16 反射
16 反射
16.1 通过案例体会反射的好处
案例:美团外卖 -》 付款
package com.liweixiao.test01;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/21
* @description:接口的制定方,美团外卖
*/
public interface Mtwm {
void payOnline();
}
package com.liweixiao.test01;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/21
* @description:
*/
public class WeChat implements Mtwm{
@Override
public void payOnline() {
//具体实现微信支付功能
System.out.println("我点了外卖,在使用微信支付");
}
}
package com.liweixiao.test01;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/21
* @description:
*/
public class Alipay implements Mtwm{
@Override
public void payOnline() {
//具体实现支付宝支付
System.out.println("我已经点了外卖,正在使用支付宝付款");
}
}
package com.liweixiao.test01;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/21
* @description:
*/
public class BankCard implements Mtwm{
@Override
public void payOnline() {
System.out.println("我已经点了外卖,使用银行卡付款");
}
}
测试类
package com.liweixiao.test01;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/21
* @description:
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义一个字符串,用来模拟前台的支付方式
String str="招商银行";
if ("微信".equals(str)){//str.equals,容易空指针异常
//微信支付
//new WeChat().payOnline();
pay(new WeChat());
}
if("支付宝".equals(str)){
//支付宝支付
//new Alipay().payOnline();
pay(new Alipay());
}
if("招商银行".equals(str)){
pay(new BankCard());
}
}
//微信支付
public static void pay(WeChat wc){
wc.payOnline();
}
//支付宝支付
public static void pay(Alipay ap){
ap.payOnline();
}
//招商银行卡支付
public static void pay(BankCard bc){
bc.payOnline();
}
}
多态
package com.liweixiao.test01;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/21
* @description:
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义一个字符串,用来模拟前台的支付方式
String str="支付宝";
if ("微信".equals(str)){//str.equals,容易空指针异常
pay(new WeChat());
}
if("支付宝".equals(str)){
pay(new Alipay());
}
if("招商银行".equals(str)){
pay(new BankCard());
}
}
//形参是接口,具体传入接口实现类的对象,多态的一种形式
public static void pay(Mtwm mt){
mt.payOnline();
}
}
多态确实可以提高代码的扩展性,但是:扩展性没有达到最好。
怎么没有达到最好:上面的分支,还是需要手动的删除或者添加。
解决办法:反射机制。
package com.liweixiao.test01;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/22
* @description:
*/
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//定义一个字符串,用来模拟前台的支付方式
String str="com.liweixiao.test01.Alipay";//全路径
//利用反射
Class cls = Class.forName(str);
Object o = cls.newInstance();
Method method = cls.getMethod("payOnline");
method.invoke(o);
}
}
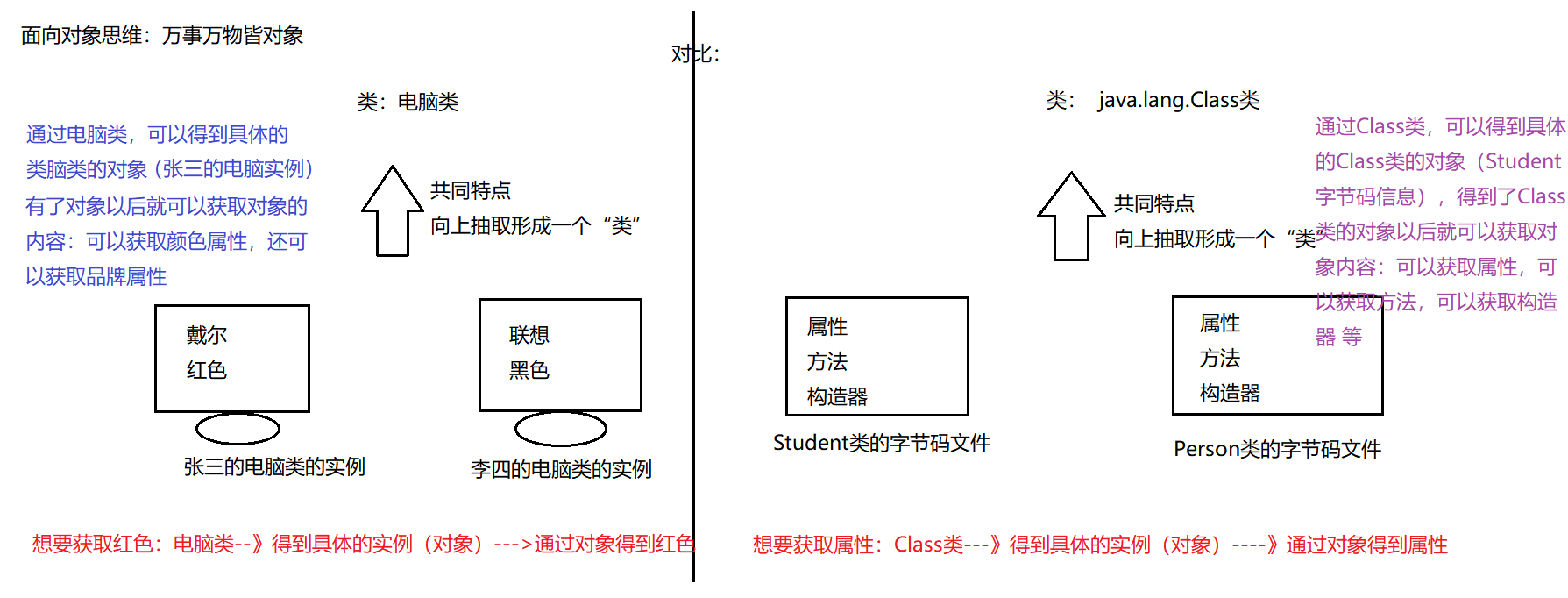
16.2 通过概念再体会反射
JAVA反射机制是在运行状态中,对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法;对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意方法和属性;这种动态获取信息以及动态调用对象方法的功能称为java语言的反射机制。
在编译后产生字节码文件的时候,类加载器子系统通过二进制字节流,负责从文件系统加载class文件。
在执行程序(java.exe)时候,将字节码文件读入JVM中--->这个过程叫做类的加载。然后在内存中对应创建一个java.lang.Class对象-->这个对象会被放入字节码信息中,这个Class对象,就对应加载那个字节码信息,这个对象将被作为程序访问方法区中的这个类的各种数据的外部接口。
所以:我们可以通过这个对象看到类的结构,这个对象就好像是一面镜子,透过镜子看到类的各种信息,我们形象的称之为反射
这种“看透”class的能力(the ability of the program to examine itself)被称为introspection(内省、内观、反省)。Reflection和introspection是常被并提的两个术语。
说明:在运行期间,如果我们要产生某个类的对象,Java虚拟机(JVM)会检查该类型的Class对象是否已被加载。
如果没有被加载,JVM会根据类的名称找到.class文件并加载它。一旦某个类型的Class对象已被加载到内存,就可以用它来产生该类型的所有对象。
补充:
动态语言vs静态语言
1、动态语言
是一类在运行时可以改变其结构的语言:例如新的函数、对象、甚至代码可以
被引进,已有的函数可以被删除或是其他结构上的变化。通俗点说就是在运
行时代码可以根据某些条件改变自身结构。
主要动态语言: Object-C、 C#、JavaScript、 PHP、 Python、 Erlang 。
2、静态语言
与动态语言相对应的,运行时结构不可变的语言就是静态语言。如Java、C、C++。
所以Java不是动态语言,但Java可以称之为“准动态语言”。即Java有一定的动态性,我们可以利用反射机制、字节码操作获得类似动态语言的特性。
Java的动态性让编程的时候更加灵活!
16.3 Class类的理解
以上图片来自网络
16.4 提供丰富的类
package com.liweixiao.test02;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/22
* @description:
*/
public class Person {
//属性
private int age;//年龄
public String name;//姓名
//方法
private void eat(){
System.out.println("Person---eat");
}
public void sleep(){
System.out.println("Person---sleep");
}
}
package com.liweixiao.test02;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/22
* @description:
*/
public class Student extends Person{
//属性
private int sno;//学号
double height;//身高
protected double weight;//体重
public double score;//成绩
//方法
public String showInfo(){
return "我是一名三好学生";
}
private void work(){
System.out.println("我以后会找工作");
}
//构造器
public Student(){
System.out.println("空参构造器");
}
private Student(int sno){
this.sno=sno;
}
Student(int sno,double weight){
this.sno=sno;
this.weight=weight;
}
}
16.5 获取字节码信息的四种形式
package com.liweixiao.test02;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/22
* @description:
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//案例:以Person的字节码信息为案例
//方式1:通过getClass()方法获取
Person p = new Person();
Class c1 = p.getClass();
System.out.println("c1:"+c1);
//方式2:通过内置class属性
Class c2 = Person.class;
System.out.println("c2:"+c2);
System.out.println("c1==c2:"+(c1 == c2));
//注意:方式1和方式2 不常用
//方式3,用的最多,调用Class类提供的静态方法forName
Class c3 = Class.forName("com.liweixiao.test02.Person");
System.out.println("c3:"+c3);
//方式4:利用类的加载器(了解技能点)
ClassLoader loader = Test.class.getClassLoader();
Class c4 = loader.loadClass("com.liweixiao.test02.Person");
System.out.println("c4:"+c4);
}
}
16.6 可以作为Class类的实例的种类
Class类的具体的实例:
(1)类:外部类,内部类
(2)接口
(3)注解
(4)数组
(5)基本数据类型
(6)void
package com.liweixiao.test02;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/22
* @description:
*/
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
Class类的具体的实例:
(1)类:外部类,内部类
(2)接口
(3)注解
(4)数组
(5)基本数据类型
(6)void
*/
Class c1 = Person.class;//类
System.out.println(c1);//class com.liweixiao.test02.Person
Class c2 = Comparable.class;//接口
System.out.println(c2);//interface java.lang.Comparable
Class c3 = Override.class;//注解
System.out.println(c2);//interface java.lang.Comparable
int[] arr1={1,2,3};//数组
Class c4 = arr1.getClass();
System.out.println(c4);//class [I
int[] arr2={5,6,7};
Class c5 = arr2.getClass();//class [I
System.out.println(c4 == c5);//true,同一个维度,同一个元素类型,得到的字节码就是同一个
int[][] arr3={};
Class c50 = arr3.getClass();
System.out.println(c50);//class [[I
System.out.println(c5 == c50);//false
Class c6 = int.class;//基本数据类型
System.out.println(c6);//int
Class c7 = void.class;//void
System.out.println(c7);//void
}
}
16.7 获取运行时类的完整结构
16.7.1 补充完善上面提供的丰富的类
package com.liweixiao.test03;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/22
* @description:自定义的接口
*/
public interface MyInterface {
//随便定义一个抽象方法
void myMethod();
}
package com.liweixiao.test03;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType.*;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.*;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/22
* @description:
* @Target,定义当前注解能够修饰程序中哪些元素
* @Retetion,定义注解的声明周期
*/
@Target({TYPE, FIELD, METHOD, PARAMETER, CONSTRUCTOR, LOCAL_VARIABLE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyAnnotation {
String value();//属性
}
package com.liweixiao.test03;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/22
* @description:
*/
public class Person implements Serializable {
//属性
private int age;//年龄
public String name;//姓名
//方法
private void eat(){
System.out.println("Person---eat");
}
public void sleep(){
System.out.println("Person---sleep");
}
}
package com.liweixiao.test03;
import com.liweixiao.test02.Person;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/22
* @description:
*/
@MyAnnotation(value = "hello")
public class Student extends Person implements MyInterface{
//属性
private int sno;//学号
double height;//身高
protected double weight;//体重
public double score;//成绩
//方法
@MyAnnotation(value = "hiMethod")
public String showInfo(){
return "我是一名三好学生";
}
//重载方法
public String showInfo(int a,int b){
return "重载方法:我是一名三好学生";
}
private void work(){
System.out.println("我以后会找工作");
}
void happy(){
System.out.println("开心每一天");
}
protected int getSno(){
return sno;
}
//构造器
public Student(){
System.out.println("空参构造器");
}
public Student(double weight,double height){
this.weight=weight;
this.height=height;
}
private Student(int sno){
this.sno=sno;
}
Student(int sno, double weight){
this.sno=sno;
this.weight=weight;
}
protected Student(int sno,double weight,double height){
this.sno=sno;
}
@Override
@MyAnnotation(value = "helloMyMethod")
public void myMethod()throws RuntimeException {
System.out.println("我重写了myMethod方法");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"sno=" + sno +
", height=" + height +
", weight=" + weight +
", score=" + score +
'}';
}
}
16.7.2 获取构造器和创建对象
package com.liweixiao.test03;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/23
* @description:
*/
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
//获取字节码信息
Class cls = Student.class;
//通过字节码信息,获取构造器
//getConstructors只能获取运行时类的public修饰的构造器
Constructor[] c1 = cls.getConstructors();
for (Constructor c: c1) {
System.out.println(c);
}
System.out.println("------------");
//getDeclaredConstructors获取运行时类的全部修饰符的构造器
Constructor[] c2 = cls.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor c:c2) {
System.out.println(c);
}
System.out.println("------------");
//获取指定的构造器
//getConstructor得到空构造器,public修饰的构造器
Constructor con1 = cls.getConstructor();
System.out.println(con1);
System.out.println("------------");
//得到两个参数的有参构造器,public修饰的构造器
Constructor con2 = cls.getConstructor(double.class, double.class);
System.out.println(con2);
System.out.println("------------");
////得到有参构造器,全部修饰符的构造器
Constructor con3 = cls.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class);
System.out.println(con3);
System.out.println("------------");
//有了构造器,就可以创建对象
Object o1 = con1.newInstance();
System.out.println(o1);
Object o2 = con2.newInstance(140.5, 170.6);
System.out.println(o2);
}
}
16.7.3 获取属性和对象进行赋值
package com.liweixiao.test03;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/23
* @description:
*/
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
//Class cls0 = Student.class;
Class cls = Class.forName("com.liweixiao.test03.Student");
//获取属性
//getFields获取运行时类和父类的被public修饰的属性
Field[] fields = cls.getFields();
for (Field f:fields) {
System.out.println(f);
}
System.out.println("---------------");
//getDeclaredFields获取运行时类全部修饰的属性
Field[] df = cls.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field f:df) {
System.out.println(f);
}
System.out.println("---------------");
//获取指定的属性,public修饰的
Field score = cls.getField("score");
System.out.println(score);
//获取指定的属性,全部修饰的
Field sno = cls.getDeclaredField("sno");
System.out.println(sno);
System.out.println("---------------");
//属性的具体结构
//获取修饰符
int modifiers = sno.getModifiers();
System.out.println(modifiers);//2
System.out.println(Modifier.toString(modifiers));//private
//获取属性的数据结构
Class clazz = sno.getType();
System.out.println(clazz);//int
//获取属性的名字
String name = sno.getName();
System.out.println(name);//sno
System.out.println("---------------");
//给属性赋值
Field sco = cls.getField("score");
Object obj = cls.newInstance();//空参构造器
System.out.println(obj);//Student{sno=0, height=0.0, weight=0.0, score=0.0}
sco.setInt(obj,98);
System.out.println(obj);//Student{sno=0, height=0.0, weight=0.0, score=98.0}
}
}
16.7.4 获取方法和调用方法
package com.liweixiao.test03;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
import java.lang.reflect.Parameter;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/23
* @description:
*/
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {
//获取字节码信息
Class cls = Student.class;
//获取方法
//getMethods获取运行时类的和所有父类的方法,被public修饰
Method[] m1 = cls.getMethods();
for (Method m: m1) {
System.out.println(m);
}
System.out.println("--------------");
//getDeclaredMethods获取运行时类的所有方法
Method[] m2 = cls.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method m:m2) {
System.out.println(m);
}
System.out.println("--------------");
//获取指定方法,被public修饰的
Method showInfo1 = cls.getMethod("showInfo", int.class, int.class);
System.out.println(showInfo1);
Method showInfo2 = cls.getMethod("showInfo");
System.out.println(showInfo2);
System.out.println("--------------");
//获取指定方法,全部的
Method work = cls.getDeclaredMethod("work");
System.out.println(work);
Method getSno = cls.getDeclaredMethod("getSno");
System.out.println(getSno);
System.out.println("--------------");
//获取方法具体的结构
//方法名
System.out.println(work.getName());
//方法修饰符
int modifiers = work.getModifiers();
System.out.println(Modifier.toString(modifiers));
//返回值类型
Class type = showInfo1.getReturnType();
System.out.println(type);
//参数列表
Parameter[] parameters = showInfo1.getParameters();
for (Parameter p:parameters) {
System.out.println(p);
}
//注解
//没有获取到@Override,因为生命周期在编译期,不在运行期
Method myMethod = cls.getMethod("myMethod");
Annotation[] annotations = myMethod.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation a:annotations) {
System.out.println(a);
}
//获取异常throws
Class[] exceptionTypes = myMethod.getExceptionTypes();
for (Class c:exceptionTypes) {
System.out.println(c);
}
System.out.println("--------------");
//调用方法
Object o = cls.newInstance();
myMethod.invoke(o);
System.out.println(showInfo1.invoke(o, 12, 45));
}
}
16.7.5 获取类的接口,所在包,注解
package com.liweixiao.test03;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/23
* @description:
*/
public class Test04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取字节码信息:
Class cls = Student.class;
//获取运行时类的接口
Class[] interfaces = cls.getInterfaces();
for (Class c :
interfaces) {
System.out.println(c);
}
//获取父类的接口,先得到父类的字节码信息
Class superclass = cls.getSuperclass();
Class[] interfaces1 = superclass.getInterfaces();
for (Class c :
interfaces1) {
System.out.println(c);
}
//获取运行时类所在的包
Package aPackage = cls.getPackage();
System.out.println(aPackage);
System.out.println(aPackage.getName());
//获取运行时类的注解
Annotation[] annotations = cls.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation a :
annotations) {
System.out.println(a);
}
}
}
16.7.6 关于反射的面试题
【1】问题1:创建Person的对象,以后用new Person() 还是 反射创建?
日常用new Person()创建对象
运行中创建对象用反射
【2】问题2:反射是否破坏了面向对象的封装性?
表面上破坏了封装性
private私有、protected保护,建议外面别用,起到警示作用



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号