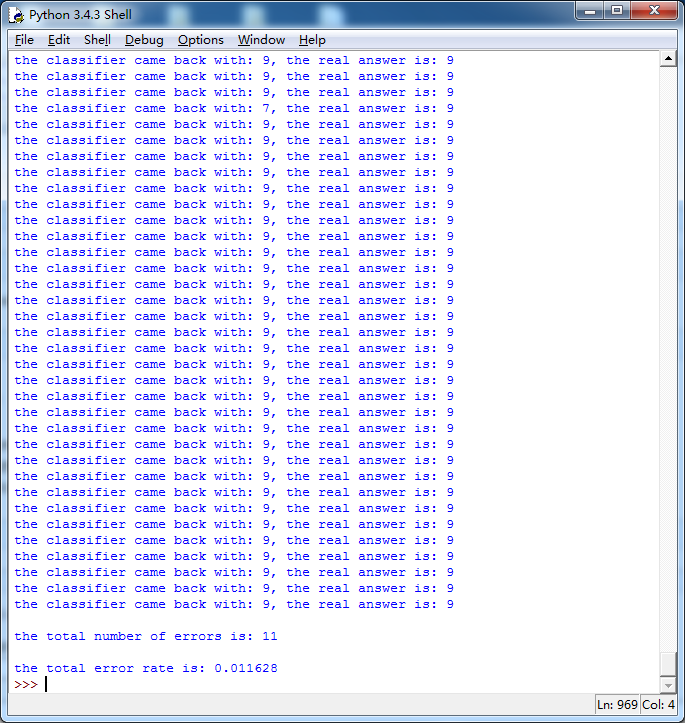
这个算法效率并不高,最后一张图2000次距离计算,900次1024个维度浮点计算,等了我好长时间,但效果还不错,字体识别成功率为1.1628%,这个成功率很牛逼了。
约会配对和字体识别数据百度网盘见。。。。。
链接:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1slqa85f 密码:dcr8
很想高飞,但我不能;不想天空,剩我一人。




